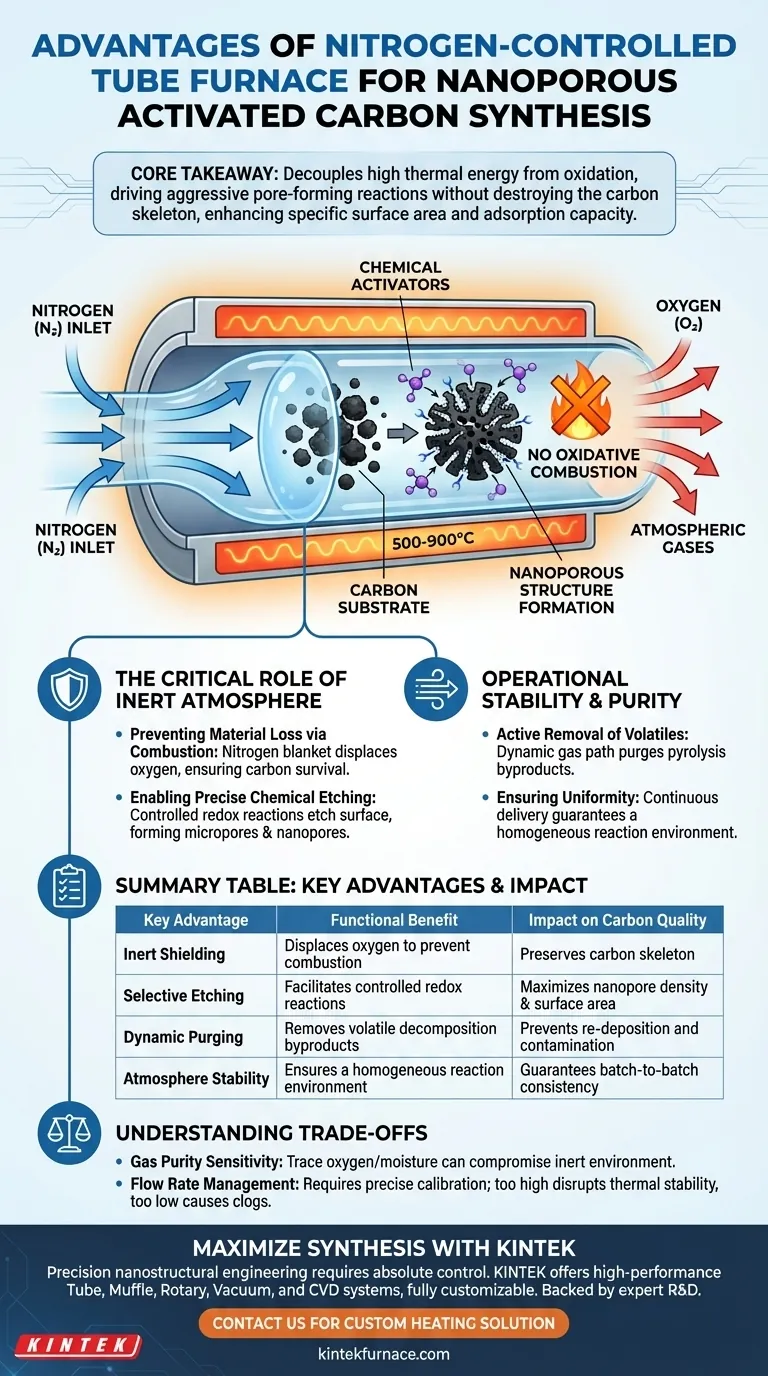
The primary advantage of using a tube furnace with a nitrogen control system is the creation of a strictly controlled inert environment essential for high-temperature activation. By maintaining an oxygen-free atmosphere between 500 and 900 degrees Celsius, the system prevents the oxidative combustion of your carbon material. This protection allows chemical activators to precisely etch the substrate rather than burning it, directly resulting in the formation of abundant microporous and nanoporous structures.
Core Takeaway The nitrogen control system decouples high thermal energy from oxidation. This allows you to drive aggressive pore-forming reactions without destroying the carbon skeleton, significantly enhancing the material's specific surface area and adsorption capacity.

The Critical Role of the Inert Atmosphere
Preventing Material Loss via Combustion
At activation temperatures (500–900°C), carbon is highly reactive with oxygen. Without a nitrogen shield, the carbon substrate would simply burn away (oxidize) into ash and carbon dioxide.
