Vacuum drying offers a definitive advantage over conventional methods by decoupling temperature from evaporation speed. By operating in a low-pressure environment at moderate temperatures (typically around 80°C), this method accelerates the removal of solvents like water and ethanol while completely neutralizing the risks of oxidation and structural collapse.
Conventional drying often forces a compromise between drying speed and material quality. Vacuum drying eliminates this trade-off, utilizing reduced pressure to evacuate solvents from deep pores without triggering the chemical degradation or particle agglomeration that compromises precursor performance.

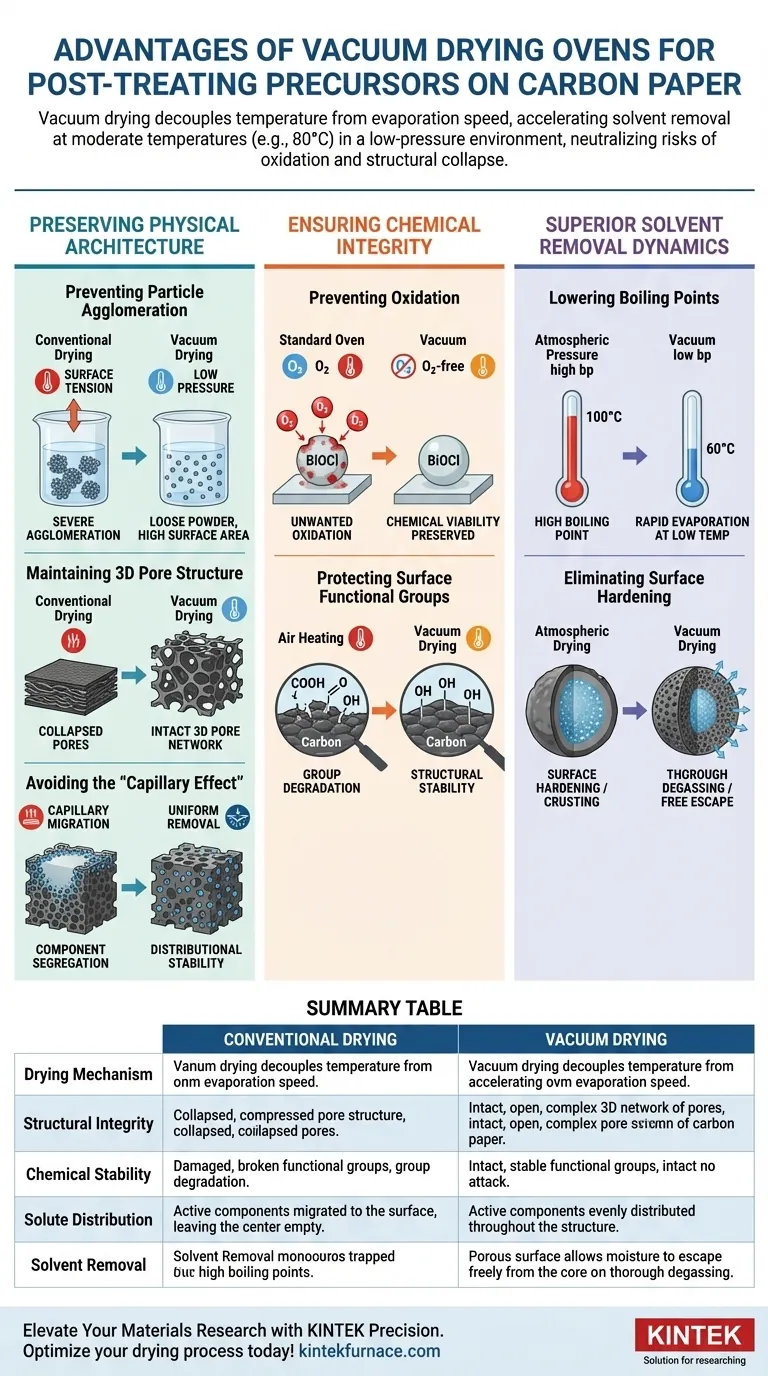
Preserving Physical Architecture
The primary value of vacuum drying lies in its ability to protect the physical geometry of your material.
Preventing Particle Agglomeration
In conventional drying, the surface tension of evaporating solvents can pull nanoparticles together, causing them to clump.
The vacuum environment allows for rapid solvent removal at lower temperatures (e.g., 70°C–80°C). This prevents the precursor material from undergoing severe agglomeration, ensuring the resulting powder remains in a loose, high-surface-area state.
Maintaining 3D Pore Structure
Carbon paper supports rely on a complex, three-dimensional pore structure for their effectiveness.
Vacuum drying prevents the collapse of these structures. By avoiding high heat and surface tension stress, the process preserves the three-dimensional pore network, which is critical for maintaining the accessibility of active sites in the final application.
Avoiding the "Capillary Effect"
A subtle but critical mechanism in drying is the migration of solutes.
