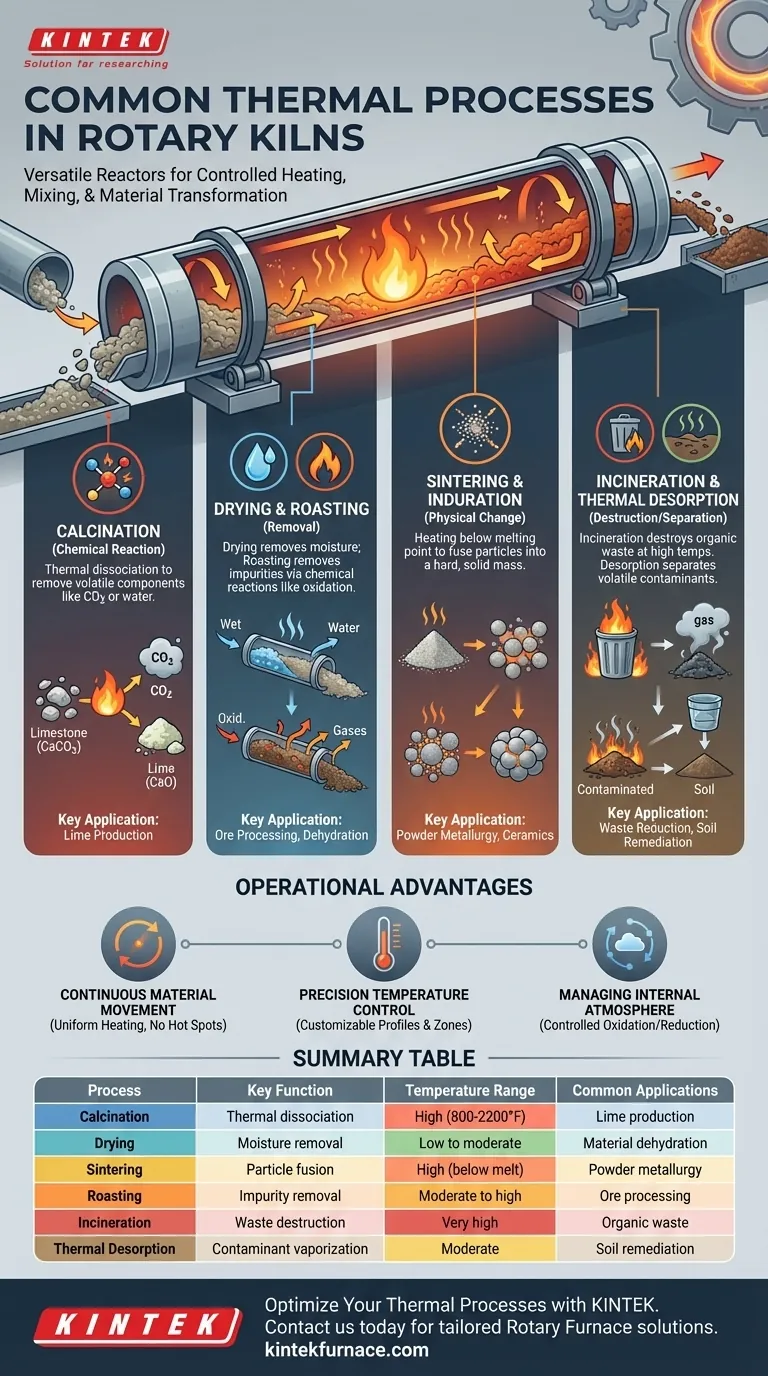
In essence, a rotary kiln is a highly versatile thermal reactor used to induce specific chemical or physical changes in solid materials. The most common thermal processes performed in these units are calcination, drying, sintering, roasting, and thermal treatment methods like incineration and thermal desorption. These operations leverage the kiln's ability to uniformly heat, mix, and transport material at controlled temperatures, which can range from 800°F to over 2,200°F.
