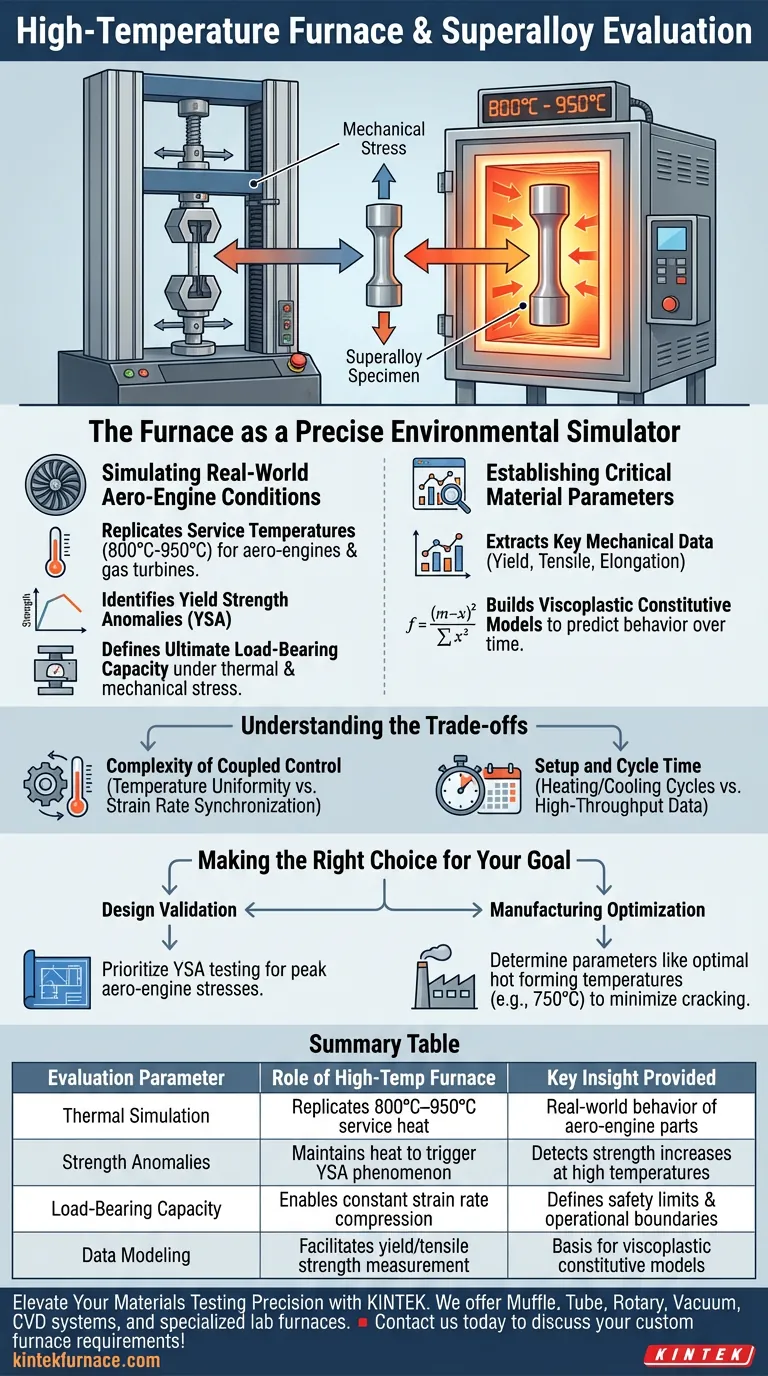
The high-temperature furnace functions as a precise environmental simulator when integrated with an electronic universal testing machine. It enables the evaluation of superalloys by replicating the extreme thermal conditions of aero-engines and gas turbines while the machine applies mechanical stress.
By maintaining a controlled thermal environment between 800°C and 950°C, this setup reveals critical temperature-dependent behaviors like the Yield Strength Anomaly (YSA). It moves beyond simple stress testing to determine the actual load-bearing capacity of materials under service conditions.
Simulating Real-World Aero-Engine Conditions
Replicating Service Temperatures
The primary role of the furnace is to elevate the specimen to the operating temperatures found in high-performance machinery.
For superalloys used in aero-engines, this typically requires a stable environment ranging from 800°C to 950°C.
Testing at these temperatures ensures that the data collected reflects the material's behavior during actual flight or power generation operations.