In standard ovens, rapid surface evaporation draws liquid from the center to the outside (the capillary effect), bringing active components with it. Vacuum drying ensures solvents escape from deep pores uniformly. This prevents component segregation and ensures the distributional stability of metal salts throughout the carbon support.
Ensuring Chemical Integrity
Beyond physical structure, the chemical viability of the precursor is paramount.
Preventing Oxidation
Standard drying ovens expose heat-sensitive materials to oxygen for extended periods.
By operating under vacuum, you remove the oxygen source. This is essential for preventing the unwanted oxidation of precursor nanoparticles and the carbon support’s surface functional groups. This is particularly vital for materials like BiOCl or activated carbon, where oxidation equals degradation.
Protecting Surface Functional Groups
The chemical activity of a catalyst often depends on specific surface groups.
Heating carbon materials in air can degrade these groups. Vacuum drying at 80°C thoroughly removes moisture while ensuring the structural stability of these functional groups remains intact prior to electrochemical testing.
Superior Solvent Removal Dynamics
The mechanism of solvent removal in a vacuum is fundamentally different from atmospheric drying.
Lowering Boiling Points
Vacuum drying reduces the pressure within the chamber, which significantly lowers the boiling point of solvents.
This allows for the rapid evaporation of water and ethanol residues at temperatures as low as 60°C. This capability is non-negotiable for heat-sensitive chemical substances that would decompose or deteriorate at the higher temperatures required by standard ovens.
Eliminating Surface Hardening
Atmospheric drying often causes the outer layer of a sample to dry and harden first.
This "crust" traps internal moisture, leading to incomplete drying. The vacuum environment prevents this surface hardening, allowing moisture to escape freely from the material's interior. This ensures the thorough degassing of ultra-fine micropores, which is critical for accurate surface area (BET) analysis.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
While vacuum drying is superior for quality, it requires precise operational control.
Temperature Selection
Even under vacuum, temperature matters. While 80°C is standard for many carbon paper precursors, highly sensitive intermediates (like washed BiOCl) may require lower temperatures (60°C) to prevent deterioration. You must match the temperature to the thermal sensitivity of your specific precursor.
Process Complexity
Vacuum drying is not a passive process. It requires maintaining a consistent low-pressure environment to ensure deep pore degassing. Failure to maintain adequate vacuum levels can result in residual solvent molecules blocking micropores, which will skew analytical data (such as PSD analysis) and reduce catalytic performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Vacuum drying is rarely the wrong choice for post-treating carbon paper precursors, but the specific benefit depends on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Performance: Vacuum drying is essential to prevent oxidation of surface functional groups and maintain the high chemical activity of nanoparticles.
- If your primary focus is Structural Analysis (BET/PSD): The vacuum environment is critical to remove trapped solvent molecules from ultra-fine micropores to prevent data deviation.
- If your primary focus is Material Uniformity: Vacuum drying prevents the capillary effect, ensuring active components do not migrate to the surface and remain evenly distributed.
Vacuum drying transforms post-treatment from a damaging thermal stress test into a precision preservation process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Drying | Vacuum Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Mechanism | High-heat evaporation | Low-pressure, low-temp sublimation/boiling |
| Structural Integrity | Risk of pore collapse & agglomeration | Preserves 3D pore networks & high surface area |
| Chemical Stability | High risk of surface oxidation | Oxygen-free environment prevents degradation |
| Solute Distribution | Capillary effect causes component migration | Uniform solvent removal from deep pores |
| Solvent Removal | Slow; risk of surface hardening/crusting | Fast; thorough degassing of micropores |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let conventional drying compromise your high-performance precursors. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Vacuum systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD furnaces—all customizable for your unique lab requirements. Whether you are aiming for precise electrochemical performance or accurate BET analysis, our equipment ensures your carbon paper supports maintain their critical 3D architecture.
Ready to optimize your drying process? Contact us today to find the perfect thermal solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Shasha Song, Xingqun Zhu. Synthesis and Lithium Storage Performance of CoO/CoSe Composite Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon Paper. DOI: 10.54691/k2djhp47
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of the Thermal Oxidation (TO) process in Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy? Enhancing Hardness and Wear
- What is the purpose of using an industrial oven for low-temperature drying? Expert Glass Processing Guide
- How does an autoclave assist in modifying bio-carbon with cobalt oxide? Unlock High-Performance Nano-Composites
- What is the specific purpose of pre-treating Terbium chloride hexahydrate? Ensure Purity in Cs3Cu2I5:Tb Synthesis
- Why are high-precision nitrogen flow meters essential during pyrolysis? Ensure Perfect Char Preparation
- How does the Flash Heating (FH) process impact the growth of REBCO films? Master Rapid Thermal Ramp Requirements
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature electric furnace during solution treatment? Achieve Alloy Homogeneity
- What advantages does a microwave sintering furnace offer for LLZTO? Speed and Performance Compared



















