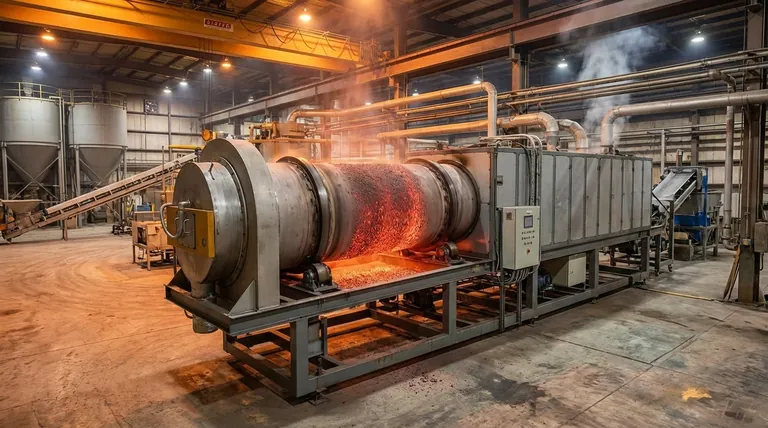
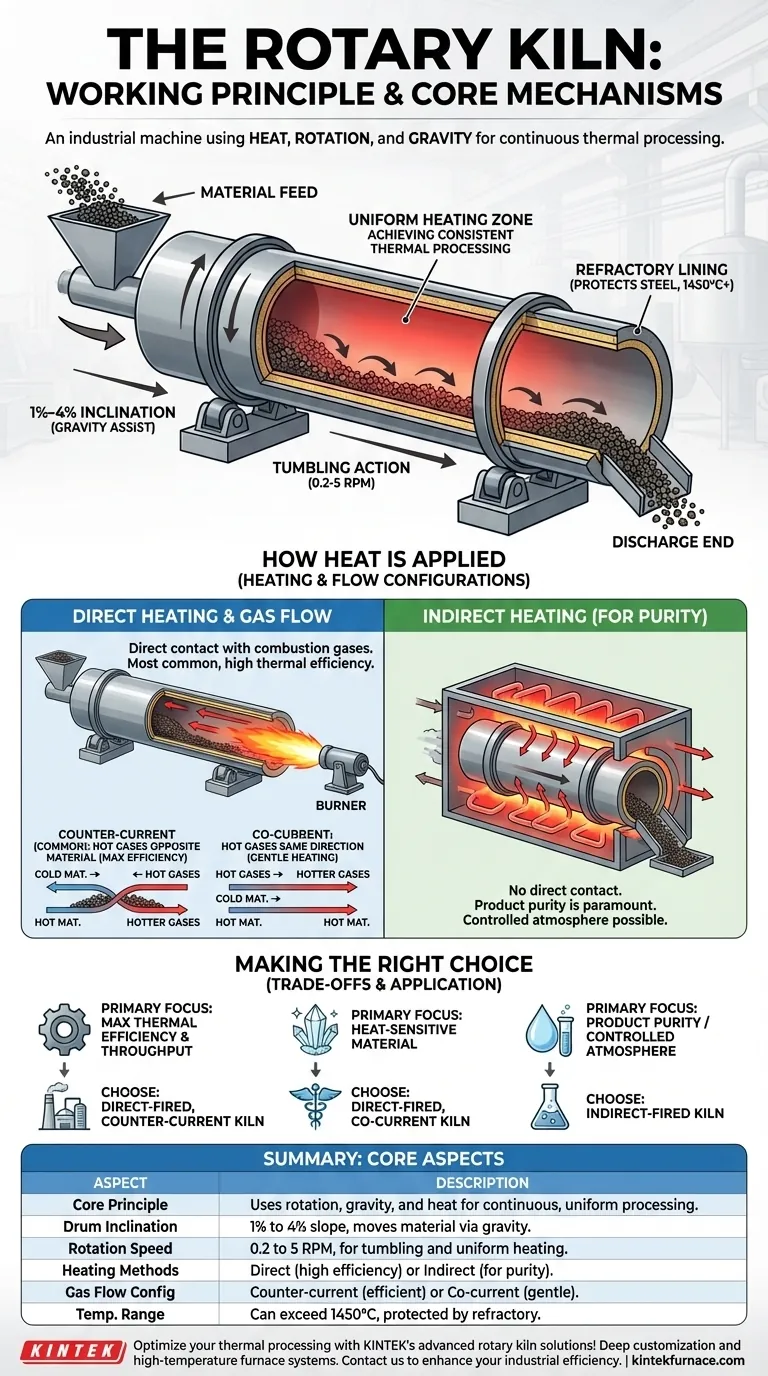
At its core, a rotary kiln is an industrial machine that uses a combination of heat, rotation, and gravity to cause a physical or chemical change in a material. It consists of a long, rotating cylindrical tube, known as a drum, which is set at a slight angle. Material is fed into the higher end and slowly tumbles down toward the lower end as the drum rotates, getting continuously mixed and exposed to a controlled heat source along the way.
