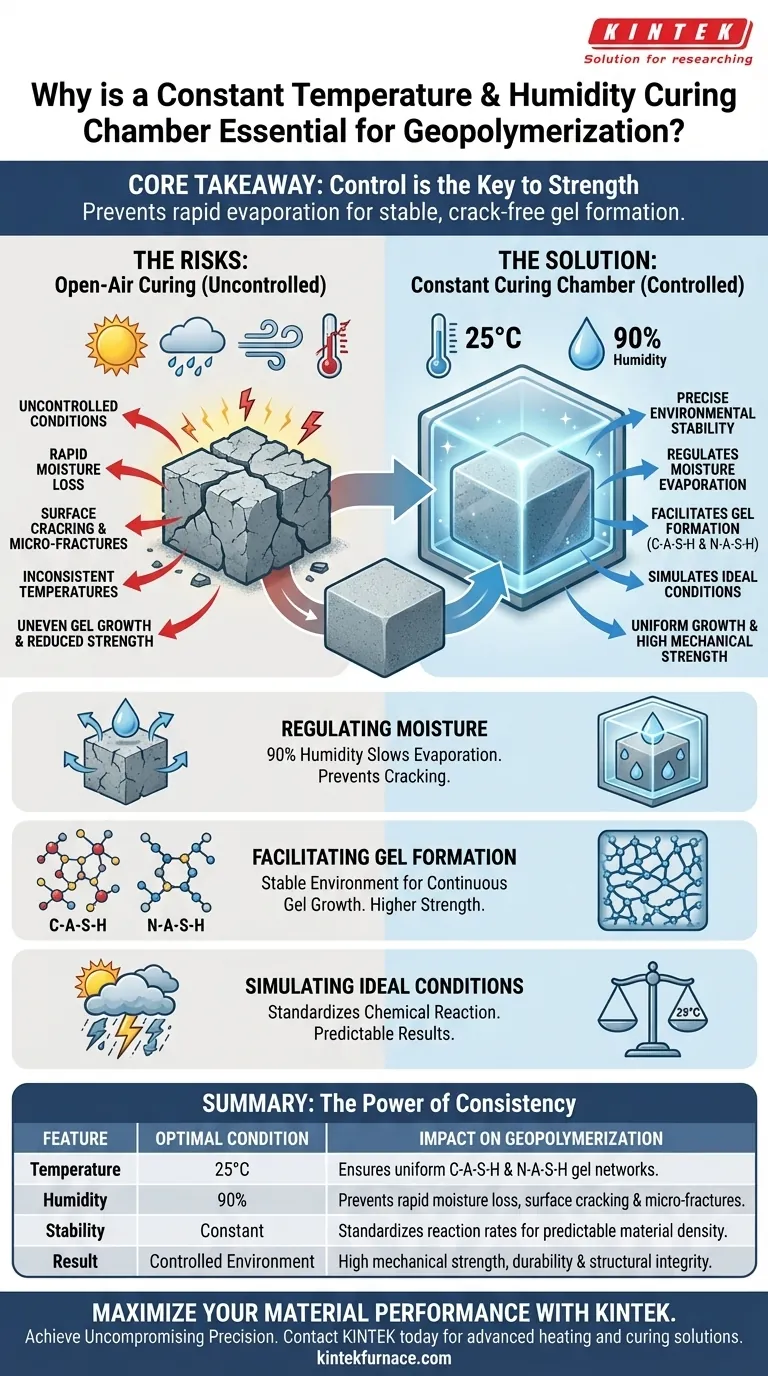
A constant temperature and humidity curing chamber is essential because it guarantees the precise environmental stability required for successful geopolymerization. By maintaining specific conditions, typically 25 degrees Celsius and 90% humidity, the chamber prevents rapid moisture loss that leads to structural failure.
Core Takeaway: Control is the key to strength. A curing chamber prevents the destructive effects of rapid evaporation, ensuring the stable chemical formation of binding gels necessary for a durable, crack-free final product.
