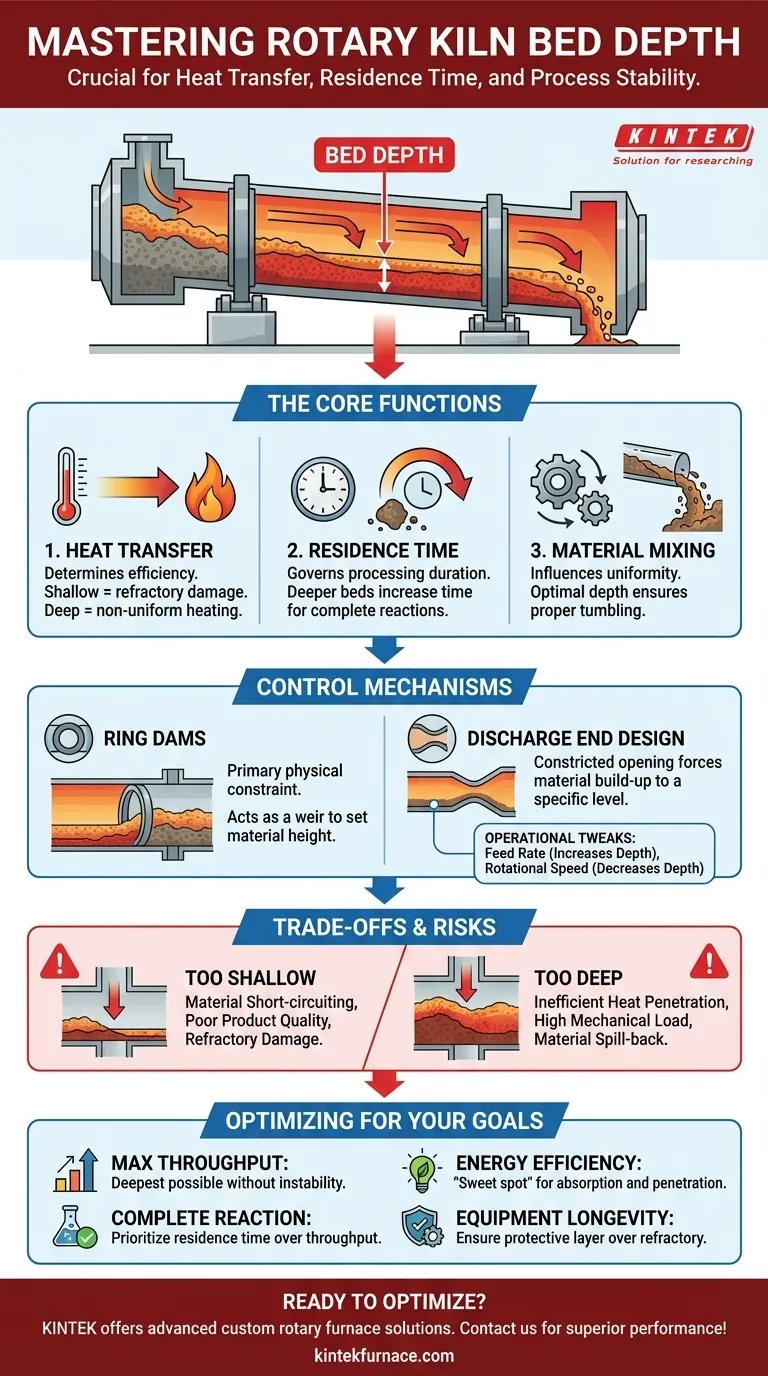
In a rotary kiln, bed depth is controlled primarily through mechanical obstructions, most commonly a ring dam or a specifically designed discharge-end configuration. This control is critical because bed depth directly dictates heat transfer efficiency, the amount of time material spends in the kiln (residence time), and the overall stability and effectiveness of the entire thermal process.
Controlling bed depth is not simply a matter of managing volume; it is the fundamental lever for mastering the contact time and surface area exposure of material to the heat source. Getting this parameter right optimizes product quality and energy use, while getting it wrong leads to inefficiency, inconsistent product, and potential equipment damage.
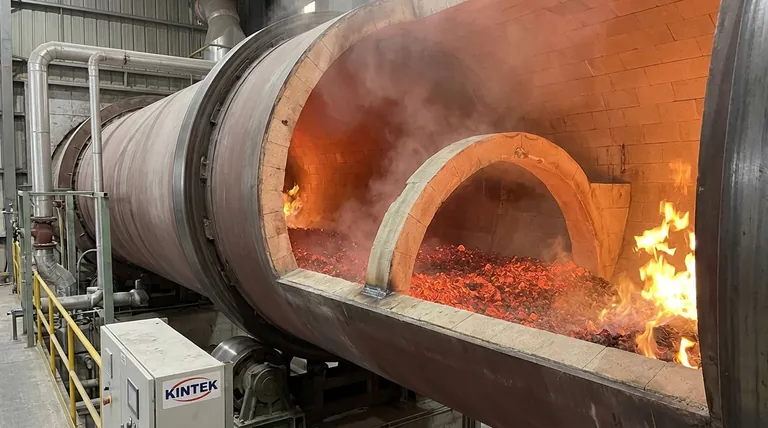

The Core Function of Bed Depth
Understanding bed depth is to understand the heart of the kiln's thermal and mechanical dynamics. It is not a static number but a key process variable with direct consequences.