The fundamental principle is not just heating, but achieving highly uniform and continuous thermal processing. The genius of the rotary kiln lies in using the simple mechanics of rotation and inclination to precisely control how long material is exposed to heat, ensuring a consistent end product at an industrial scale.

The Core Mechanism: How a Rotary Kiln Works
The operation of a rotary kiln is a carefully orchestrated interaction between mechanical movement and thermal energy.
The Inclined, Rotating Drum
A rotary kiln's body is a steel cylinder mounted on support bearings that allow it to rotate. It is set at a slight inclination, typically between 1% and 4% (a drop of 1 to 4 feet for every 100 feet of length).
This slight downward slope is critical. It uses gravity to ensure the material constantly moves from the feed end to the discharge end.
Material Transport and Tumbling
The drum rotates slowly, usually between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (RPM). This slow rotation lifts the material partway up the side of the drum before it tumbles back down into the bed of material.
This tumbling action is essential for two reasons: it ensures uniform heating by continuously exposing new particles to the heat source, and it provides the motive force that moves the material through the kiln.
The Refractory Lining
The inside of the steel drum is lined with a heat-resistant material called refractory. This lining protects the outer steel structure from the extreme internal temperatures, which can exceed 1450°C (2640°F) in applications like cement manufacturing.
The Critical Element: Heat Application
How heat is introduced and managed is fundamental to the kiln's function. There are two primary methods for heating and two main configurations for gas flow.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Direct heating is the most common method. A burner, typically located at the discharge end, shoots a flame and hot combustion gases directly into the kiln's interior. The material comes into direct contact with these hot gases.
Indirect heating is used when the material cannot be exposed to combustion gases. In this design, the rotating drum is enclosed in a furnace or fitted with external heating elements. Heat transfers through the kiln shell wall to the material inside, keeping the process atmosphere separate and controlled.
Counter-Current vs. Co-Current Flow
This principle applies to direct-fired kilns and describes the direction of hot gas flow relative to the material.
Counter-current flow is the most common and thermally efficient configuration. Hot gases from the burner at the discharge end flow uphill, opposite the direction of the material. This allows for maximum heat transfer as the hottest gases meet the hottest material.
Co-current flow involves the hot gases entering at the feed end and flowing in the same direction as the material. This is used for materials that are sensitive to thermal shock, as the coldest material meets the hottest gases first, allowing for more gradual heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between direct and indirect heating is the most significant design decision, driven entirely by the process requirements.
When to Use Direct Heating
Direct-fired kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry. They are chosen for high-temperature, high-capacity applications where direct contact with combustion gas is acceptable.
This method is more thermally efficient because heat is transferred directly to the material. It is ideal for robust processes like cement production, lime calcination, and mineral processing.
When to Use Indirect Heating
Indirect-fired kilns are chosen when product purity is paramount. They are essential for processes where the material must not be contaminated by combustion byproducts (like sulfur or ash) or when a specific internal atmosphere (e.g., inert or reducing) is required.
The trade-off is lower thermal efficiency and typically lower processing temperatures and capacities compared to direct-fired kilns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the right configuration for a specific industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency and throughput: A direct-fired, counter-current kiln is the standard choice for bulk materials.
- If your primary focus is processing a heat-sensitive material: A direct-fired, co-current kiln provides gentler heating to prevent material damage.
- If your primary focus is product purity or a controlled atmosphere: An indirect-fired kiln is the only option to isolate the material from combustion gases.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's enduring value comes from its simple, scalable, and highly adaptable design for continuous thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses rotation, gravity, and heat for continuous, uniform thermal processing of materials. |
| Drum Inclination | Typically 1% to 4% slope to move material via gravity from feed to discharge end. |
| Rotation Speed | 0.2 to 5 RPM for tumbling action, ensuring uniform heating and material transport. |
| Heating Methods | Direct heating (high efficiency, direct contact) or indirect heating (for purity, controlled atmospheres). |
| Gas Flow Configurations | Counter-current (efficient, hot gases opposite material) or co-current (gentle, gases same direction). |
| Temperature Range | Can exceed 1450°C, with refractory lining to protect the drum. |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your industrial efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















