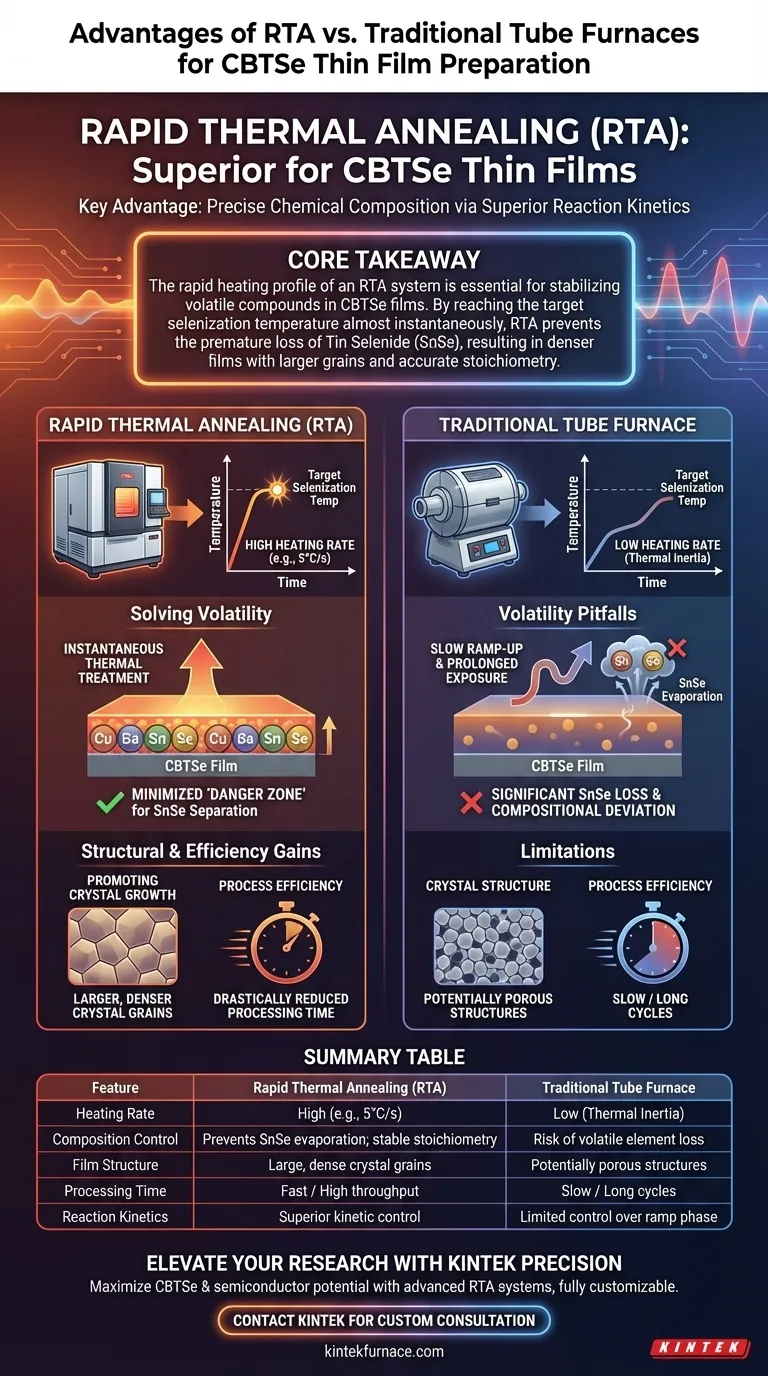
The primary advantage of using a Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) system for Cu2BaSnSe4 (CBTSe) thin film preparation is the ability to maintain precise chemical composition through superior reaction kinetics. By utilizing significantly higher heating rates (approximately 5°C/s) compared to traditional tube furnaces, RTA allows the material to bypass critical temperature zones where volatile elements are liable to evaporate.
