Zinc Oxide (ZnO) acts as a high-efficiency catalyst that fundamentally alters the thermal degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). It accelerates the decomposition process, significantly shortens reaction times, and shifts the final product distribution toward valuable liquids and waxes while minimizing solid waste.
Zinc Oxide does more than speed up reactions; it promotes "directional molecular cleavage," allowing operators to target specific product morphologies like molten wax while drastically reducing furnace maintenance by limiting carbon residue.

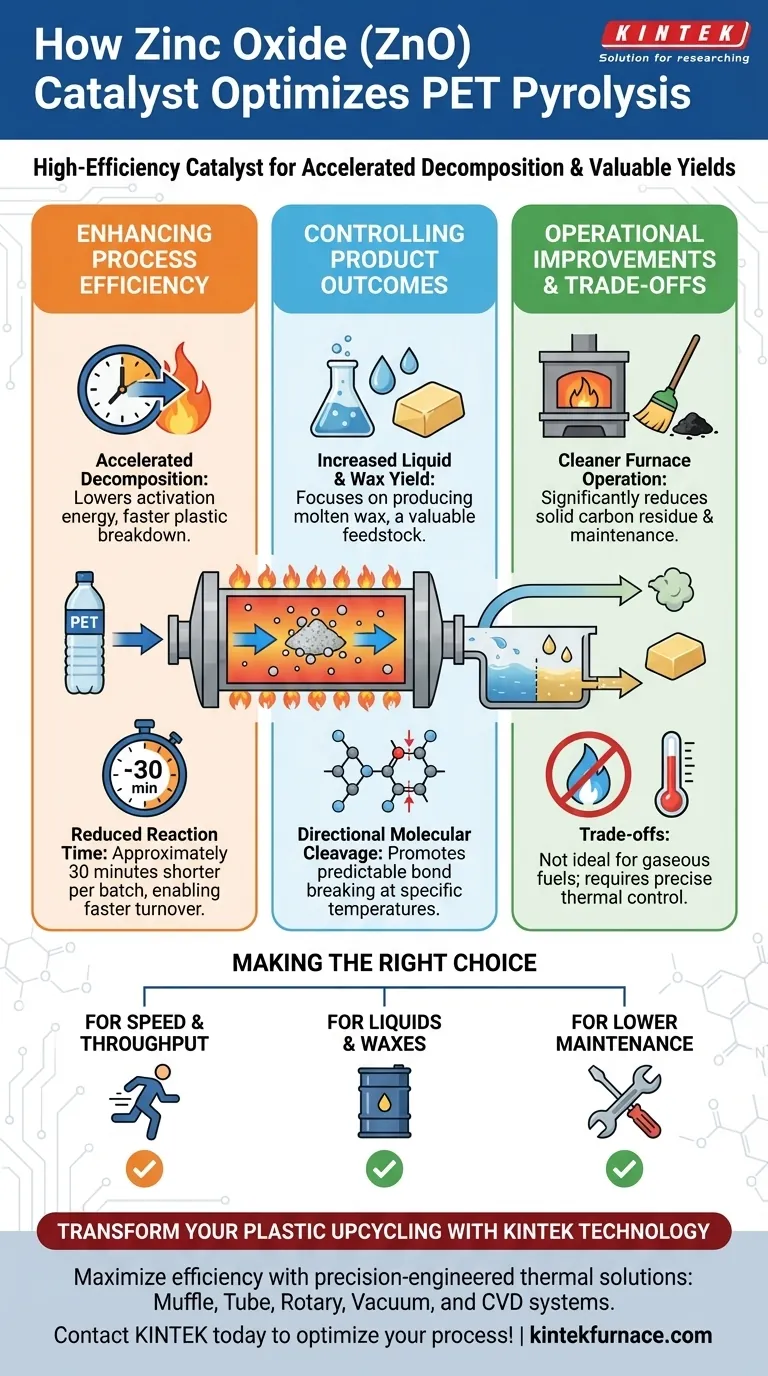
Enhancing Process Efficiency
Accelerated Decomposition Rate
ZnO significantly increases the rate at which plastic polymers break down. By lowering the activation energy required for pyrolysis, it allows the PET chains to crack more readily.
