At their core, the primary advantages of electric furnaces are unparalleled precision, high operational efficiency, and the ability to achieve extreme process conditions. Unlike fuel-fired alternatives, electric furnaces convert electrical energy directly into heat within the workspace, giving operators a level of control that directly translates to improved product quality and reduced waste.
The decision to use an electric furnace is fundamentally a choice for process control. While fuel-fired furnaces provide heat, electric furnaces provide a highly controllable thermal environment, enabling manufacturing outcomes that are often difficult or impossible to achieve otherwise.

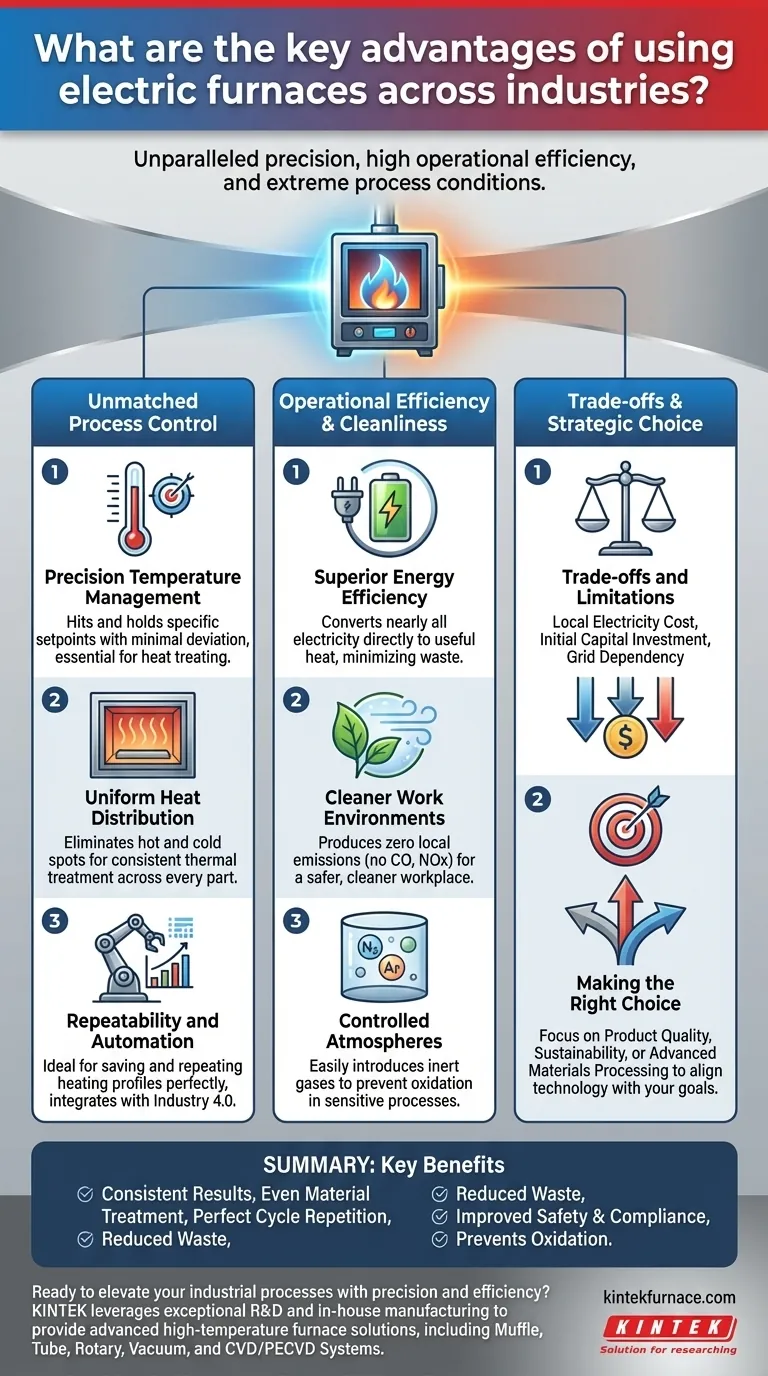
The Core Advantage: Unmatched Process Control
The defining characteristic of an electric furnace is its ability to be precisely managed. This control is the root of most of its other benefits.