Nitrogen acts as a protective blanket. It displaces atmospheric oxygen, ensuring that the carbon material survives the thermal treatment. This preservation of the carbon skeleton is the prerequisite for any subsequent surface modification or pore development.
Enabling Precise Chemical Etching
Once the risk of combustion is eliminated, the focus shifts to structural engineering. In this inert environment, chemical activators can perform controlled redox reactions on the carbon surface.
Instead of consuming the material indiscriminately, the activators "etch" the carbon. This selective removal of carbon atoms creates a vast network of micropores and nanopores. This porosity is what defines the material's final utility, particularly regarding its capacity for carbon dioxide adsorption.
Operational Stability and Purity
Active Removal of Volatiles
Synthesis involves more than just heating; it involves decomposition. During pyrolysis and activation, the raw material releases volatile components and byproducts.
The nitrogen system provides a dynamic gas path. A constant flow of nitrogen actively purges the furnace chamber. This removes these volatile compounds, preventing them from re-depositing on the carbon surface or destabilizing the reaction environment.
Ensuring Uniformity
A static atmosphere can lead to inconsistent results due to pockets of gas or temperature gradients. The continuous delivery of nitrogen ensures a homogeneous reaction environment.
By maintaining a stable protective atmosphere, the system guarantees that the physical conditions—and therefore the resulting pore structures—are consistent throughout the entire batch of activated carbon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Gas Purity Sensitivity
The effectiveness of the system is entirely dependent on the purity of the nitrogen source. Even trace amounts of oxygen or moisture in the gas supply can compromise the inert environment at high temperatures, leading to unwanted surface oxidation or degradation of the pore structure.
Flow Rate Management
More gas flow is not always better. An excessively high nitrogen flow rate can disrupt the thermal stability of the "hot zone" inside the tube. Conversely, a flow rate that is too low may fail to adequately purge volatile pyrolysis byproducts, leading to clogs or contamination. Precise calibration of the flow rate is required for optimal results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a nitrogen-equipped tube furnace, align your operational parameters with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is maximum surface area: Prioritize a high-purity nitrogen source to prevent any unplanned oxidation that could collapse micropores during the etching phase.
- If your primary focus is consistency across batches: rigorous control of the nitrogen flow rate is critical to ensure identical volatile removal and thermal conditions in every run.
Ultimately, the nitrogen control system transforms a tube furnace from a simple heating device into a precision instrument for nanostructural engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Functional Benefit | Impact on Carbon Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Shielding | Displaces oxygen to prevent combustion | Preserves carbon skeleton at 500–900°C |
| Selective Etching | Facilitates controlled redox reactions | Maximizes nanopore density & surface area |
| Dynamic Purging | Removes volatile decomposition byproducts | Prevents re-deposition and surface contamination |
| Atmosphere Stability | Ensures a homogeneous reaction environment | Guarantees batch-to-batch structural consistency |
Maximize Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision nanostructural engineering requires absolute control over your thermal environment. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research needs. Whether you are scaling up nanoporous carbon production or refining chemical activation protocols, our furnaces provide the stability and gas-path precision your work demands.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to find your custom heating solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Ebrahim H. Al‐Ghurabi, Mohammad Asif. Optimizing the synthesis of nanoporous activated carbon from date-palm waste for enhanced CO2 capture. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00498-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces and muffle furnaces differ in design and application? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- Why must a tube furnace used for the pyrolysis of tungsten-based nanocomposites be equipped with a precision gas flow?
- What metallurgical processes are performed in horizontal furnaces? Unlock Precision Heat Treatment and Sintering
- Why is a high-performance tube furnace required for chemical activation? Achieve Precision Pore Control at 700°C
- Why use a graphite box in tube furnaces for Sb2Se3 annealing? Achieve Precise Crystal Growth & Vapor Control
- What is the role of a tube furnace system in the growth of bilayer MoS2? Master CVD Synthesis with Precision Control
- Why is precise atmosphere control necessary in a laboratory tube furnace for Ni-ZIF-8 to Ni-N-C conversion?
- Can a vacuum tube furnace be used with controlled gas atmospheres? Yes, for precise high-temperature processing.



















