High-temperature thermal treatment is the critical final step for optimizing Boron Tin Oxide (BSnO) thin films. Specifically, subjecting these films to a rapid annealing process at 900 °C for 30 seconds is performed to fundamentally restructure the material, enhancing both its physical quality and its ability to detect light and electrical signals.
The Core Takeaway This process is not merely about heating; it is a mechanism for lattice repair and homogenization. By briefly exposing BSnO films to high heat, you trigger atomic redistribution that heals internal defects, directly resulting in a detector with higher sensitivity and superior long-term stability.

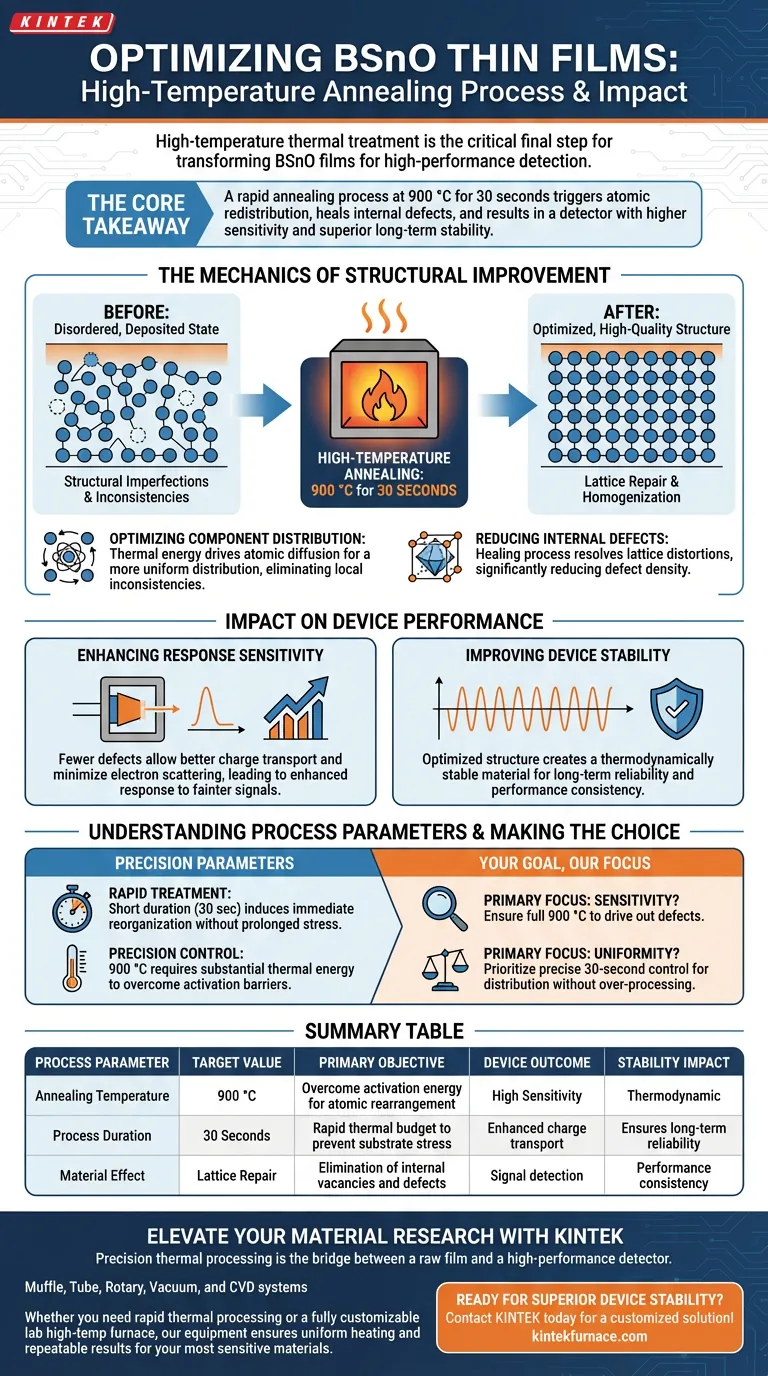
The Mechanics of Structural Improvement
The primary function of annealing BSnO films is to move the material from a disordered, deposited state to an optimized, high-quality structure.
Optimizing Component Distribution
During the deposition process, the atoms within the film may not be perfectly aligned or evenly distributed.
