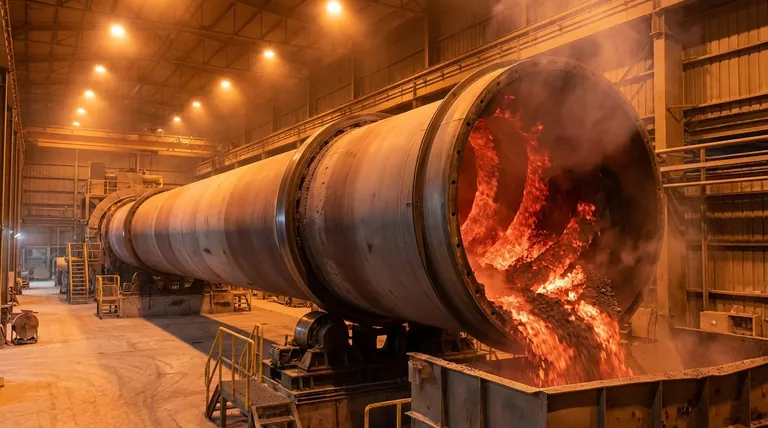
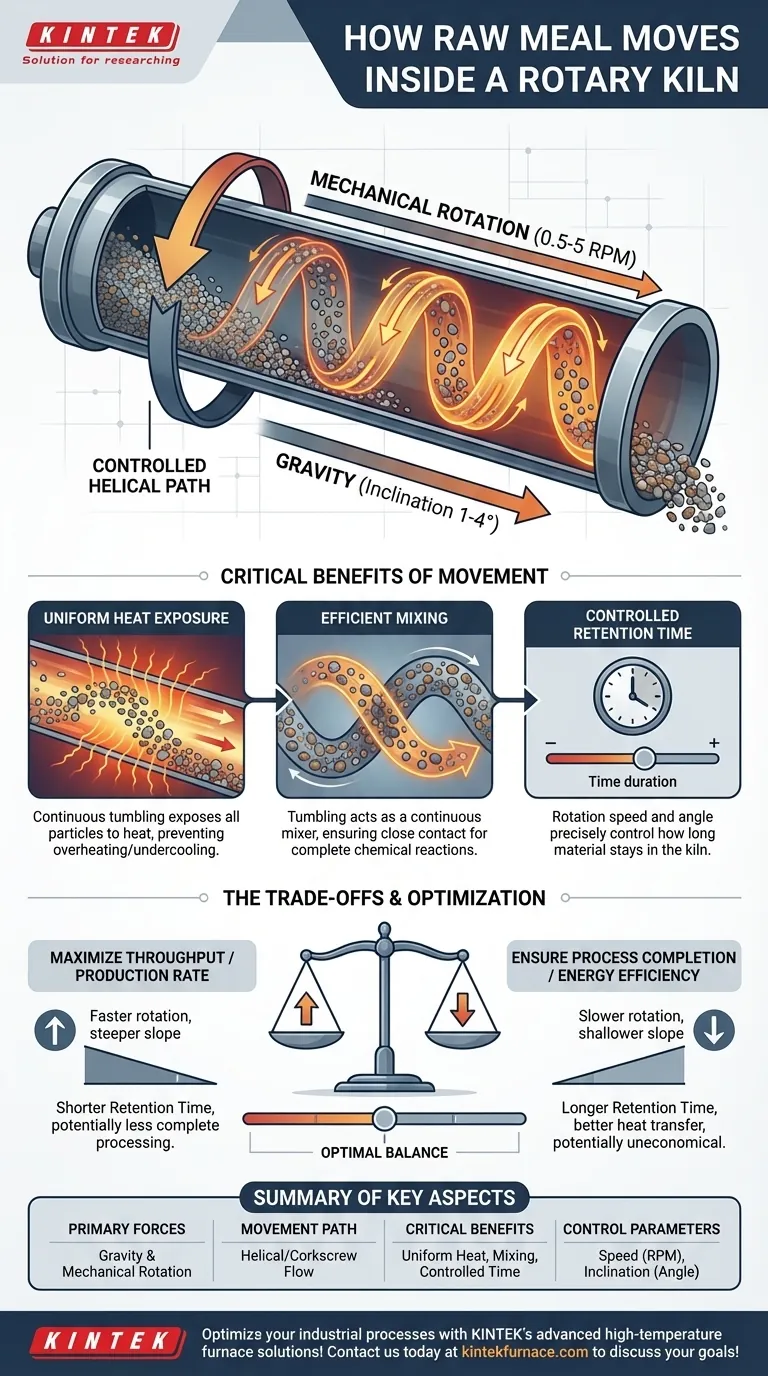
At its core, the movement of raw meal inside a rotary kiln is governed by two fundamental principles working in concert: gravity and mechanical rotation. The kiln is a long cylinder set at a slight downward angle, and as it slowly turns, the material is lifted and then tumbles forward, creating a slow, continuous flow from the feed end to the discharge end.
