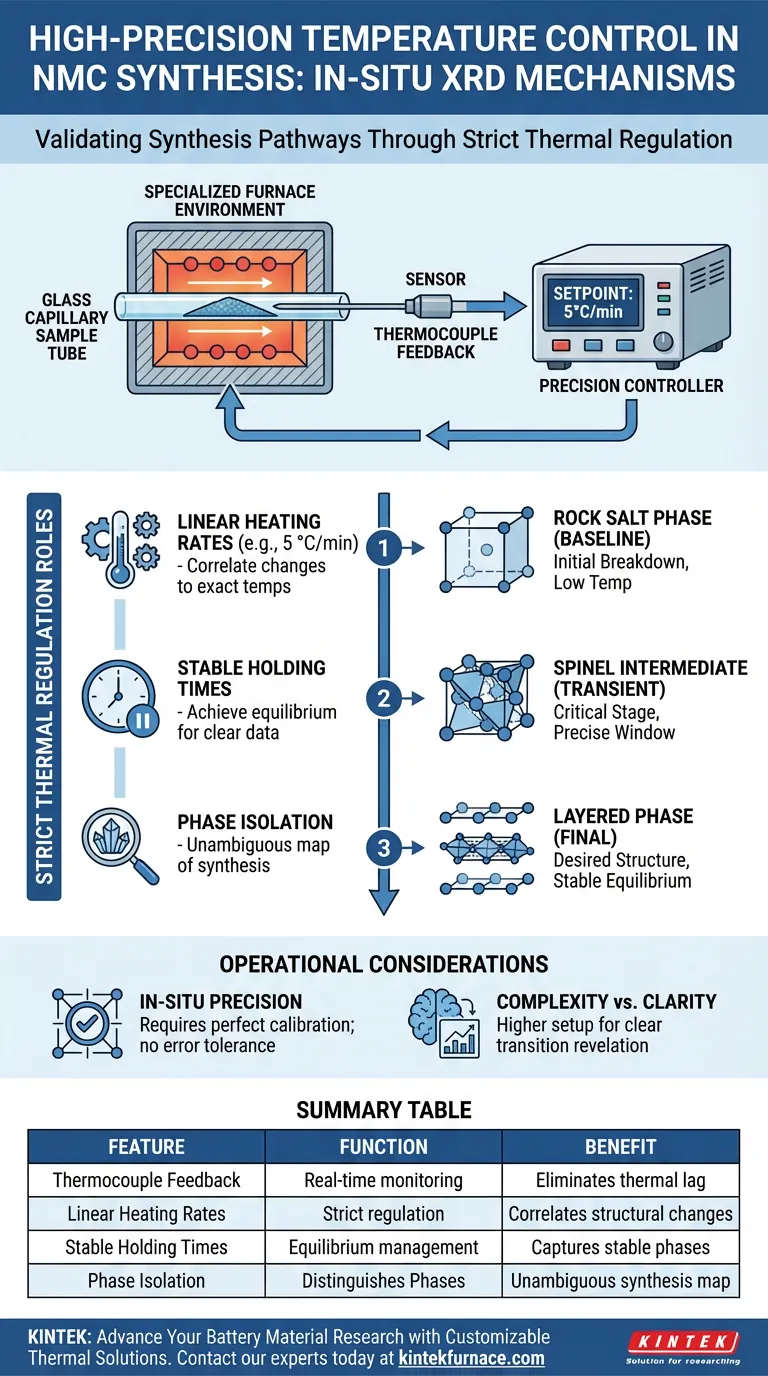
High-precision temperature control is the definitive factor in validating the synthesis mechanisms of Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) cathode materials. By integrating thermocouple feedback into in-situ heating X-ray diffraction (XRD) setups, researchers can strictly regulate heating rates and holding times to pinpoint the exact moments structural transformations occur within a sample capillary.
By enforcing strict thermal parameters, this system enables the precise isolation of critical phase changes—specifically the transitions between rock salt, spinel, and layered phases—providing an unambiguous map of the dry synthesis pathway.

The Role of Strict Thermal Regulation
Integrating Thermocouple Feedback
The core of this system lies in the use of thermocouple feedback loops. This technology continuously monitors the sample environment to ensure the actual temperature matches the programmed setpoint. It eliminates the guesswork often associated with thermal lag in high-temperature experiments.
