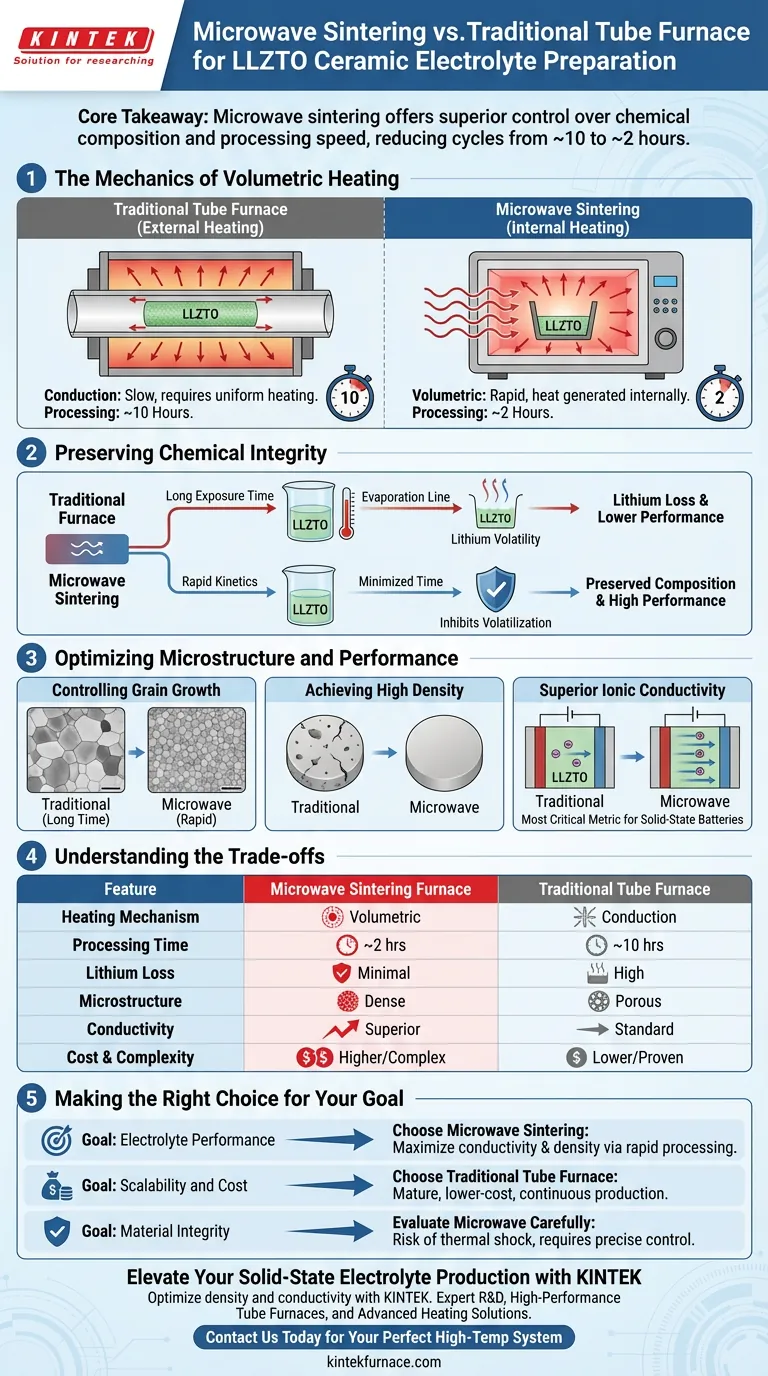
Microwave sintering offers superior control over chemical composition and processing speed compared to traditional high-temperature tube furnaces. By utilizing volumetric heating, microwave sintering can reduce processing cycles from approximately 10 hours to just 2 hours, a critical factor in preventing lithium loss and ensuring optimal performance for LLZTO ceramic electrolytes.
Core Takeaway While traditional tube furnaces rely on external heat conduction, microwave sintering generates heat internally within the material. This rapid internal heating solves the primary challenge of LLZTO synthesis—lithium volatilization—resulting in a denser ceramic with higher ionic conductivity.

The Mechanics of Volumetric Heating
Internal vs. External Heating
Traditional tube furnaces heat materials from the outside in using heating elements. This relies on thermal conduction, which requires time to ensure the temperature is uniform throughout the sample.
Instantaneous Penetration
In contrast, microwave sintering utilizes volumetric heating. Microwaves penetrate the material itself, causing the molecules to generate heat internally.
