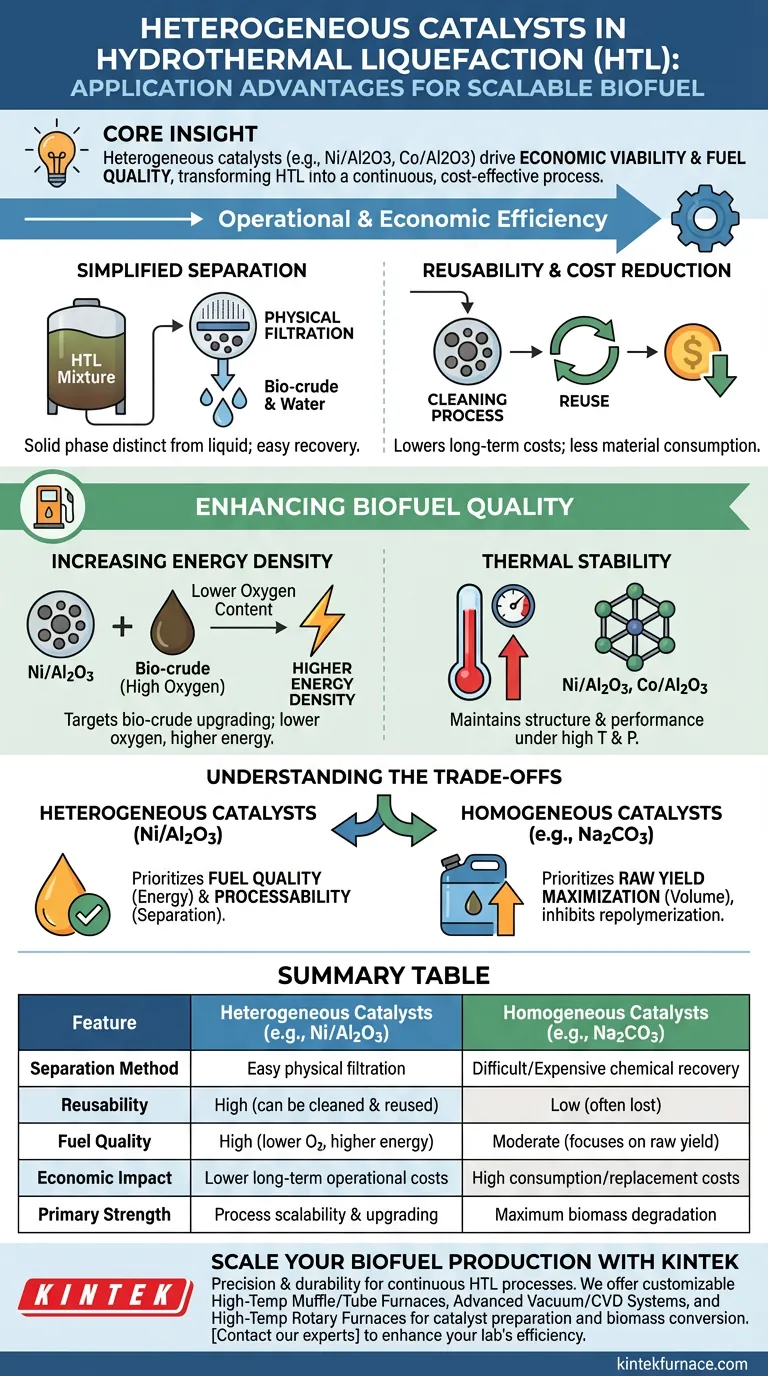
The decisive application advantages of heterogeneous catalysts in Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL) center on process scalability and product upgrading. Unlike homogeneous catalysts that dissolve into the mixture, heterogeneous options like Ni/Al2O3 or Co/Al2O3 allow for seamless separation via physical filtration, facilitating reuse and significantly enhancing the energy density of the resulting biofuel.
Core Insight: While homogeneous catalysts are effective for biomass breakdown, heterogeneous catalysts are the superior choice for economic viability and fuel quality. They transform HTL from a single-use batch process into a potentially continuous, cost-effective operation by allowing catalyst recovery and producing a lower-oxygen, higher-energy fuel.
Operational and Economic Efficiency
The most immediate benefit of using heterogeneous catalysts is the simplification of downstream processing. This addresses the "Deep Need" of making HTL commercially feasible.
Simplified Separation
In HTL, the reaction medium is a complex mixture of water, bio-crude, and solids. Homogeneous catalysts dissolve completely, making them difficult and expensive to recover.
