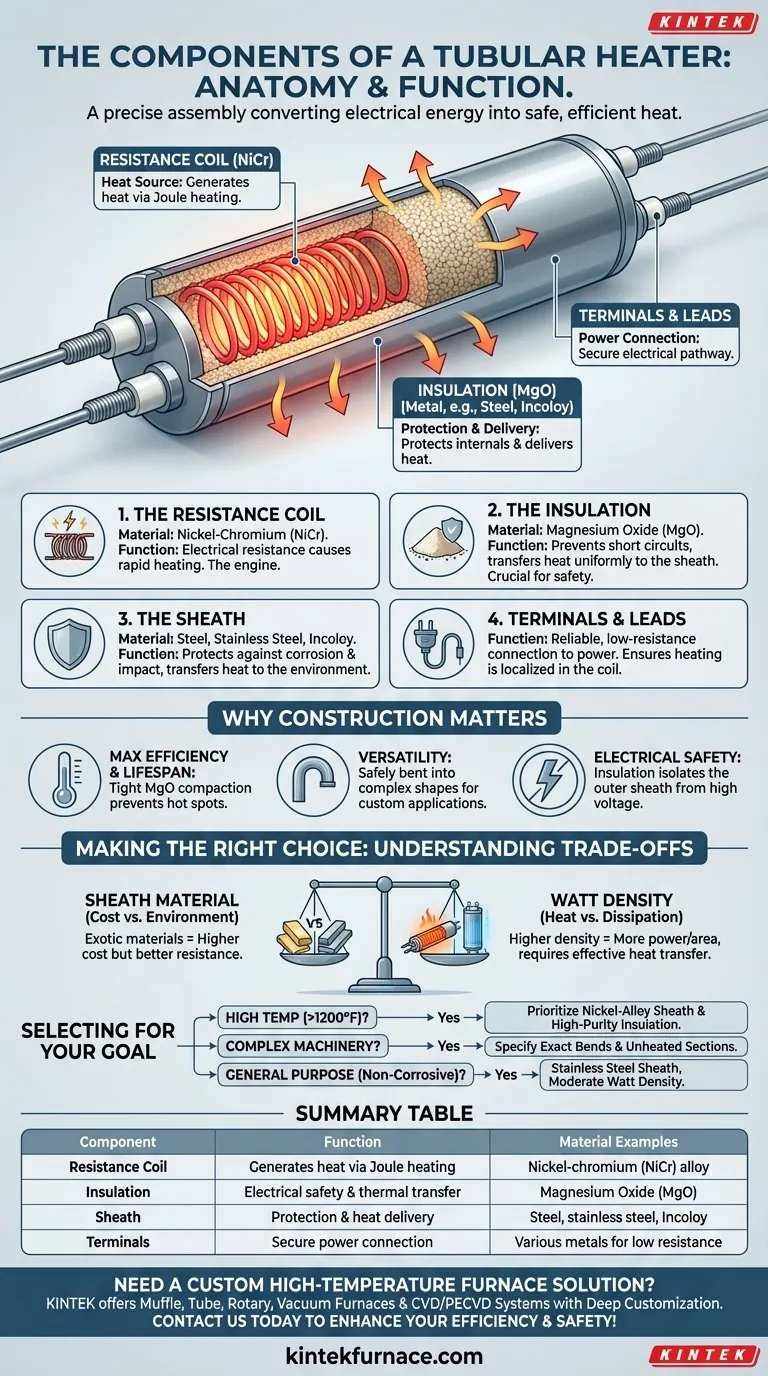
At its core, a tubular heater is a precisely engineered assembly consisting of a resistance heating coil, ceramic electrical insulation, and a protective outer metal sheath. These components work in unison to convert electrical energy into heat safely and efficiently, with terminals at each end providing a secure connection to a power source.
The genius of the tubular heater isn't in any single component, but in how these simple parts are combined. The design creates a robust, versatile heating element that is both electrically isolated and thermally efficient, allowing it to be bent and formed for countless industrial applications.