The thermal energy provided by the annealing furnace drives atomic diffusion. This allows the constituents of the film to rearrange themselves into a more uniform distribution, eliminating local inconsistencies in the material's composition.
Reducing Internal Defects
Freshly deposited films often contain structural imperfections, such as vacancies or interstitial defects, which disrupt electron flow.
High-temperature treatment acts as a healing process. It provides the energy required to resolve these lattice distortions, significantly reducing the density of internal defects that would otherwise act as traps for charge carriers.
Impact on Device Performance
The structural changes induced by the furnace translate directly into measurable performance gains for optoelectronic devices.
Enhancing Response Sensitivity
A film with fewer defects allows for better charge transport.
By minimizing the internal obstacles that scatter electrons, the annealing process ensures that the final detector is highly responsive. The result is a device with enhanced response sensitivity, capable of detecting fainter signals with greater accuracy.
Improving Device Stability
Performance is useless without reliability.
The optimization of the film's structure creates a more thermodynamically stable material. This ensures that the detector maintains its performance characteristics over time, providing the stability necessary for practical applications.
Understanding the Process Parameters
While the benefits are clear, the specific parameters of the treatment are non-negotiable for success.
The Importance of Rapid Treatment
The standard protocol for BSnO is a short-duration treatment (typically 30 seconds).
Unlike other materials that may require long soak times to induce recrystallization, BSnO benefits from a rapid thermal budget. This suggests the goal is to induce immediate surface and lattice reorganization without subjecting the substrate or film to prolonged thermal stress that could cause diffusion issues or degradation.
Precision Control
The high temperature (900 °C) is significantly higher than annealing temperatures used for many other common oxides (often 300°C–600°C).
This indicates that BSnO requires substantial thermal energy to overcome the activation energy barriers for atomic rearrangement. Precise control of this temperature is essential to achieve the desired optoelectronic properties without over-processing the film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When integrating BSnO films into detector fabrication, the annealing step defines the final quality of your sensor.
- If your primary focus is Sensitivity: Ensure the temperature reaches the full 900 °C to sufficiently drive out the internal lattice defects that dampen signal response.
- If your primary focus is Uniformity: Prioritize the precise control of the 30-second duration to allow for component distribution without over-saturating the film with heat.
By strictly adhering to this high-temperature, short-duration protocol, you transform a raw deposited film into a high-performance detection component.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Target Value | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing Temperature | 900 °C | Overcome activation energy for atomic rearrangement |
| Process Duration | 30 Seconds | Rapid thermal budget to prevent substrate stress |
| Material Effect | Lattice Repair | Elimination of internal vacancies and defects |
| Device Outcome | High Sensitivity | Enhanced charge transport and signal detection |
| Stability Impact | Thermodynamic | Ensures long-term reliability and performance consistency |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision thermal processing is the bridge between a raw film and a high-performance detector. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all designed to meet the rigorous 900°C precision required for BSnO thin film optimization. Whether you need rapid thermal processing or a fully customizable lab high-temp furnace, our equipment ensures uniform heating and repeatable results for your most sensitive materials.
Ready to achieve superior device stability? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Cunhua Xu, Wei Zheng. Boron tin oxide for filterless intrinsic-narrowband solar-blind ultraviolet detectors with tunable photoresponse peak from 231 to 275 nm. DOI: 10.1063/5.0174556
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is multiple remelting necessary for Bi-Sb alloys? Achieve Perfect Compositional Uniformity Today
- What is the role of electric furnaces in the direct reduction of iron? Powering the Future of Green Metallurgy
- What are the temperature ranges for low, medium, and high-temperature industrial heating processes? Optimize Your Process with KINTEK
- What role do high-precision laboratory ovens play in assessing the energy potential of MSW? Enhancing Biomass Accuracy
- What are the technical advantages of using a six-zone resistance heating furnace in VGF-VB? Unlock Precision Growth
- Why is a constant temperature and humidity curing chamber essential for geopolymerization? Ensure Structural Strength
- Why are industrial-grade drying and crushing equipment necessary for pretreatment? Optimize Chemical Reactions
- How does a circulating cooling water system contribute to the removal of impurities? Optimize Rubidium Chloride Purity



















