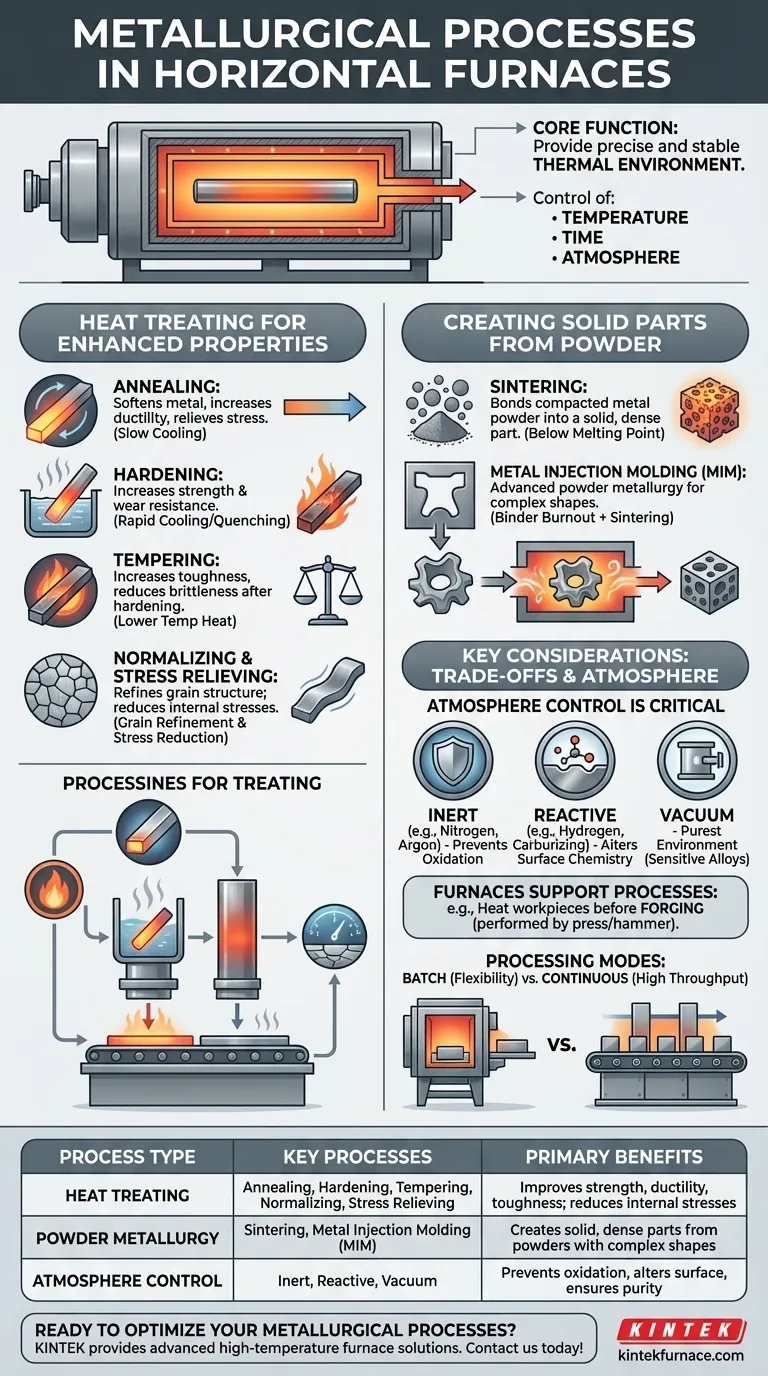
In metallurgy, horizontal furnaces are essential thermal workhorses used for a wide range of processes designed to alter the fundamental properties of metals. The most common applications include heat treatments like annealing, hardening, and tempering, as well as powder metallurgy processes like sintering. These furnaces provide the controlled, high-temperature environment necessary to modify a material’s internal microstructure and enhance its performance.
The core function of a horizontal furnace is not to perform a single process, but to provide a precise and stable thermal environment. The specific metallurgical process that can be performed is ultimately determined by the furnace's ability to control temperature, time, and—most critically—its internal atmosphere.