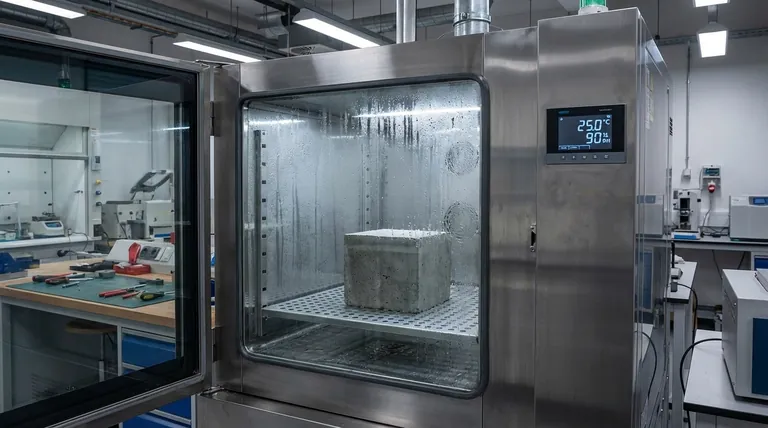

The Role of Environmental Control
Regulating Moisture Evaporation
The early stages of geopolymerization are highly sensitive to water content. If the material is exposed to uncontrolled air, moisture evaporates too quickly.
A curing chamber maintains high humidity (90%), which drastically slows this evaporation rate. This prevention of rapid drying is the primary defense against surface cracking and internal micro-fractures.
Facilitating Gel Formation
The strength of a geopolymer comes from the growth of specific chemical structures. Specifically, these are C-A-S-H (Calcium-Aluminate-Silicate-Hydrate) and N-A-S-H (Sodium-Aluminate-Silicate-Hydrate) gels.
These gels require a stable environment to develop a continuous, solid matrix. The curing chamber provides the consistency needed for these gels to grow uninterrupted, directly resulting in higher mechanical strength.
Simulating Ideal Ambient Conditions
Real-world conditions are rarely consistent, fluctuating in temperature and dryness. The chamber eliminates these variables by simulating a "perfect" ambient environment (25°C).
This standardization ensures that the chemical reaction proceeds at a predictable rate, regardless of the weather outside the lab or factory.
The Risks of Environmental Fluctuation
The Trade-off of Open-Air Curing
Attempting to cure geopolymers without a chamber introduces significant risk. Without humidity control, the differential between the internal moisture of the material and the dry air causes tension.
This tension manifests as physical cracks, which permanently compromise the structural integrity of the material before it has even fully hardened.
Impact on Final Strength
Inconsistent temperatures interfere with the chemical bonding process. If the temperature drops or spikes unexpectedly, the C-A-S-H and N-A-S-H gel networks may form unevenly.
This results in a final product with variable density and reduced load-bearing capacity, making the material unreliable for engineering applications.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
If your primary focus is Durability:
- Prioritize maintaining 90% humidity to prevent rapid evaporation and the formation of surface cracks.
If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength:
- Ensure the temperature remains constant at 25°C to facilitate the uniform growth of C-A-S-H and N-A-S-H gels.
Consistency in the curing stage is the single most critical factor in transforming a raw chemical mixture into a robust construction material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Optimal Condition | Impact on Geopolymerization |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 25°C | Ensures uniform growth of C-A-S-H and N-A-S-H gel networks. |
| Humidity | 90% | Prevents rapid moisture loss, surface cracking, and micro-fractures. |
| Stability | Constant | Standardizes chemical reaction rates for predictable material density. |
| Result | Controlled Environment | High mechanical strength, durability, and structural integrity. |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Achieve uncompromising precision in your geopolymerization research and production. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces and environmental chambers, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific curing requirements.
Don't let environmental fluctuations compromise your structural integrity. Contact KINTEK today to discover how our advanced heating and curing solutions can deliver the stability and strength your project demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Nidhya Rathinavel, Mohamed Ismail. Energy-Efficient geopolymer wall panels: optimizing mechanical, thermal, and acoustic properties for sustainable construction. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11783-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the core technical advantages of a flash sintering system? Elevate KNN Ceramic Manufacturing Performance
- What industries commonly use batch furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Electronics
- How is the influence of permeation temperature on steel hardness quantified? Precision Modeling for Plasma Nitriding
- What occurs during the recrystallization stage of annealing? Restore Ductility and Reset Microstructure
- What role does an electric heating industrial furnace play in biomass pyrolysis? Unlock High-Quality Biochar Yields
- What are the primary functions of a high-precision dilatometer in hot ductility? Optimize Steel Casting Precision
- What role does X-ray diffraction (XRD) play in evaluating ZIF thermal treatment? Master Material Transformation
- How does a Zinc Oxide (ZnO) catalyst affect PET pyrolysis? Optimize Yields & Efficiency



