Precision Temperature Management
Electric heating elements, such as resistance coils or induction systems, allow for very fine adjustments to power output. This enables the furnace to hit and hold a specific temperature setpoint with minimal deviation, often within a single degree.
This level of precision is critical in processes like heat treating, annealing, and sintering, where slight temperature variations can ruin an entire batch of material.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Because the heating elements can be strategically placed throughout the furnace chamber, they provide uniform heat. This eliminates the hot and cold spots common in fuel-fired furnaces, where heat originates from a single burner.
Uniformity ensures that every part of the product receives the exact same thermal treatment, leading to consistent material properties and predictable results.
Repeatability and Automation
The digital nature of electric furnace controls makes them ideal for automation. Once a successful heating profile is established, it can be saved and repeated perfectly for thousands of cycles.
This removes operator variability and integrates seamlessly with modern, data-driven manufacturing systems (Industry 4.0), allowing for complete process logging and quality assurance.
Translating Control into Operational Efficiency
Precise control and a cleaner heating method create tangible benefits for a facility's bottom line and operating environment.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Electric furnaces are significantly more energy-efficient at the point of use. Nearly all the electricity consumed is converted directly into useful heat.
In contrast, combustion furnaces lose a substantial amount of energy as hot exhaust gases up a flue stack. This means more of your energy budget is spent heating your product, not the air outside.
Cleaner Work Environments
Because there is no on-site combustion, electric furnaces produce zero local emissions. There are no byproducts like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), or particulates.
This results in a safer and cleaner environment for employees and drastically reduces the need for complex ventilation and emissions monitoring systems, simplifying regulatory compliance.
Controlled Atmospheres
The absence of combustion makes it simple to control the atmosphere inside the furnace. You can easily introduce inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation of sensitive materials.
This capability is essential for producing high-quality metals, advanced ceramics, and electronic components that would be damaged by exposure to oxygen at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, electric furnaces are not the universal solution. Their effectiveness is dependent on specific operational and economic factors.
The Cost of Electricity
The most significant factor is the local cost of electricity. In regions where electricity is expensive, the operational cost of an electric furnace can exceed that of a natural gas alternative, even when accounting for its higher efficiency.
Initial Capital Investment
High-performance electric furnaces, especially those designed for specialty applications or very high temperatures, can have a higher upfront cost than comparable fuel-fired units.
Grid Dependency
An electric furnace is entirely dependent on a stable supply of electricity. Power outages will halt production, and large furnaces can place a significant load on a facility's electrical infrastructure, sometimes requiring costly service upgrades.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology requires aligning its advantages with your primary industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: An electric furnace's precise temperature control and uniformity are its most valuable assets.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and operational cleanliness: The zero on-site emissions and high energy efficiency of an electric furnace are the key drivers.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials processing: An electric furnace's ability to achieve high temperatures and controlled atmospheres enables otherwise impossible applications.
Ultimately, choosing an electric furnace is a strategic investment in process control and manufacturing capability.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Management | Holds specific temperatures within minimal deviation for consistent results |
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Eliminates hot/cold spots for even material treatment |
| Repeatability and Automation | Enables perfect cycle repetition and integration with Industry 4.0 |
| Superior Energy Efficiency | Converts nearly all electricity to useful heat, reducing waste |
| Cleaner Work Environments | Zero local emissions, improving safety and compliance |
| Controlled Atmospheres | Allows inert gas use to prevent oxidation in sensitive processes |
Ready to elevate your industrial processes with precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our electric furnaces can enhance your product quality and operational sustainability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