Reduction in Reaction Time
The presence of ZnO has a measurable impact on operational throughput. It can reduce the total reaction time by approximately 30 minutes, allowing for faster batch turnover.
Improved Heating Efficiency
Beyond chemical kinetics, ZnO improves the overall heating efficiency of the system. This ensures that thermal energy is utilized more effectively during the breakdown of the polymer matrix.
Controlling Product Outcomes
Directional Molecular Cleavage
Unlike non-catalytic pyrolysis, which can be chaotic, ZnO promotes directional cleavage. This means the molecular bonds break in a more predictable pattern at specific temperatures.
Increased Liquid and Wax Yield
This catalyst is specifically effective for maximizing liquid yields or modifying product morphology. It is particularly noted for generating molten wax, a valuable feedstock for various industrial applications.
Operational Improvements
Reduction of Solid Residue
One of the most practical benefits of using ZnO is the reduction of solid waste. The catalyst effectively lowers the amount of solid carbon residue remaining in the furnace after the process is complete.
Cleaner Furnace Operation
By minimizing char formation, ZnO helps maintain a cleaner reactor environment. This directly correlates to reduced downtime for cleaning and maintenance.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Product Specificity Limitations
The "directional" nature of ZnO is a double-edged sword. Because it promotes specific morphologies like molten wax or liquid, it may not be suitable if your primary goal is maximizing gaseous fuel production.
Thermal Dependency
The effectiveness of ZnO in promoting directional cleavage is tied to specific temperatures. Operators must maintain precise thermal control to ensure the catalyst activates the desired molecular breakdown rather than leading to incomplete decomposition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goals
To determine if Zinc Oxide is the right catalyst for your PET pyrolysis setup, consider your specific production targets:
- If your primary focus is Speed and Throughput: Utilizing ZnO is highly recommended to leverage the approximate 30-minute reduction in reaction time per batch.
- If your primary focus is Product Morphology: Choose ZnO if you specifically intend to produce liquids or molten waxes rather than gaseous fuels.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Maintenance: Implement ZnO to significantly reduce solid carbon residue and minimize the frequency of furnace cleaning.
By integrating Zinc Oxide, you move from simple waste destruction to a targeted, efficient chemical recovery process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact of ZnO on PET Pyrolysis |
|---|---|
| Decomposition Speed | Significantly accelerated via lower activation energy |
| Reaction Time | Reduced by approximately 30 minutes per batch |
| Primary Product | High-quality liquid oils and molten waxes |
| Solid Residue | Minimal carbon char; cleaner furnace operation |
| Molecular Control | Directional cleavage for predictable outcomes |
Transform Your Plastic Upcycling with KINTEK Technology
Maximize your PET pyrolysis efficiency and product quality with precision-engineered thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific catalytic requirements.
Whether you are targeting molten wax production or seeking to minimize carbon residue, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability and control needed for advanced Zinc Oxide catalysis. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique research or production needs and let our experts help you optimize your chemical recovery process!
Visual Guide
References
- Hitesh Panchal. Fuel Extraction from Plastic Waste. DOI: 10.22214/ijraset.2025.66489
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is pre-sintering of Ga2O3 raw material powder required? Unlock Beta-Phase Stability for High-Performance Thin Films
- How are magnetic stirrers and constant temperature drying ovens utilized in the wet chemical synthesis of copper selenide nanorods?
- Why is it necessary to preheat the mold for Mg-8Li-3Al-0.3Si alloy? Unlock Peak Casting Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play for superalloy evaluation? Simulate Extreme Aero-Engine Environments
- What occurs during the recrystallization stage of annealing? Restore Ductility and Reset Microstructure
- What is the function of a high-pressure reactor in SHS? Optimize Tungsten Carbide Synthesis with Precision
- Why is high-purity argon gas used to purge the furnace? Ensure Precision in TGA Oxidation Kinetic Tests
- How does a crucible furnace work? A Guide to Efficient Metal Melting



