Governing Heat Transfer
A rotary kiln transfers heat to material through direct flame radiation, hot gas convection, and conduction from the hot refractory wall. Bed depth determines how effectively this occurs.
If the bed is too shallow, the material may pass through too quickly or overheat on the surface. More importantly, the shallow bed fails to adequately protect the refractory lining from direct flame impingement, increasing wear and energy loss.
If the bed is too deep, heat cannot penetrate to the core of the material bed. This results in a non-uniform product where the outer layers are processed but the inner layers remain untouched, wasting significant energy.
Controlling Residence Time
Residence time—the duration a particle spends inside the kiln—is critical for most chemical reactions and physical phase changes. Bed depth, in conjunction with kiln slope and rotational speed, governs this.
A dam increases bed depth, effectively slowing the material's forward progress and increasing residence time. This ensures that processes requiring a specific duration, like calcination or organic combustion, are brought to completion.
Influencing Material Mixing
The characteristic tumbling motion of a rotary kiln is essential for exposing all particle surfaces to heat and ensuring a uniform product. Bed depth directly influences the quality of this mixing.
An optimal depth promotes a continuous cascade of material down the face of the bed. If the bed is too deep, it can lead to "slumping" or "avalanching" where large sections move at once, resulting in poor mixing and mechanical stress on the kiln drive.
Mechanisms for Controlling Bed Depth
While feed rate and rotation speed have an influence, bed depth is primarily set by physical design features within the kiln.
The Role of Ring Dams
A ring dam, also known as a retaining ring, is the most common control mechanism. It is a circular steel structure, lined with refractory, that is welded to the inside of the kiln shell.
This dam acts as a weir. Material builds up behind it until the bed depth reaches the height of the dam, at which point it spills over and continues its path down the kiln. The height and position of the dam are engineered specifically for the process requirements.
Discharge End Design
In some kilns, especially those without a mid-kiln dam, the design of the discharge end itself controls the bed depth. A constricted opening or a built-in dam at the discharge chute forces the material to build to a certain level before it can exit, effectively setting the bed depth for the entire unit.
Interplay with Operational Parameters
While dams provide the primary physical constraint, operators use other variables to make fine adjustments. Increasing the material feed rate will dynamically increase the bed depth, while increasing the kiln's rotational speed tends to spread the material out, slightly decreasing the depth.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing a bed depth involves balancing competing objectives. Misjudging this parameter can lead to significant operational problems.
The Risk of Insufficient Bed Depth
A bed that is too shallow can cause material short-circuiting, where fine particles are carried out by the gas stream before being fully processed. This leads to low yield and poor product quality. It also exposes the refractory lining to excessive thermal stress, shortening its lifespan.
The Danger of an Excessive Bed Depth
An overly deep bed is inefficient, as heat fails to reach the material core. It dramatically increases the mechanical load on the kiln's drive system, bearings, and shell. In severe cases, it can cause material to spill back out of the feed end, creating a safety and operational hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal bed depth is not a universal value but is dictated by your specific material and process goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: You will aim for a bed depth that is as deep as possible without compromising product uniformity or causing operational instability.
- If your primary focus is ensuring complete chemical reaction: You will prioritize a bed depth and dam configuration that guarantees the required residence time, even if it means a slightly lower throughput.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: You will seek the "sweet spot" where the bed is deep enough to absorb the majority of the available heat but shallow enough for that heat to fully penetrate the material.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: You will always ensure the bed is deep enough to provide a protective layer over the refractory, avoiding direct exposure to the flame and minimizing thermal shock.
Ultimately, mastering bed depth is about transforming a simple physical dimension into a precise tool for process optimization.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Bed Depth | Control Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Affects efficiency; too shallow risks refractory damage, too deep causes non-uniform heating | Ring dams, discharge-end design |
| Residence Time | Determines processing duration; deeper beds increase time for reactions | Dams, feed rate, rotational speed |
| Material Mixing | Influences uniformity; optimal depth ensures proper tumbling, avoiding slumping | Bed depth adjustments via mechanical obstructions |
| Operational Risks | Too shallow leads to short-circuiting; too deep increases mechanical load and inefficiency | Balancing depth with process goals |
Ready to optimize your rotary kiln's bed depth for superior performance? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces and more. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing heat transfer, efficiency, and product quality. Don't let inefficiencies hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















