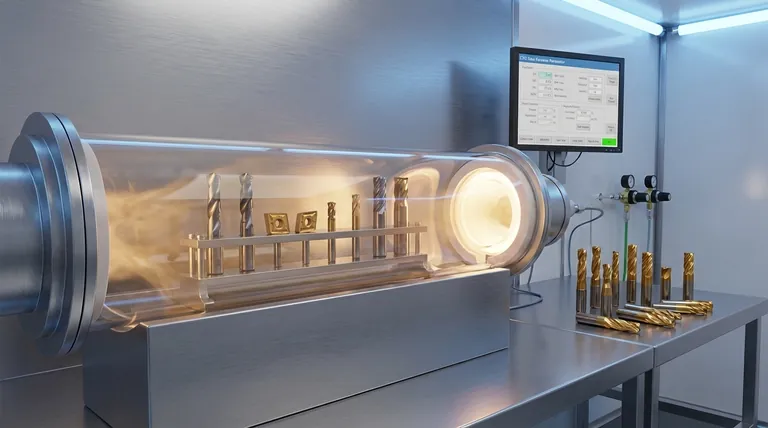
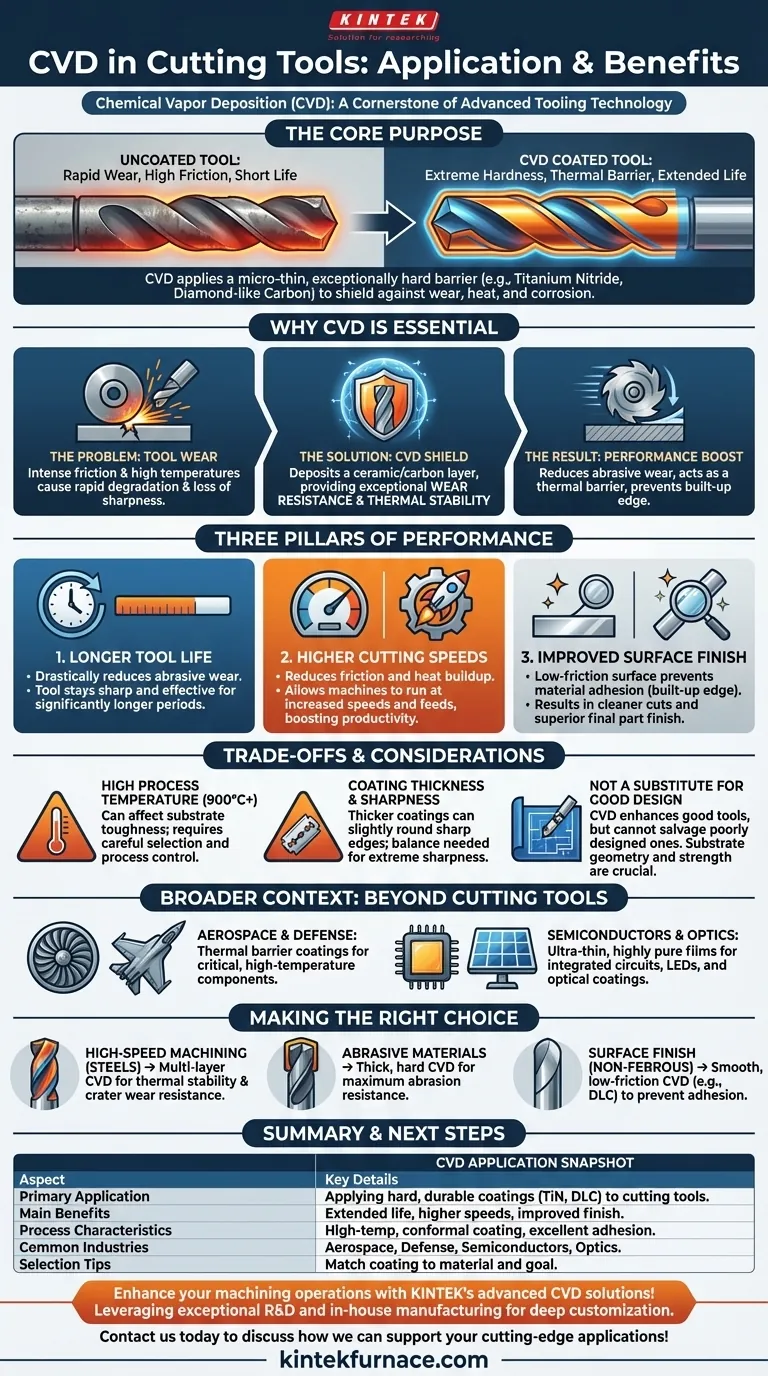
In cutting tool technology, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a cornerstone process used to apply an exceptionally hard and durable coating onto the surface of tools like drills, milling cutters, and inserts. Materials such as titanium nitride or diamond-like carbon are deposited as a thin film, fundamentally enhancing the tool's resistance to wear, heat, and corrosion. This directly improves the tool's performance, extends its operational life, and increases machining efficiency.