Controlling Heating Rates
Precise control allows for the strict regulation of specific heating rates, such as 5 °C/min. Maintaining a consistent ramp rate is essential for distinguishing between kinetic events and thermodynamic stability. Without this linearity, researchers cannot accurately correlate specific structural changes to specific temperature points.
Managing Holding Times
Beyond the ramp, the system manages the holding times for samples contained within the capillary. Stable holding periods allow the material to reach equilibrium at specific temperatures. This ensures that the diffraction data captured represents a completed phase transition rather than a transient state.
Mapping the NMC Synthesis Pathway
Detecting the Rock Salt Phase
The primary value of this precision is the ability to capture the emergence of the rock salt phase. By locking in the temperature where this phase appears, researchers establish the baseline for the synthesis reaction. This phase often represents the initial breakdown of precursors.
Observing the Spinel Intermediate
Perhaps the most critical contribution is the identification of the spinel intermediate phase. This transient phase can be easily missed if the temperature overshoots or fluctuates. Precise control slows the observation window, allowing the XRD to record the distinct crystal structure of the intermediate before it transforms further.
Confirming the Layered Phase
Finally, the system validates the formation of the desired layered phase. Accurate temperature control ensures that the material has received sufficient thermal energy to order itself correctly without degrading. This confirms the successful completion of the dry synthesis pathway.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
The Necessity of "In-Situ" Precision
While powerful, this method relies heavily on the strict regulation of the environment inside a small capillary. The trade-off is that the system must be perfectly calibrated; any error in the thermocouple feedback can lead to a misinterpretation of the phase transition temperature.
Complexity vs. Clarity
Achieving this level of precision adds complexity to the experimental setup compared to ex-situ methods. However, the "clear revelation" of transition pathways is impossible without it. Researchers must accept the higher setup requirements to gain visibility into the dynamic evolution of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage high-precision temperature control effectively in your NMC research:
- If your primary focus is determining reaction kinetics: Prioritize the strict regulation of heating rates (e.g., 5 °C/min) to observe how fast phases transform.
- If your primary focus is identifying intermediate structures: Focus on optimizing holding times at predicted transition points to capture high-quality diffraction data of the spinel intermediate phase.
This system transforms temperature from a simple variable into a precise analytical tool, granting you total clarity over the formation of high-performance cathode materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in NMC Synthesis | Benefit to Research |
|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple Feedback | Real-time environment monitoring | Eliminates thermal lag and guesswork |
| Linear Heating Rates | Strict regulation (e.g., 5 °C/min) | Correlates structural changes to exact temps |
| Stable Holding Times | Equilibrium management in capillary | Captures diffraction data of stable phases |
| Phase Isolation | Distinguishes Rock Salt, Spinel, Layered | Unambiguous map of the dry synthesis pathway |
Advance Your Battery Material Research with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is the difference between guessing a reaction and witnessing a breakthrough. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance thermal solutions necessary for sensitive in-situ experiments.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of your lab. Whether you are mapping NMC synthesis or developing next-gen materials, our high-temperature furnaces deliver the stability and accuracy your data depends on.
Ready to elevate your thermal precision? Contact our experts today to find the perfect customized solution for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Svena Yu, J. R. Dahn. In‐Situ Heating X‐Ray Diffraction of LiNi<sub>0.6</sub>Mn<sub>0.3</sub>Co<sub>0.1</sub>O<sub>2</sub> and LiNi<sub>0.7</sub>Mn<sub>0.3</sub>O<sub>2</sub> Made Using the All‐Dry Synthesis Process. DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202500632
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do laboratory high-temperature furnaces facilitate the control of nano-scale TiC and VC precipitates? | KINTEK
- What is the primary function of a high vacuum drying oven in B4C/Al powder pretreatment? Protect Purity & Prevent Pores
- How does a batch furnace differ from a continuous furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Production Needs
- How does a batch furnace operate and what are its advantages? Boost Precision and Flexibility in Heat Treatment
- What is the purpose of using an industrial oven for flax fiber pretreatment? Ensure Superior Composite Integrity
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace ensure structural integrity? Expert Thermal Management Guide
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum dryer for PU and AlN composite sheets? Enhance Thermal & Structural Integrity
- Why Use the Modified Two-Temperature Synthesis for ZnGeP2? Ensure Safety and Material Quality



