Identifying Yield Strength Anomalies (YSA)
Superalloys often exhibit complex behaviors that do not manifest at room temperature.
The integrated furnace allows engineers to detect Yield Strength Anomalies (YSA), a phenomenon where yield strength may increase with temperature up to a certain point.
Without the thermal component provided by the furnace, these critical performance characteristics would remain hidden.
Defining Ultimate Load-Bearing Capacity
The combination of thermal and mechanical stress defines the true limit of a material.
By performing constant strain rate compression tests within the furnace, engineers can determine the ultimate load-bearing capacity of the alloy.
This data is essential for safety certification and establishing the operational limits of the final component.
Establishing Critical Material Parameters
Extracting Key Mechanical Data
Beyond simple failure points, the furnace setup facilitates the measurement of specific mechanical properties across a spectrum of temperatures.
Testing reveals fundamental parameters such as yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation.
These metrics provide a comprehensive "fingerprint" of how the alloy deforms and resists stress under heat.
Building Viscoplastic Constitutive Models
The data gathered from these high-temperature tests serves as the physical basis for advanced mathematical modeling.
Engineers use the results to establish viscoplastic constitutive models, which predict how the material will behave over time under load.
These models are vital for predicting risks such as springback or cracking during manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Coupled Control
Integrating a furnace introduces significant variables regarding temperature uniformity and control.
Achieving a constant strain rate requires precise synchronization between the mechanical loading system and the thermal expansion of the setup itself.
Any fluctuation in temperature can skew the mechanical data, leading to inaccurate conclusions about the alloy's strength.
Setup and Cycle Time
High-temperature testing is inherently more time-consuming than ambient testing due to heating and cooling cycles.
Rapid testing is often sacrificed for the sake of thermal equilibrium and accuracy.
Operators must balance the need for high-throughput data with the necessity of stabilizing the specimen at extreme temperatures (e.g., 950°C).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of your testing setup, align your methodology with your specific engineering objectives:
- If your primary focus is design validation: Prioritize tests that identify the Yield Strength Anomaly (YSA) to ensure the material can withstand peak aero-engine stresses.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing optimization: Use the system to determine parameters like optimal hot forming temperatures (e.g., around 750°C for compatible alloys) to minimize cracking risks.
Successful superalloy evaluation relies not just on breaking the sample, but on breaking it under the exact thermal conditions it was designed to survive.
Summary Table:
| Evaluation Parameter | Role of the High-Temp Furnace | Key Insight Provided |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Simulation | Replicates 800°C–950°C service heat | Real-world behavior of aero-engine parts |
| Strength Anomalies | Maintains heat to trigger YSA phenomenon | Detects strength increases at high temperatures |
| Load-Bearing Capacity | Enables constant strain rate compression | Defines safety limits and operational boundaries |
| Data Modeling | Facilitates yield/tensile strength measurement | Basis for viscoplastic constitutive models |
Elevate Your Materials Testing Precision with KINTEK
Don't let room-temperature data limit your engineering breakthroughs. KINTEK provides high-performance heating solutions specifically designed for seamless integration with mechanical testing systems. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces that are fully customizable for your unique superalloy evaluation needs.
Whether you are validating aero-engine safety or optimizing hot-forming manufacturing, our furnaces ensure the thermal stability and uniformity required for critical data.
Ready to simulate the extreme? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- A. Bezold, Steffen Neumeier. Segregation-induced strength anomalies in complex single-crystalline superalloys. DOI: 10.1038/s43246-024-00447-x
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a stable constant temperature environment influence the structural development of LDHs during aging?
- How does high-temperature filtration equipment facilitate molten salt separation? Boost Your Slag Treatment Recovery
- What factors should be considered when selecting a furnace based on material properties? Ensure Optimal Heat Treatment
- What is the role of industrial drying ovens equipped with fan systems in the convective hot air drying of fruit materials? Boost Quality & Preserve Nutrients
- How does a high-precision temperature control system contribute to NMC synthesis? Precision in XRD In-Situ Experiments
- What heat treatment conditions are required for SDSS2507 solution treatment? Achieve Precise 1100°C Thermal Profiles
- How is mechanochemical grinding used in lithium battery recovery? Unlock Efficient Solid-State Material Repair
- What are the technical advantages of using the molten salt method? Elevate Your Biomass Carbon Support Synthesis



















