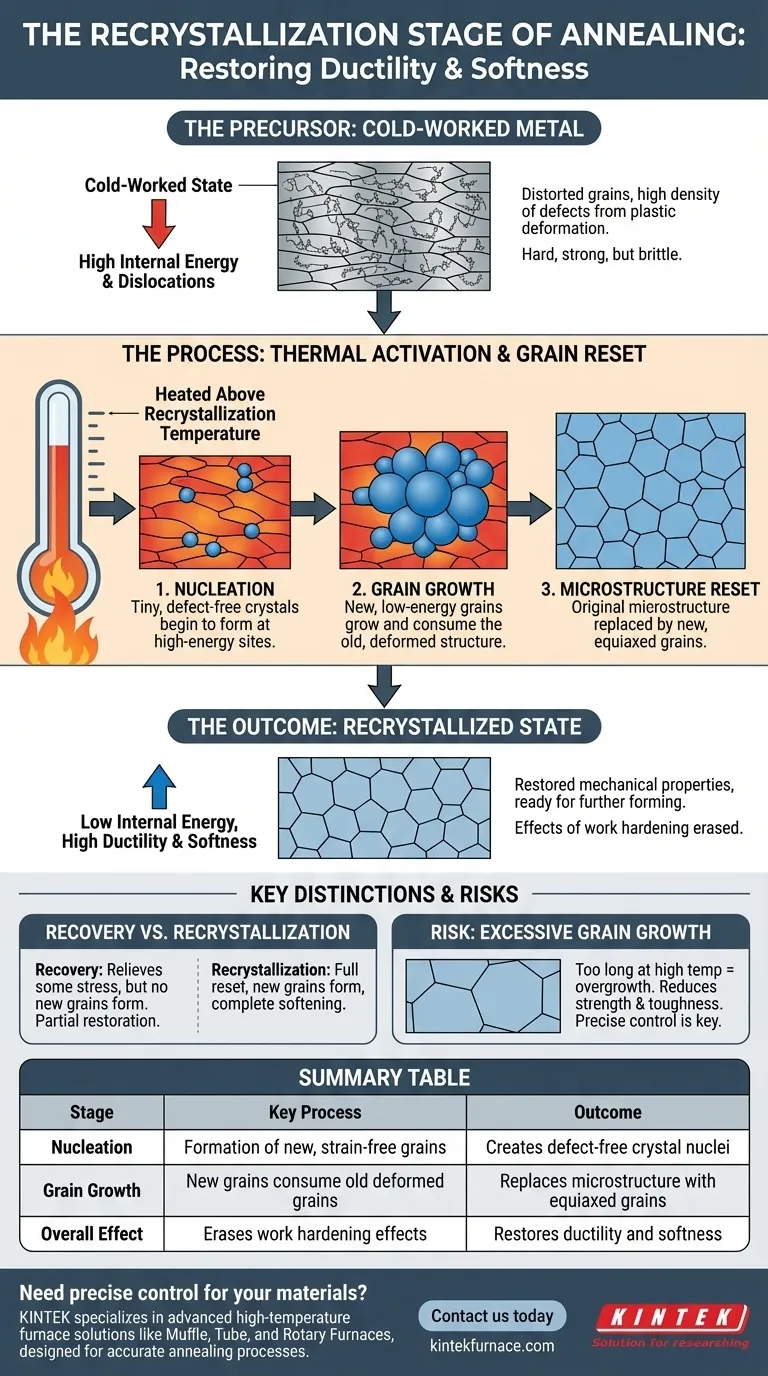
In short, the recrystallization stage of annealing is a thermally activated process where new, strain-free grains form and grow to replace the deformed, high-energy grains created during cold working. By heating a metal above its specific recrystallization temperature (but below its melting point), this stage effectively erases the effects of work hardening, restoring the material's original ductility and softness.
The core purpose of recrystallization is to reset the material's internal microstructure. It's a controlled demolition and reconstruction on a microscopic level, replacing a stressed and brittle grain structure with a new, unstressed one.
The Precursor: Why Recrystallization is Necessary
The State of a Cold-Worked Metal
When a metal is plastically deformed at room temperature—through processes like rolling, forging, or drawing—its internal grain structure becomes distorted and elongated. This process, known as cold working, introduces a high density of crystal defects called dislocations.
This tangled web of dislocations makes the metal harder and stronger but significantly reduces its ductility, making it brittle and difficult to work with further.
The Role of Stored Energy
The distorted grains and dislocations from cold working represent a state of high internal energy. This stored energy is the fundamental driving force for recrystallization. The material is in an unstable state and, when given enough thermal energy (heat), will naturally seek to return to a lower-energy configuration.
Deconstructing the Recrystallization Process
Reaching the Critical Temperature
To initiate recrystallization, the material must be heated above its recrystallization temperature. This is not a fixed point like a melting point but a temperature range that depends on the specific alloy and, crucially, the amount of prior cold work.
More heavily cold-worked materials have more stored energy and will recrystallize at a lower temperature.
Nucleation of New Grains
Once the critical temperature is reached, tiny, new, strain-free crystals begin to form. These nuclei are defect-free and typically appear at high-energy sites within the deformed structure, such as the boundaries of the old, distorted grains.
Grain Growth and Microstructure Reset
These new, low-energy grains then grow, consuming the old, high-energy, deformed grains around them. This process continues until the original deformed microstructure has been completely replaced by a new set of equiaxed (equal-sided) grains.
This new granular structure is what restores the material's pre-treatment mechanical properties, primarily its ductility and softness, making it suitable for subsequent forming operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Distinctions
Differentiating from the Recovery Stage
Recrystallization is often preceded by a lower-temperature stage called recovery. During recovery, some internal stresses are relieved as dislocations rearrange themselves into lower-energy patterns.
However, recovery does not create new grains. It provides a partial restoration of properties, but only full recrystallization can completely erase the effects of work hardening by resetting the grain structure.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
Controlling the process is critical. If the material is held at the recrystallization temperature for too long or heated to an excessively high temperature, the new grains will continue to grow larger.
This excessive grain growth can be detrimental, often reducing the material's strength and toughness. Precise control of temperature and time is therefore essential to achieve the desired final grain size and properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving the correct material properties requires selecting the right thermal process for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is to relieve internal stress with minimal impact on hardness: A lower-temperature recovery anneal, below the recrystallization point, is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is to fully restore ductility for significant further forming: You must achieve full recrystallization by heating above the critical temperature for a sufficient time.
- If your primary focus is to optimize final strength and toughness: You must carefully control the recrystallization process to achieve a fine, uniform grain size and avoid excessive grain growth.
Mastering recrystallization allows you to precisely engineer a material's properties, transforming a hardened, brittle component back into a highly formable asset.

Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleation | Formation of new, strain-free grains at high-energy sites | Creates defect-free crystal nuclei |
| Grain Growth | Growth of new grains consuming old deformed grains | Replaces microstructure with equiaxed grains |
| Overall Effect | Erases work hardening effects | Restores ductility and softness |
Need precise control over recrystallization for your materials? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, designed for accurate annealing processes. With our deep customization capabilities, we can tailor equipment to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring optimal grain structure and material properties. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















