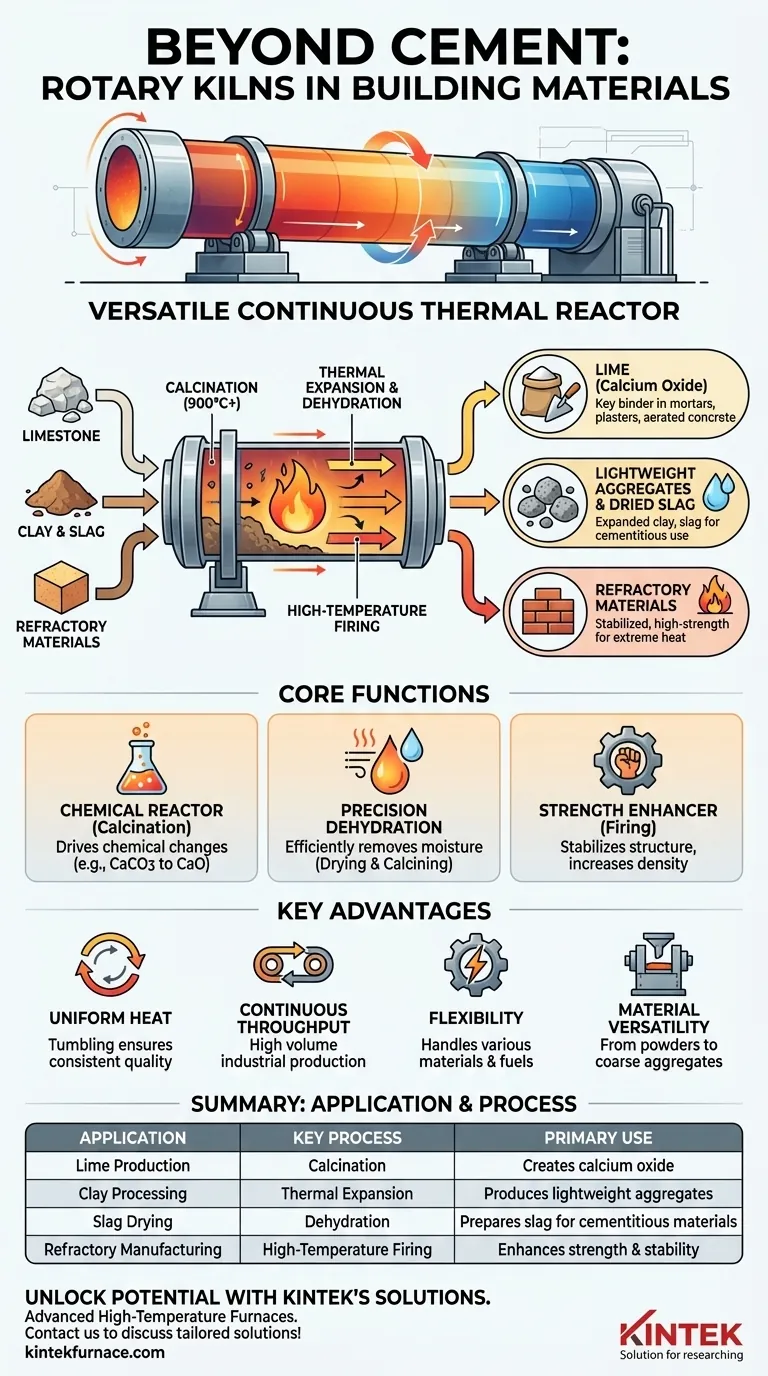
Beyond cement clinker, rotary kilns are fundamental to the building materials sector for several other critical processes. They are widely used for the calcination of limestone to produce lime, the thermal processing and expansion of clay, the drying of industrial slag, and the manufacturing of high-strength refractory materials.
A rotary kiln’s value extends far beyond a single application. Its core strength lies in its ability to function as a versatile, continuous thermal reactor, capable of precisely controlling high-temperature chemical and physical transformations in a wide variety of raw materials.

The Kiln as a Multi-Process Tool
While its role in cement is famous, a rotary kiln is fundamentally a piece of heavy-duty processing equipment designed for versatility. Its utility comes from its ability to perform several distinct thermal functions on an industrial scale.
A High-Temperature Chemical Reactor
The most common alternative use is calcination, a process that uses heat to drive a chemical reaction. A prime example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) by heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to high temperatures, driving off carbon dioxide.
This process is essential for creating lime, a key binder in mortars, plasters, and aerated concrete blocks.
A Precision Dehydration Unit
Rotary kilns are highly effective for drying and dehydrating bulk materials. The constant tumbling motion and controlled flow of hot gas ensure that every particle is exposed to heat, efficiently removing moisture.
This capability is used for slag drying, preparing it for use as a supplementary cementitious material, and for calcining clay, which removes its chemically bound water to create stable, lightweight aggregates.
A Material Strength Enhancer
In the manufacturing of refractory materials—products designed to withstand extreme heat—rotary kilns play a vital role. Raw materials are heated to stabilize their crystalline structure and increase their density and strength.
This pre-firing step ensures the final refractory bricks or castables will not shrink or crack when put into service in furnaces, reactors, or other high-heat environments.
Why the Rotary Kiln Excels at These Tasks
The rotary kiln's design gives it several inherent advantages that make it the preferred tool for these demanding applications. Its effectiveness is not just about getting hot, but about how it controls and applies that heat.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The slow rotation of the kiln cylinder ensures the material inside tumbles continuously. This action guarantees uniform heat transfer throughout the entire batch, preventing hot spots and ensuring a consistent, high-quality final product.
Continuous, High-Throughput Processing
Unlike a batch oven, a rotary kiln operates as a continuous system. Raw material is fed into one end and processed as it travels to the other, allowing for high throughput and making it ideal for large-scale industrial production.
Flexibility in Materials and Fuels
Rotary kilns are robust and can be designed to handle a wide variety of feedstocks, from fine powders to coarse aggregates. Modern kilns also offer flexibility in fuel sources, including alternative and secondary fuels, which can support sustainability goals and reduce operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its versatility, a rotary kiln is a major industrial asset with significant considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to appreciating its proper application.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kilns are massive, heavy-duty machines. The engineering, construction, and installation represent a substantial upfront capital cost that is only justifiable for large-scale, continuous operations.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining the internal temperatures required for calcination—often well over 900°C (1650°F)—is an energy-intensive process. Energy efficiency is a primary concern in kiln design and operation.
Operational Complexity
While the principle is simple, optimizing a kiln for peak efficiency, product quality, and safety requires significant operator skill and process control expertise. Maintaining stable conditions within the dynamic environment of the kiln is a constant challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of a rotary kiln should be directly tied to the desired transformation of the material.
- If your primary focus is inducing a chemical change: The kiln is your reactor for calcination processes like turning limestone into lime or creating expanded clay aggregates.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture: The kiln's efficiency at drying makes it ideal for preparing materials like industrial slag or dehydrating clays.
- If your primary focus is enhancing physical properties: The kiln is a thermal treatment tool used to fire refractory materials to achieve necessary strength and dimensional stability.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is the industrial workhorse for any process that requires precise, continuous, and uniform high-temperature treatment of bulk solids.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Lime Production | Calcination | Creates calcium oxide for mortars and plasters |
| Clay Processing | Thermal Expansion | Produces lightweight aggregates |
| Slag Drying | Dehydration | Prepares slag for cementitious materials |
| Refractory Manufacturing | High-Temperature Firing | Enhances strength and stability of heat-resistant products |
Unlock the full potential of your building materials processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer rotary kilns and other products like Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your efficiency and quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















