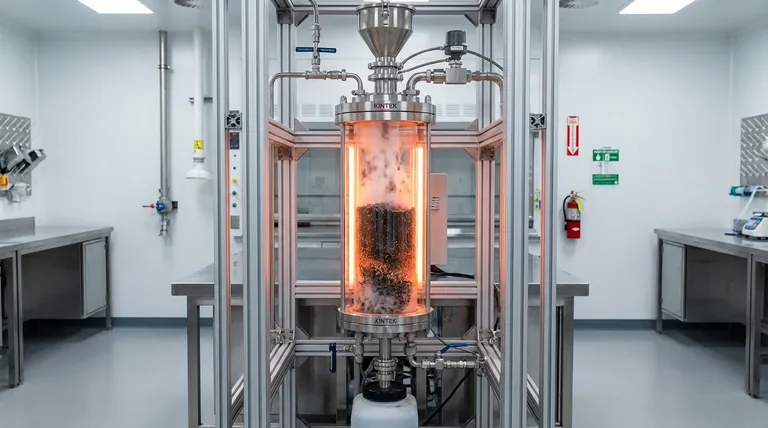
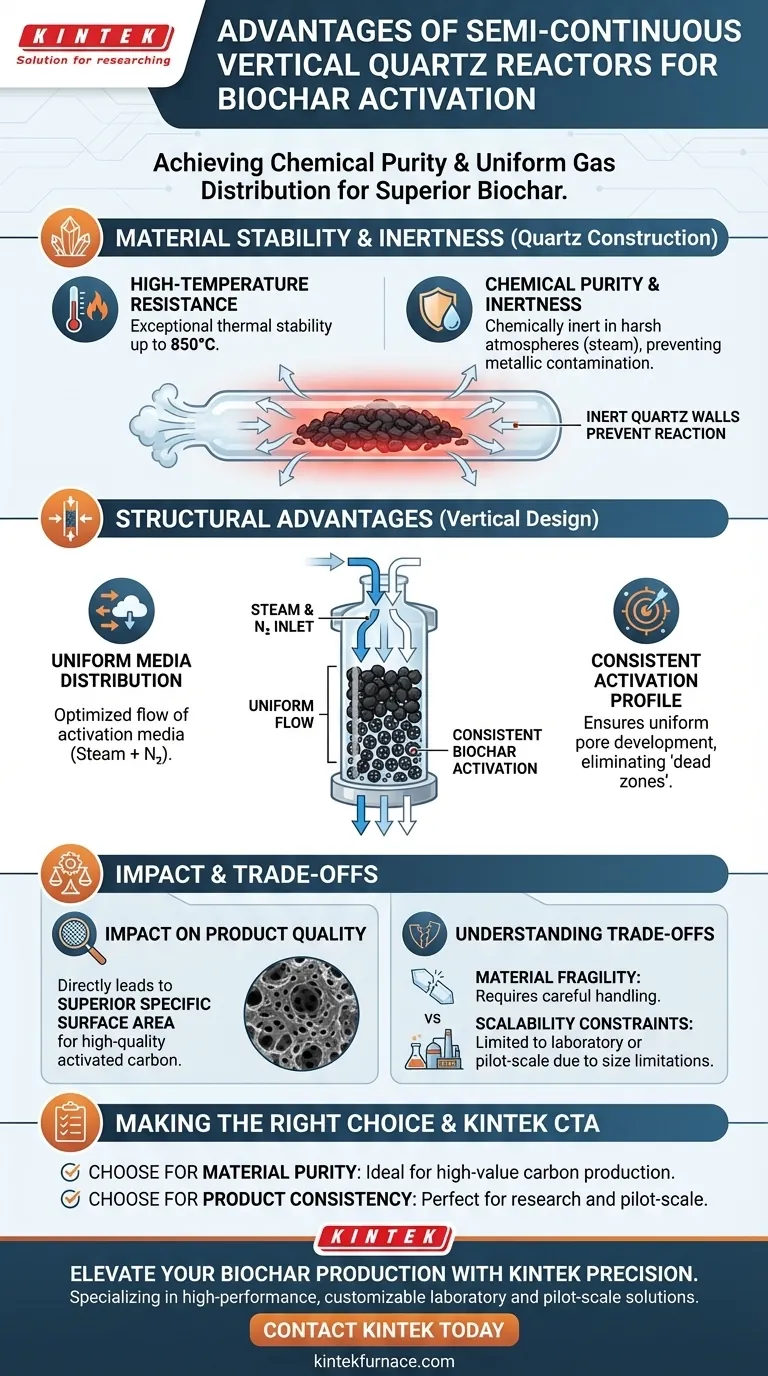
The primary advantages of using a semi-continuous vertical quartz reactor lie in its ability to maintain chemical purity while ensuring uniform gas distribution during the activation process. This specific configuration combines high-temperature resistance with a geometry that forces activation media to pass evenly through the biochar, directly leading to a higher quality end product.