The Core Components in Detail
To truly understand how a tubular heater functions, we must examine each of its fundamental parts and the role it plays in the system.
The Resistance Coil: The Heat Source
The resistance coil is the engine of the heater. It is typically made from a nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloy wire.
When an electric current flows through this wire, its inherent electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly—a principle known as Joule heating. This coil is the source of all the thermal energy the heater produces.
The Insulation: Safety and Transfer
Surrounding the coil is a layer of highly compacted ceramic powder, most commonly Magnesium Oxide (MgO). This material serves two critical, simultaneous functions.
First, it is an excellent electrical insulator, preventing the live coil from making contact with the outer metal sheath and causing a dangerous short circuit.
Second, it is an effective thermal conductor. It efficiently pulls heat away from the fragile resistance coil and transfers it uniformly to the much more robust outer sheath, preventing the coil from overheating and burning out.
The Sheath: Protection and Delivery
The outer metal sheath is the component that interfaces with the environment. It protects the delicate internal components from moisture, corrosion, and physical impact.
Crucially, the sheath is the surface that delivers the heat to the substance being heated, whether it's air, a liquid, or a solid metal block. The material used for the sheath (e.g., steel, stainless steel, Incoloy) is selected based on the application's operating temperature and corrosive potential.
Terminals and Leads: The Power Connection
Terminals provide the connection point between the internal resistance coil and the external power leads.
These are carefully designed to create a reliable, low-resistance electrical pathway. They ensure that heating occurs primarily in the coil, not at the connection points, which is essential for safety and longevity.
Why This Construction Matters
The specific arrangement of these components is not arbitrary. It is the result of decades of engineering refinement to solve key challenges in electric heating.
Maximizing Efficiency and Lifespan
The tight compaction of the MgO insulation is key. It eliminates air gaps, ensuring heat moves efficiently from the coil to the sheath. This prevents "hot spots" from forming on the coil, which is a primary cause of premature heater failure.
Ensuring Versatility
Because the internal components are protected and electrically isolated, the entire tubular element can be safely bent and formed into complex shapes. This allows heaters to be custom-fit into machined grooves, wrapped around pipes, or configured for specific airflow patterns, making them one of the most versatile heating solutions available.
Providing Electrical Safety
The insulation layer is fundamental to the heater's safety. It guarantees that the outer metal sheath, which is often in contact with other machine parts or accessible areas, remains safely isolated from the high voltage of the internal coil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the design of a tubular heater involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for selecting the right heater for a job.
Sheath Material vs. Cost and Environment
More exotic sheath materials like Incoloy or titanium offer superior resistance to high temperatures and corrosion. However, they are significantly more expensive than standard stainless or carbon steel. The choice is a direct trade-off between the demands of the application and the project budget.
Watt Density vs. Heat Dissipation
Watt density refers to the heat output per square inch of the heater's surface. A higher watt density allows for more power in a smaller package, but it also means the sheath gets hotter, faster. If this intense heat is not effectively transferred away (e.g., in forced air or a circulating liquid), the heater can easily overheat and fail. The component selection directly impacts the maximum safe watt density.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary goal will dictate which component characteristics are most important.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance (>1200°F / 650°C): Prioritize a heater with a high-grade nickel-alloy sheath (like Incoloy) and high-purity insulation.
- If your primary focus is fitting into complex machinery: The formability of the heater is key, so ensure you specify the exact bends, curves, and unheated sections required.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in a non-corrosive environment: A heater with a stainless steel sheath and a moderate watt density offers the best balance of performance and cost.
By understanding how each component contributes to the whole, you can specify a heater that is perfectly suited to its task.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Material Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Coil | Generates heat via Joule heating | Nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloy |
| Insulation | Electrical safety and thermal transfer | Magnesium Oxide (MgO) |
| Sheath | Protection and heat delivery | Steel, stainless steel, Incoloy |
| Terminals | Secure power connection | Various metals for low resistance |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your heating efficiency and safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