The true value of a rotary kiln isn't just its high temperature, but its ability to precisely control heat transfer while continuously mixing and moving material. This unique combination makes it the ideal environment for processes that require uniform heating, specific chemical reactions, or physical phase changes in solids.

Breaking Down the Core Thermal Processes
A rotary kiln’s primary function is to serve as a contained, dynamic reaction vessel. Its gentle tumbling action and controlled temperature profile are what enable a wide variety of industrial transformations.
Driving Chemical Reactions: Calcination
Calcination is a process that uses heat to break down compounds, often by removing a volatile component like carbon dioxide or water. It is a thermal dissociation reaction.
A common example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). The rotary kiln's uniform heating ensures the entire mass of material reaches the required temperature for the reaction to complete efficiently.
Removing Unwanted Components: Drying and Roasting
Drying is a low-temperature process focused solely on removing moisture from a material. The kiln's tumbling action constantly exposes new surfaces to the hot gas stream, accelerating evaporation.
Roasting, by contrast, is a higher-temperature process designed to remove specific impurities. This is often achieved by inducing chemical reactions, such as oxidation, to convert impurities into a gaseous form that can be carried away.
Inducing Physical Changes: Sintering and Induration
Sintering (or induration) is the process of heating a fine powder or aggregate to a temperature just below its melting point. This causes the particles to fuse together, creating a hard, solid mass.
The precise temperature control of a rotary kiln is critical here, as overheating would cause the material to melt. The slow, continuous movement helps form a strong, homogenous product.
Destroying or Separating Substances: Incineration and Desorption
Incineration is a high-temperature combustion process used to destroy organic materials, significantly reducing waste volume. Rotary kilns provide the long residence time and high heat needed for complete destruction.
Thermal Desorption is a lower-temperature alternative used to separate volatile contaminants (like hydrocarbons) from a solid medium (like soil). The heat vaporizes the contaminants, which are then collected and treated, leaving the cleaned solid behind.
Understanding the Operational Advantage
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln stems from a few key design principles that make it more than just a hot tube. These features are why it is chosen for such a diverse set of applications, from mining and metallurgy to waste management.
The Impact of Continuous Material Movement
The slow rotation of the kiln cylinder continuously tumbles the material. This action ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source, preventing hot spots and resulting in a highly consistent and homogenous final product.
The Need for Precision Temperature Control
Modern kilns offer customizable heat patterns and advanced controls. This allows operators to create specific temperature zones along the length of the kiln, which is essential for complex processes that require a gradual heating or cooling profile.
Managing the Internal Atmosphere
A kiln's enclosed design allows for strict control over the internal gaseous environment. Processes like reduction (removing oxygen, as in iron ore processing) or oxidation require specific atmospheres to proceed correctly, a feature that kilns readily support.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The process you utilize in a rotary kiln is dictated entirely by your end goal and starting material.
- If your primary focus is creating a new compound: Calcination is the key process for thermally dissociating materials like limestone or activating catalysts.
- If your primary focus is purifying a solid: Drying, roasting, or thermal desorption are the methods for removing moisture, chemical impurities, or volatile contaminants.
- If your primary focus is changing physical form: Sintering is used to create a dense, solid mass from fine particles without melting them.
- If your primary focus is waste treatment: Incineration is used for high-temperature destruction and volume reduction of organic materials.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln's strength lies in its ability to transform materials by applying controlled heat in a dynamic, highly-managed environment.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Function | Temperature Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal dissociation to remove volatiles | High (e.g., 800-2200°F) | Lime production, catalyst activation |
| Drying | Moisture removal | Low to moderate | Material dehydration |
| Sintering | Particle fusion without melting | High, below melting point | Powder metallurgy, ceramics |
| Roasting | Impurity removal via oxidation | Moderate to high | Ore processing, metal refining |
| Incineration | High-temperature waste destruction | Very high | Organic waste reduction |
| Thermal Desorption | Contaminant vaporization | Moderate | Soil remediation, cleaning solids |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for calcination, sintering, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material transformations and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