Conversely, heterogeneous catalysts exist as a solid phase distinct from the liquid product. This allows for recovery through standard physical filtration immediately after the reaction.
Reusability and Cost Reduction
Because these catalysts can be physically separated, they can be reused after a simple cleaning process.
This reusability drastically lowers long-term operational costs. You are not constantly consuming and replacing the catalyst material with every batch, as is often the case with dissolved homogeneous agents.
Enhancing Biofuel Quality
Beyond process mechanics, heterogeneous catalysts like nickel or cobalt supported on alumina (Ni/Al2O3 or Co/Al2O3) fundamentally change the chemical composition of the fuel for the better.
Increasing Energy Density
These supported metal catalysts possess high catalytic activity specifically targeted at upgrading the bio-crude.
They are highly effective at reducing the oxygen content of the biofuel. Lower oxygen content directly translates to significantly increased energy density, making the final product more comparable to conventional petroleum fuels.
Thermal Stability
HTL occurs at high temperatures and pressures. Catalysts like Ni/Al2O3 and Co/Al2O3 are engineered for high thermal stability.
This ensures they maintain their structural integrity and catalytic performance even under the harsh conditions required to liquefy biomass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an informed engineering decision, you must recognize where heterogeneous catalysts may differ from their homogeneous counterparts.
Yield vs. Quality
Homogeneous catalysts, such as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) or potassium hydroxide (KOH), excel at promoting the degradation of polysaccharides like cellulose.
They are particularly effective at inhibiting repolymerization (the re-forming of solids), which can help maximize the raw volume of bio-crude yield.
However, choosing a heterogeneous catalyst prioritizes the quality (energy content) and processability (separation) of the oil over simply maximizing the raw mass of the yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right catalyst depends on balancing the need for high biomass conversion against the need for a high-quality, cost-effective fuel product.
- If your primary focus is Commercial Viability and Fuel Quality: Prioritize heterogeneous catalysts (Ni/Al2O3, Co/Al2O3) to enable catalyst reuse, reduce costs, and produce high-energy, low-oxygen fuel.
- If your primary focus is Raw Yield Maximization: Consider homogeneous catalysts to effectively break down polysaccharides and inhibit repolymerization, maximizing the total volume of bio-crude produced.
By leveraging the physical properties of heterogeneous catalysts, you secure a path toward a more sustainable and economically scalable fuel production process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Heterogeneous Catalysts (e.g., Ni/Al2O3) | Homogeneous Catalysts (e.g., Na2CO3) |
|---|---|---|
| Separation Method | Easy physical filtration | Difficult/Expensive chemical recovery |
| Reusability | High (can be cleaned and reused) | Low (often lost in the process) |
| Fuel Quality | High (lower oxygen, higher energy density) | Moderate (focuses on raw yield) |
| Economic Impact | Lower long-term operational costs | High consumption/replacement costs |
| Primary Strength | Process scalability and upgrading | Maximum biomass degradation |
Scale Your Biofuel Production with KINTEK
Transitioning from batch experiments to continuous, commercially viable HTL processes requires precision and durability. At KINTEK, we understand that the right high-temperature environment is critical for catalyst performance and biomass conversion.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of laboratory solutions, including:
- Customizable Muffle and Tube Furnaces for catalyst preparation.
- Advanced Vacuum and CVD Systems for specialized material synthesis.
- High-Temp Rotary Furnaces designed for consistent thermal processing.
Whether you are testing Ni/Al2O3 stability or upgrading bio-crude, KINTEK provides the customizable high-temperature equipment your research demands.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your HTL and catalysis needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Mathiyazhagan Narayanan. Biorefinery products from algal biomass by advanced biotechnological and hydrothermal liquefaction approaches. DOI: 10.1007/s42452-024-05777-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using nano-magnesium oxide as a template? Optimize Sulfur-Doped Porous Carbon Synthesis
- Why is thermal insulation applied to cylindrical components in thermal stress tests? Enhance Calculation Precision
- How does 500°C annealing affect NiO-doped Ga2O3 thin films? Optimize Your High-Precision Thermal Treatment
- What is the role of an electric blast drying oven in the pretreatment of SBD? Optimize Your Biomass Research
- What is the significance of using different sizes of steel working ampoules? Precision vs. Efficiency in Lab Research
- What are the key advantages of using electric furnaces across industries? Boost Efficiency and Precision in Your Processes
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in catalyst supports? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Dispersion
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?



