The reactor's ability to remain inert at temperatures up to 850°C, combined with a vertical structure that promotes uniform steam and nitrogen flow, is critical for producing activated carbon with a high specific surface area.

Material Stability and Inertness
High-Temperature Resistance
The quartz construction of the reactor is fundamental to its performance. It offers exceptional thermal stability, allowing the system to operate effectively at temperatures as high as 850°C.
Chemical Purity in Harsh Atmospheres
Unlike metal reactors that might react with aggressive activation agents, quartz remains chemically inert. This stability is maintained even in the presence of steam atmospheres, preventing contamination of the biochar sample.
Structural Advantages for Activation
Uniform Media Distribution
The vertical structure of the reactor is designed to optimize the flow of gases. It ensures that the activation media—typically a mixture of steam and nitrogen—passes uniformly through the sample layer rather than bypassing it.
Consistent Activation Profile
Because the gas flow is uniform, every particle of biochar is exposed to the same activation conditions. This eliminates "dead zones" or uneven activation, ensuring the entire batch achieves consistent properties.
Impact on Final Product Quality
superior Surface Area
The combination of stable high temperatures and uniform gas contact directly influences the microstructure of the biochar. This process facilitates the development of high specific surface areas, a key metric for high-quality activated carbon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material Fragility
While quartz offers superior chemical resistance, it is physically brittle. Unlike stainless steel, it requires careful handling to prevent breakage during loading, unloading, or thermal cycling.
Scalability Constraints
Vertical quartz tubes generally have limitations regarding diameter and length due to manufacturing costs and structural integrity. This often limits this specific reactor type to laboratory or pilot-scale operations rather than massive industrial throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this reactor suits your specific activation requirements, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is material purity: This reactor is ideal because the inert quartz prevents metallic contamination during high-temperature steam activation.
- If your primary focus is product consistency: The vertical flow design ensures uniform pore development, making it the right choice for research or high-value carbon production.
By leveraging the thermal and structural benefits of a vertical quartz reactor, you ensure the production of consistently high-performing activated carbon.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for Biochar Activation | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Quartz Material | Chemically inert up to 850°C | Prevents sample contamination |
| Vertical Design | Optimizes steam and nitrogen flow | Ensures uniform activation and pore development |
| Thermal Stability | High-temperature resistance | Supports consistent high-quality production |
| Flow Dynamics | Eliminates "dead zones" | Achieves high specific surface area |
Elevate Your Biochar Production with KINTEK Precision
Ready to achieve superior material purity and consistent activation results? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance laboratory solutions backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing.
Whether you need advanced Quartz Reactors, Muffle, Tube, or CVD systems, our high-temperature equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique research and pilot-scale requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discover how our specialized furnace systems can optimize your lab's efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
References
- Jakub Čespiva, Wei‐Hsin Chen. Sustainable off-grid gasification: co-production of electricity, heat, and activated carbon. DOI: 10.20517/energymater.2024.104
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the application of CVD in cutting tools? Boost Tool Life and Machining Efficiency
- What type of power supply is used in CVD furnaces? Discover Precision SCR Systems for Superior Thin Films
- Why is NaCl used in WTe2 CVD synthesis? Enhance Crystal Growth with Salt-Assisted Flux
- How does a CVD machine work? Master the Technology for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the uses of CVD? Unlocking Advanced Materials & Coatings
- What is the function of a horizontal hot-wall quartz tube CVD system? Expert Insights on Superlattice Fabrication
- What is the basic principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Unlock High-Purity Thin-Film Synthesis
- What is the purpose of using a mechanical vacuum pump for CVD MoS2 preparation? Ensure High-Purity Material Synthesis



