The core purpose of applying CVD to cutting tools is to create a protective barrier that is far harder and more chemically stable than the underlying tool material. This coating shields the cutting edge from the intense friction, heat, and abrasion of machining, enabling higher cutting speeds, longer tool life, and superior workpiece finishes.

Why CVD is Essential for Modern Machining
CVD is not merely an addition; it is a transformative process that redefines the limits of a cutting tool's capability. It addresses the fundamental challenges inherent in all material-cutting operations.
The Fundamental Problem: Tool Wear
The primary failure mode for any cutting tool is wear. This occurs through intense friction, high temperatures that soften the cutting edge, and chemical reactions between the tool and the workpiece material. An uncoated tool degrades quickly, losing its sharpness and dimensional accuracy.
How CVD Coatings Provide a Solution
A CVD coating acts as a shield. By depositing a micro-thin layer of an extremely hard ceramic or carbon-based material, the process isolates the relatively weaker tool substrate from the harsh cutting environment. This layer provides exceptional wear resistance and thermal stability.
The Three Pillars of Performance
The application of a CVD coating delivers three primary benefits:
- Longer Tool Life: The high hardness of the coating drastically reduces abrasive wear, meaning the tool stays sharp and effective for a significantly longer period.
- Higher Cutting Speeds: CVD coatings act as a thermal barrier and reduce friction, allowing machines to be run at higher speeds and feeds without prematurely failing the tool. This directly increases productivity.
- Improved Surface Finish: The smooth, low-friction surface of the coating prevents workpiece material from sticking to the cutting edge (a phenomenon known as built-up edge), resulting in a cleaner cut and a better surface finish on the final part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the CVD process is not without its specific characteristics and trade-offs. A clear understanding of these factors is critical for proper application and tool selection.
High Process Temperature
Traditional CVD processes operate at high temperatures (often over 900°C). While this helps create a very dense and well-adhered coating, it can potentially affect the underlying tool material, such as reducing the toughness of some carbide grades. This must be managed through careful substrate selection and process control.
Coating Thickness and Edge Sharpness
CVD coatings are "conformal," meaning they coat all surfaces evenly. However, a thicker coating can slightly increase the radius of a razor-sharp cutting edge. For applications requiring extreme sharpness, this trade-off between edge integrity and wear resistance must be carefully balanced.
Not a Substitute for Good Tool Design
A coating cannot fix a poorly designed tool. The substrate must have the appropriate geometry, strength, and toughness for the application. A CVD coating enhances a good tool; it does not salvage a bad one.
The Broader Context of CVD Applications
The reliability of CVD in cutting tools is underscored by its widespread use in other demanding, high-tech fields. This demonstrates the robustness and versatility of the technology.
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace industry, CVD is used to apply thermal barrier and wear-resistant coatings to critical components like turbine blades, which must operate reliably in extremely high-temperature and corrosive environments.
Semiconductors and Optics
The electronics industry relies heavily on CVD to deposit the ultra-thin, highly pure films required for manufacturing integrated circuits, LEDs, and solar panels. Similarly, it is used in optics to create anti-reflective and protective coatings on lenses and other instruments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coated tool requires matching its properties to your specific machining objective. The coating is a key part of the tool system.
- If your primary focus is high-speed machining of steels: Choose a tool with a multi-layer CVD coating optimized for thermal stability and crater wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is extending tool life in abrasive materials: Select a tool with a thick, hard CVD coating designed specifically for maximum abrasion resistance.
- If your primary focus is improving surface finish on non-ferrous materials: A tool with a very smooth, low-friction coating like diamond-like carbon (DLC) will prevent material adhesion and produce superior results.
By leveraging the protective power of CVD coatings, you can select tools that directly translate to increased productivity, lower operational costs, and higher quality parts.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Application | Applying hard, durable coatings (e.g., titanium nitride, diamond-like carbon) to cutting tools |
| Main Benefits | Extended tool life, higher cutting speeds, improved surface finish |
| Process Characteristics | High-temperature operation, conformal coating, excellent adhesion |
| Common Industries | Aerospace, defense, semiconductors, optics |
| Selection Tips | Match coating to material (e.g., multi-layer for steels, thick coatings for abrasives, DLC for non-ferrous) |
Enhance your machining operations with KINTEK's advanced CVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like CVD/PECVD, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, boosting tool performance and productivity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your cutting-edge applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision



