The Primary Role: Heat Treating for Enhanced Properties
Heat treatment encompasses a family of processes where solid metals are heated and cooled under tight controls to achieve desired mechanical properties. The goal is to change the material's microstructure without altering its shape.
Annealing
Annealing is a process that involves heating a metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. This softens the metal, increases its ductility, and makes it easier to machine or form. It also relieves internal stresses that may have built up during prior manufacturing steps.
Hardening
Hardening is used to increase the strength and wear resistance of a metal, particularly steel. The material is heated to a high temperature to transform its internal structure, followed by a rapid cooling process known as quenching. This locks in a hard, brittle microstructure.
Tempering
A part that has been hardened is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment performed after hardening. It reduces some of the excess hardness and brittleness, increasing the material's overall toughness.
Normalizing and Stress Relieving
Normalizing is a process that refines the grain structure of steel to improve its toughness and machinability. Stress relieving uses lower temperatures to reduce internal stresses caused by welding, machining, or cold working, minimizing the risk of distortion or cracking later in the part's life.
Creating Solid Parts from Powder
Horizontal furnaces are also central to powder metallurgy, a field where parts are manufactured from metallic powders rather than molten metal.
Sintering
Sintering is the core process of powder metallurgy. Compacted metal powder is heated in a furnace to a temperature just below its melting point. At this temperature, the individual powder particles bond together, creating a solid, dense part without ever becoming a liquid.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is an advanced form of powder metallurgy. A fine metal powder is mixed with a binder material, injection molded into a complex shape, and then placed in a furnace. The furnace cycle first burns out the binder material and then sinters the metal powder into a final, solid part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
The simple term "horizontal furnace" covers a vast range of equipment. The specific process you can run depends entirely on the furnace's features and limitations.
Atmosphere Control is Critical
Many metals react with oxygen at high temperatures, forming an undesirable oxide layer (scale). Simple furnaces that operate in ambient air are limited to processes where this is acceptable. More advanced processes require precise atmosphere control:
- Inert Atmosphere: Using gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation.
- Reactive Atmosphere: Using gases like hydrogen, carburizing gases, or nitriding gases to intentionally alter the surface chemistry of the part (e.g., case hardening).
- Vacuum: Pumping all gases out of the chamber provides the purest environment, essential for sensitive aerospace alloys, brazing, and degassing.
Furnaces Support, But Don't Perform, All Processes
It is crucial to distinguish between a furnace's role. For example, a reference might mention forging. A horizontal furnace does not perform forging; a press or hammer does. The furnace's role is to heat the metal workpiece to the correct temperature before it is moved to the forge.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Horizontal furnaces can be designed for batch processing, where a single load is processed at a time, offering high flexibility. They can also be configured as continuous furnaces (like belt or pusher furnaces), where parts move steadily through different temperature zones, allowing for very high throughput in mass production.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of process is dictated entirely by your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is improving the strength and toughness of an existing steel part: You will need a sequence of hardening and tempering heat treatments.
- If your primary focus is making a metal part easier to machine or form: The correct process is annealing to soften the material and improve its ductility.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid, net-shape part from metal powder: Your process is sintering, likely within a powder metallurgy or MIM workflow.
- If your primary focus is working with highly reactive alloys (like titanium) or joining parts without welding: You will require a furnace with vacuum or high-purity inert atmosphere capabilities for processes like brazing or solution treating.
Ultimately, understanding these metallurgical processes empowers you to select the precise thermal cycle needed to transform a simple metal into a high-performance component.

Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Processes | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treating | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering, Normalizing, Stress Relieving | Improves strength, ductility, toughness, and reduces internal stresses |
| Powder Metallurgy | Sintering, Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Creates solid, dense parts from metal powders with complex shapes |
| Atmosphere Control | Inert, Reactive, Vacuum | Prevents oxidation, alters surface chemistry, and ensures purity for sensitive alloys |
Ready to optimize your metallurgical processes with precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need heat treating, sintering, or specialized atmosphere control, we deliver reliable, tailored solutions to enhance your material performance and production efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can transform your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary in copper slag impoverishment? Maximize Your Matte Separation Efficiency
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the purpose of performing medium vacuum annealing on working ampoules? Ensure Pure High-Temp Diffusion



