The movement of material in a rotary kiln is not simply for transport. It is a precisely engineered process designed to ensure every particle is continuously mixed, tumbled, and exposed to uniform heat, which is essential for triggering the required chemical reactions or physical changes.

The Two Core Forces Driving Material Flow
The elegant simplicity of the rotary kiln's design hides a sophisticated interaction between gravitational and mechanical forces. Understanding these two components is key to understanding the entire process.
The Role of Inclination and Gravity
A rotary kiln is never perfectly horizontal. It is installed with a slight slope, typically between 1 and 4 degrees, with the feed end higher than the discharge end.
This slight incline means that gravity constantly pulls the material downhill along the length of the kiln. This is the primary force that ensures the material travels from its entry point to its exit point.
The Impact of Kiln Rotation
Simultaneously, the entire kiln cylinder rotates slowly on its axis, typically at 0.5 to 5 revolutions per minute. This rotation continuously lifts the material up the interior wall of the kiln.
Once the material reaches a certain height (the angle of repose), it cascades or tumbles back down towards the bottom of the material bed. This action is critical for mixing.
The Combined Effect: A Controlled Helical Path
The combination of the downward movement from gravity and the cross-sectional tumbling from rotation forces the material to follow a slow, corkscrew-like (helical) path.
This controlled path ensures that the material doesn't just slide down the kiln. Instead, it moves forward at a predictable, manageable rate, allowing for sufficient processing time.
Why This Movement is Critical for the Process
The specific way material moves through the kiln is directly responsible for the kiln's effectiveness as a chemical reactor and heat exchanger. The design's purpose goes far beyond simple conveyance.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Exposure
The constant tumbling action is essential for effective heat transfer. It continuously exposes new particles to the hot gases flowing through the kiln and the radiant heat from the refractory walls.
This prevents the top layer from overheating while the bottom layer remains too cool. The result is a homogenous temperature throughout the material bed, leading to a consistent final product.
Promoting Efficient Mixing
For processes like cement manufacturing, the goal is to induce chemical reactions between different components in the raw meal.
The tumbling motion acts as a continuous mixer, ensuring all particles are in close contact, which is vital for the desired reactions to occur completely and efficiently.
Controlling Retention Time
The retention time—the total time the material spends inside the kiln—is one of the most critical operational parameters.
Engineers can precisely control this duration by adjusting the kiln's rotational speed and its angle of inclination. A faster rotation or steeper slope decreases retention time, while a slower rotation or shallower slope increases it.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing material flow is a balancing act. The settings that maximize one outcome may negatively impact another, requiring careful consideration of the process goals.
Throughput vs. Retention Time
Increasing the rotational speed or slope will increase the kiln's throughput, meaning more material is processed per hour.
However, this reduces the retention time. If the material moves too quickly, it may exit the kiln before the chemical reactions are complete or before it has reached the target temperature, resulting in a poor-quality product.
Energy Efficiency vs. Production Rate
A slower material flow generally improves energy efficiency because it allows for more complete heat transfer from the fuel to the material.
This must be balanced against the required production rate. Running the kiln too slowly can make the process uneconomical, even if it is highly efficient from a thermal perspective. The goal is to find the optimal point that meets quality standards while minimizing fuel cost per ton of product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal kiln operation depends entirely on your primary objective. Adjusting the parameters of material flow allows you to fine-tune the process for different outcomes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: You will likely operate with a higher rotational speed and/or a steeper kiln slope, while closely monitoring product quality to ensure retention time remains adequate.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process completion: You will favor a longer retention time by using a slower rotational speed and a shallower slope, guaranteeing every particle is fully transformed.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: You will aim for the slowest material flow that still meets quality and production targets, maximizing heat transfer and minimizing wasted fuel.
Ultimately, the controlled movement of material is the mechanism that transforms a simple rotating tube into a highly effective continuous reactor.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Forces | Gravity (due to kiln inclination) and mechanical rotation |
| Movement Path | Helical or corkscrew-like flow from feed to discharge end |
| Critical Benefits | Uniform heat exposure, efficient mixing, controlled retention time |
| Control Parameters | Rotational speed (0.5-5 RPM) and inclination angle (1-4 degrees) |
| Impact on Process | Affects throughput, product quality, and energy efficiency |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