Rapid Kinetics
This mechanism allows for significantly faster heating rates. The total sintering cycle can be compressed dramatically, often reducing a 10-hour process down to roughly 2 hours.
Preserving Chemical Integrity
The Lithium Volatility Problem
A major challenge in preparing LLZTO (Lithium Lanthanum Zirconium Tantalum Oxide) is maintaining the correct lithium stoichiometry. At high temperatures, lithium tends to volatilize (evaporate).
Reducing Exposure Time
Because traditional tube furnaces require long dwell times to ensure uniform heating, they increase the risk of lithium loss.
The Microwave Solution
The rapid kinetics of microwave sintering minimize the time the material spends at peak temperatures. This effectively inhibits the volatilization of lithium, preserving the intended chemical composition.
Optimizing Microstructure and Performance
Controlling Grain Growth
Extended heating times in traditional furnaces can lead to abnormal or uncontrolled grain growth. Microwave sintering limits this strictly due to its speed.
Achieving High Density
The process promotes high density in the final ceramic. Eliminating pores is essential for creating a solid electrolyte that blocks dendrites and maintains structural integrity.
Superior Ionic Conductivity
The combination of preserving lithium content and achieving a dense, uniform microstructure directly translates to superior ionic conductivity, the most critical performance metric for solid-state battery electrolytes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While microwave sintering offers specific advantages for LLZTO chemistry, it is important to acknowledge the benefits of mature tube furnace technology.
Cost and Complexity
Microwave sintering equipment is generally more expensive than traditional tube furnaces. It is a more complex technology that requires significant capital investment.
Processing Sensitivity
Microwave heating requires careful handling. Because the heating is so rapid, there is a risk of thermal shock, which can cause the ceramic material to crack if the process parameters are not perfectly tuned.
The Stability of Tube Furnaces
Traditional tube furnaces are mature, simple to operate, and offer precise temperature control. They are excellent for continuous, large-scale production where the extreme speed of microwave sintering is less critical than throughput and equipment reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If your primary focus is Electrolyte Performance:
- Choose Microwave Sintering to maximize ionic conductivity and density by preventing lithium loss through rapid processing.
If your primary focus is Scalability and Cost:
- Choose a Traditional Tube Furnace for a mature, lower-cost solution that supports continuous production and simpler operation.
If your primary focus is Material Integrity:
- Evaluate Microwave Sintering carefully; while it improves density, the rapid heating rates require precise control to prevent the ceramic from cracking.
For LLZTO specifically, the chemical benefits of rapid microwave heating usually outweigh the complexity costs when high conductivity is the priority.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Microwave Sintering Furnace | Traditional Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Volumetric (Internal) | Conduction (External) |
| Processing Time | ~2 Hours (Rapid) | ~10 Hours (Slow) |
| Lithium Loss | Minimal (High stoichiometry) | High (Longer heat exposure) |
| Microstructure | Dense, controlled grain growth | Risk of abnormal grain growth |
| Conductivity | Superior ionic conductivity | Standard ionic conductivity |
| Cost & Complexity | Higher investment/complex | Lower cost/proven technology |
Elevate Your Solid-State Electrolyte Production with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize the density and conductivity of your LLZTO ceramic electrolytes? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube Furnaces and advanced heating solutions tailored for precision lab environments.
Whether you need the rapid kinetics of specialized systems or the reliable stability of our customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces, our team helps you balance cost, scalability, and material integrity.
Ready to refine your sintering process? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and find the perfect high-temp system for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Chaozhong Wu, Xin Xie. Reoxidation of IF Steel Caused by Cr2O3-Based Stuffing Sand and Its Optimization. DOI: 10.3390/ma18173945
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a Bridgman furnace control single-crystal quality? Master Precision Directional Solidification
- What role does a laboratory oven play in W-doped TiO2? Ensure Precursor Stability for High-Purity Nanopowders
- What are the primary technical advantages of using stainless steel for the construction of horizontal pyrolysis furnace bodies? Durability and Thermal Precision
- What role does a vacuum drying oven play in the post-processing of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles? Ensure Phase Purity
- Why is zone refining essential for alkali halide crystals? Achieve Pure Intrinsic Luminescence Data
- How does a gas path control system protect the materials? Ensure High Yields in Battery Smelting
- Why is temperature control precision critical for gas diffusion electrodes? Achieve Perfect PTFE Redistribution
- Why is a laboratory vacuum evaporation system essential for the preparation of electrodes in high-performance solar cells?



















