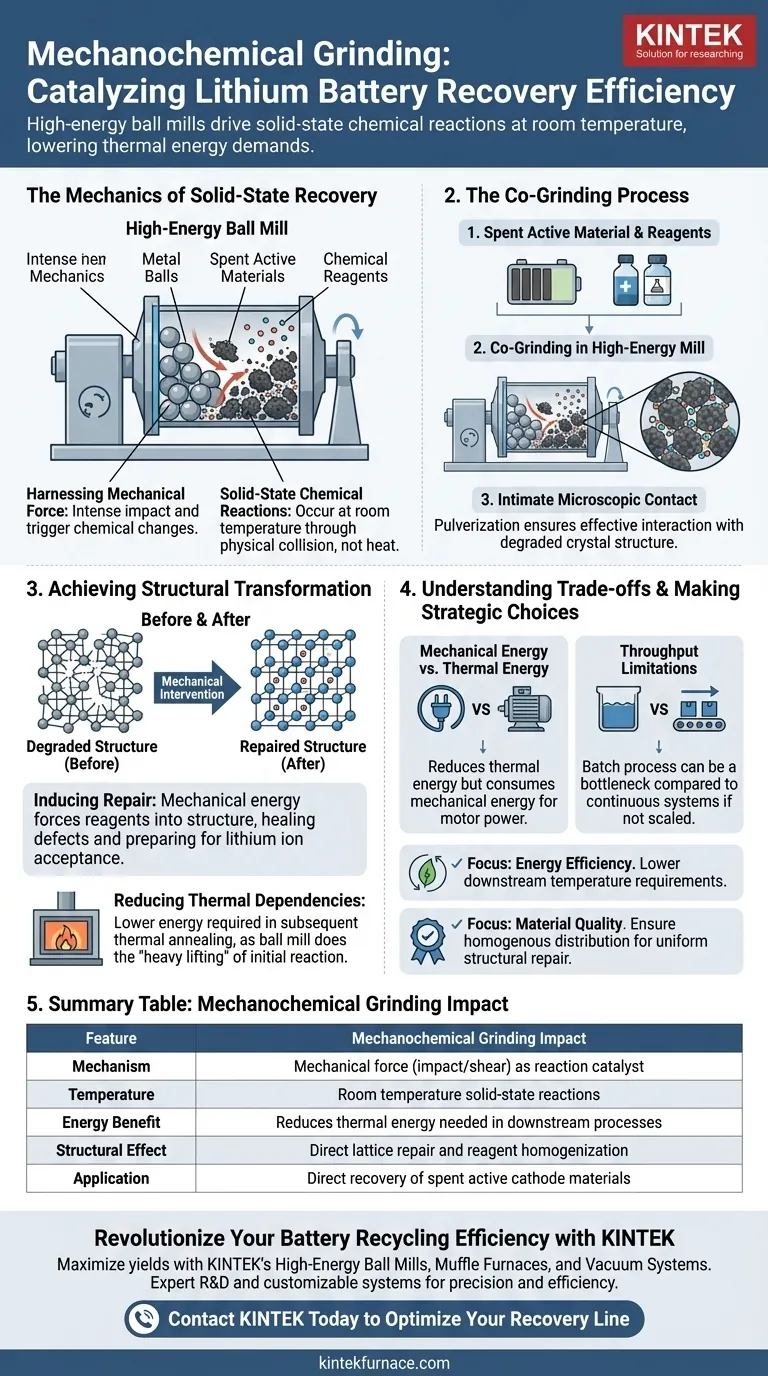
Mechanochemical grinding serves as a catalyst for efficiency in the direct recovery of lithium batteries. Specifically, high-energy ball mills are employed to co-grind spent active materials with chemical reagents, utilizing mechanical force to drive solid-state chemical reactions at room temperature.
The core value of this technology lies in its ability to initiate structural repair through kinetic energy rather than heat alone, significantly lowering the energy demands of subsequent thermal treatment processes.

The Mechanics of Solid-State Recovery
Harnessing Mechanical Force
High-energy ball mills do not simply mix materials; they act as a reactor. By subjecting materials to intense mechanical impact and shear, the equipment utilizes mechanical force to trigger chemical changes.
