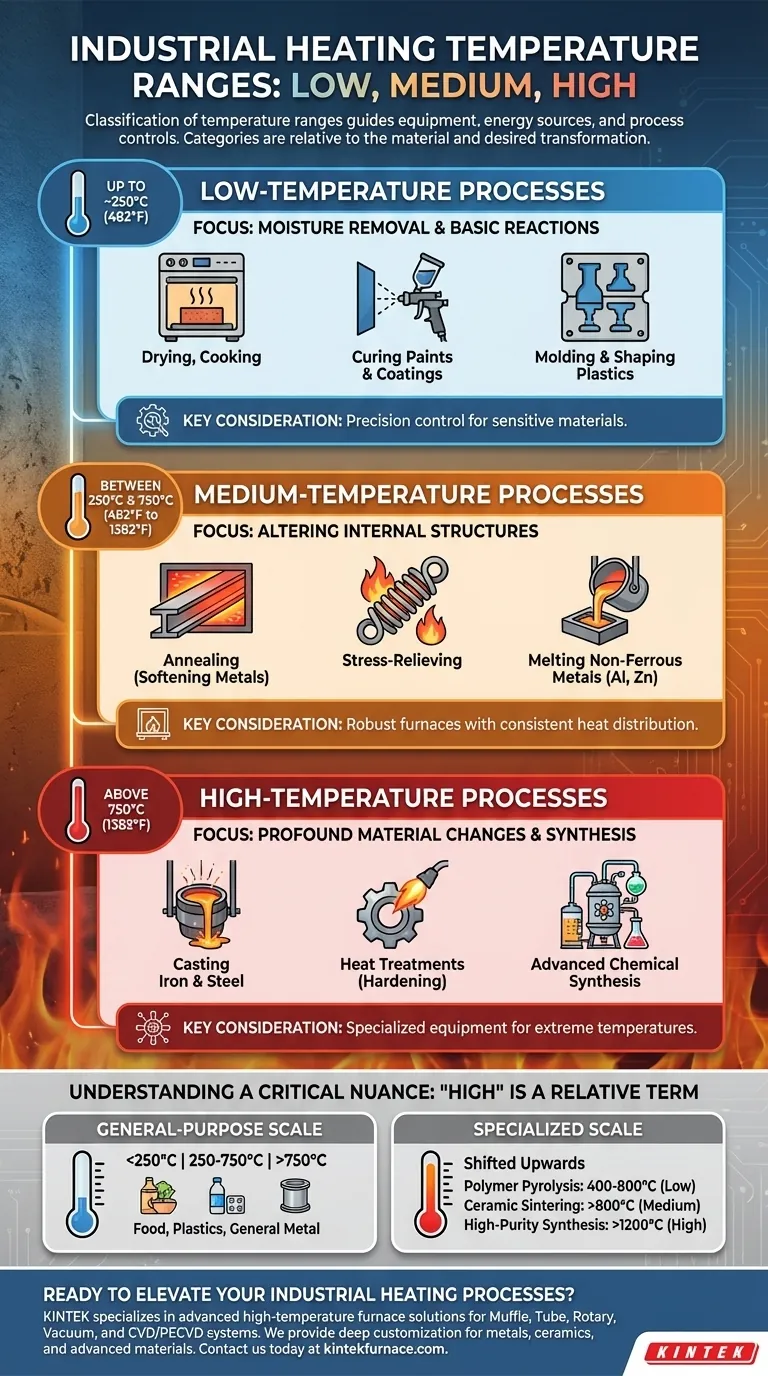
In industrial applications, temperature ranges are generally classified into three distinct categories. Low-temperature processes operate up to approximately 250°C (482°F), medium-temperature processes occur between 250°C and 750°C (482°F to 1382°F), and high-temperature processes take place above 750°C (1382°F). These classifications guide the selection of equipment, energy sources, and process controls.
The terms "low," "medium," and "high" temperature are not absolute; they are relative to the material and the desired transformation. Understanding your specific process goal is more critical than memorizing a universal temperature scale.

Defining the Industrial Heating Spectrum
Industrial heating is not a one-size-fits-all discipline. The required temperature is dictated entirely by the physical or chemical change you need to induce in a material, from simple drying to complete metallurgical transformation.
Low-Temperature Processes (Up to ~250°C)
This range is primarily concerned with removing moisture and initiating basic chemical reactions in thermally sensitive materials.
Processes here include industrial cooking, drying lumber or food, curing paints and coatings, and molding or shaping most common plastics. The energy input is relatively low, and the goal is often to alter the material's state without fundamentally changing its core chemistry.
Medium-Temperature Processes (~250°C to ~750°C)
In this range, we begin to alter the internal structure of materials, especially metals, without necessarily melting them.
This is the domain of annealing, which softens metals to improve ductility, and stress-relieving, which removes internal tensions caused by manufacturing. It also includes melting certain plastics and non-ferrous metals like aluminum or zinc for casting.
High-Temperature Processes (Above ~750°C)
This category involves significant energy input to achieve profound material changes, including melting, smelting, and advanced chemical synthesis.
High-temperature applications include casting iron and steel, performing intensive heat treatments like hardening, and enabling complex chemical reactions for material manufacturing. Plasma applications and advanced synthesis also fall into this demanding category.
Understanding a Critical Nuance: "High" Is a Relative Term
The standard classifications provide a useful baseline, but they can be misleading without proper context. For highly specialized fields, the entire temperature scale is shifted upwards.
The General-Purpose Scale
For most common industries—food processing, plastics, general metal fabrication, and finishing—the <250°C / 250-750°C / >750°C framework is the reliable standard.
The Specialized Scale
In fields like advanced materials science, the definitions change dramatically. For example, in polymer pyrolysis, 400°C to 800°C may be considered "low-temperature," as the process requires significant energy just to get started.
Similarly, for ceramic sintering, 800°C is only the beginning of the "medium" range. Processes like high-purity material synthesis can require temperatures well above 1200°C, pushing their definition of "high" far beyond the general standard.
Why This Distinction Matters
Using the wrong frame of reference leads to incorrect equipment selection and process design. A furnace designed for "high-temperature" steel treatment (e.g., 1000°C) is fundamentally different from one built for "high-temperature" material synthesis (e.g., 1700°C) in its insulation, heating elements, and control systems.
Matching the Process to Your Material
Your material's transformation point, not a generic label, should be your guide. Use these classifications to frame your requirements and communicate with vendors and engineers.
- If your primary focus is curing, drying, or molding polymers: You are operating in the low-temperature range, where precision control is often more important than raw power.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treatment of metals like annealing: You will be working in the medium- and lower-high-temperature ranges, requiring robust furnaces and consistent heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is ceramics, smelting, or advanced material synthesis: Your working temperatures are at the extreme end of the scale, and you must use specialized definitions when specifying equipment.
Ultimately, these temperature ranges are a map, and your specific process is the destination.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Typical Processes | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Low (Up to ~250°C) | Drying, curing, molding plastics | Precision control for sensitive materials |
| Medium (~250°C to ~750°C) | Annealing, stress-relieving, melting non-ferrous metals | Robust furnaces with consistent heat |
| High (Above ~750°C) | Casting steel, hardening, chemical synthesis | Specialized equipment for extreme temperatures |
Ready to elevate your industrial heating processes? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental needs, whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or advanced materials. Don't let temperature challenges hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup for superior performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