This allows solid-state chemical reactions to occur between the spent battery components and added reagents. Unlike traditional methods that rely solely on heat or liquid solutions, this process drives reaction kinetics through physical collision.
The Co-Grinding Process
The process involves co-grinding two distinct elements: the spent active material (the degraded battery cathode) and specific chemical reagents.
These materials are placed inside the mill where the grinding media (balls) pulverize them together. This ensures intimate contact at the microscopic level, which is essential for the reagents to interact effectively with the degraded crystal structure of the battery material.
Operating at Room Temperature
One of the distinct advantages of mechanochemical grinding is its operating temperature. The reactions are initiated at room temperature, avoiding the immediate need for high-heat furnaces during the initial mixing phase.
This "cold" processing step effectively pre-conditions the material, preparing it for restoration without the energy penalty associated with high-temperature processing.
Achieving Structural Transformation
Inducing Repair
The primary goal of this mechanical intervention is to induce structural repair or transformation. Spent battery materials often suffer from degraded crystal structures due to repeated charging cycles.
The mechanical energy provided by the ball mill forces the reagents into the structure of the active material. This effectively "heals" defects or prepares the lattice structure to accept lithium ions again.
Reducing Thermal Dependencies
While thermal treatment is often still necessary in direct recovery, mechanochemical grinding changes the baseline requirements. By initiating the repair process mechanically, the material requires less energy during the subsequent thermal annealing stage.
Essentially, the ball mill does the "heavy lifting" of mixing and initial reaction, meaning the furnace doesn't have to work as hard or as hot to finalize the restoration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Energy vs. Thermal Energy
While this method reduces thermal energy consumption, it substitutes it with mechanical energy consumption. Running high-energy ball mills requires robust electrical power to drive the motors and sustain the impact forces.
Throughput Limitations
Ball milling is often a batch process or requires complex continuous setups. Compared to simple continuous conveyor furnaces, the physical grinding step can introduce a bottleneck in processing speed if not correctly scaled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
High-energy ball milling is a strategic choice for recyclers looking to optimize the energy balance of their recovery line.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Utilize this equipment to lower the temperature requirements of your downstream thermal processes, trading heat energy for mechanical input.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Use the co-grinding phase to ensure homogenous distribution of reagents, leading to more uniform structural repair in the final product.
By integrating mechanochemical grinding, you move from a purely thermal recovery model to a hybrid mechanical-chemical approach that emphasizes precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanochemical Grinding Impact |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Mechanical force (impact/shear) as a reaction catalyst |
| Temperature | Room temperature solid-state reactions |
| Energy Benefit | Reduces thermal energy needed in downstream processes |
| Structural Effect | Direct lattice repair and reagent homogenization |
| Application | Direct recovery of spent active cathode materials |
Revolutionize Your Battery Recycling Efficiency with KINTEK
Maximize your lithium battery recovery yields by integrating KINTEK’s high-performance laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized High-Energy Ball Mills, Muffle Furnaces, and Vacuum Systems designed for the rigorous demands of mechanochemical processing and structural annealing. Whether you need a standard setup or a customizable system for unique material requirements, we provide the precision tools necessary to lower your energy costs and enhance material quality.
Contact KINTEK Today to Optimize Your Recovery Line
Visual Guide
References
- Muammer Kaya, Hossein Delavandani. State-of-the-Art Lithium-Ion Battery Pretreatment Methods for the Recovery of Critical Metals. DOI: 10.3390/min15050546
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the objective of coordinating mechanical stirring and heating for perovskite slurries? Achieve Homogeneity
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to the structural stability of silicon-based composite electrode sheets?
- What is the design logic behind the double-layer reactor structure used in the ITSP process? Optimize Your Fuel Quality
- Why is an industrial drying oven necessary for Boron Carbide mixed slurries? Ensure Coating Integrity & Precision
- Why is the water quenching process necessary for high-entropy alloys? Master Phase Purity and Microstructural Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature blast drying oven play in nanocomposite formation? Ensure Structural Stability
- Why is industrial-grade nitrogen flow introduced during the biochar pyrolysis process? Ensure Safety and Quality
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature sintering furnace operating at 1173 K in the preparation of porous oxide precursors? Achieve Structural Integrity for Your Precursors



