Core Takeaway The rapid heating profile of an RTA system is essential for stabilizing volatile compounds in CBTSe films. By reaching the target selenization temperature almost instantaneously, RTA prevents the premature loss of Tin Selenide (SnSe), resulting in denser films with larger grains and accurate stoichiometry.

The Impact of Heating Rates on Composition
Solving the Volatility Problem
The defining characteristic of CBTSe preparation is the sensitivity of its components to heat. In traditional tube furnaces, the slow ramp-up time exposes the film to lower temperatures for extended periods.
During this slow heating phase, volatile phases—specifically SnSe (Tin Selenide)—tend to separate and evaporate prematurely. This loss of material leads to compositional deviations that degrade the quality of the final film.
Bypassing Instability Zones
RTA systems mitigate this risk by delivering instantaneous thermal treatment.
By ramping up at rates such as 5°C/s, the system forces the reaction to reach the target selenization temperature quickly. This minimizes the time the material spends in the "danger zone" where SnSe separation occurs, ensuring the final film retains its intended chemical makeup.
Structural and Efficiency Gains
Promoting Crystal Growth
Beyond chemical composition, the thermal profile of RTA significantly influences the physical structure of the film.
The rapid thermal energy induces atomic reorganization, which promotes the growth of larger, denser crystal grains. This densification is critical for the optoelectronic performance of the thin film, superior to the often porous structures resulting from slower furnace annealing.
Process Efficiency
RTA provides a clear operational advantage regarding throughput.
Because the target temperatures are reached quickly and the dwell times are optimized for immediate reaction, the overall processing time is drastically reduced. This makes RTA a more efficient choice for fabrication compared to the prolonged cycles required by tube furnaces.
The Pitfalls of Traditional Heating
Understanding the Limitations of Tube Furnaces
While traditional tube furnaces are common, they present a specific "trade-off" when working with volatile materials like CBTSe.
The inherent thermal inertia of a tube furnace means precise control over the rate of heating is limited. If you choose a tube furnace, you accept the risk of compositional deviation due to the inevitable evaporation of volatile elements during the ramp-up phase. This often necessitates using excess precursor material to compensate for losses, adding complexity to the synthesis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a thermal processing method for CBTSe thin films, the choice depends on your tolerance for compositional variance and your specific structural requirements.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Stoichiometry: Choose RTA to minimize the evaporation of volatile SnSe and ensure the chemical ratio remains stable.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Choose RTA to drive atomic reorganization that results in larger, denser crystal grains.
- If your primary focus is Process Throughput: Choose RTA to significantly reduce the overall processing time compared to the slow cycles of a tube furnace.
For high-performance CBTSe films, the kinetic control provided by Rapid Thermal Annealing is not just an efficiency upgrade; it is a necessity for preserving material integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) | Traditional Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | High (e.g., 5°C/s) | Low (Thermal Inertia) |
| Composition Control | Prevents SnSe evaporation; stable stoichiometry | Risk of volatile element loss |
| Film Structure | Large, dense crystal grains | Potentially porous structures |
| Processing Time | Fast / High throughput | Slow / Long cycles |
| Reaction Kinetics | Superior kinetic control | Limited control over ramp phase |
Elevate Your Thin Film Research with KINTEK Precision
Maximize the potential of your CBTSe and semiconductor materials with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance RTA systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production requirements. Don't let volatile elements compromise your results; leverage our rapid heating technology to ensure perfect stoichiometry and superior crystal quality.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today for a custom consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Tuğba Bayazıt, E. Bacaksız. Influence of Rapid Thermal Annealing Temperature on Cu <sub>2</sub> BaSnSe <sub>4</sub> (CBTSe) Thin Films Prepared by Hybrid Spin Coating and Thermal Evaporation. DOI: 10.1002/pssr.202500197
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for magnesium slag? Preserving Sample Integrity
- What role does Sodium Chloride (NaCl) play as a thermal buffer? Optimizing Si/Mg2SiO4 Composite Synthesis
- What core processing conditions does a laboratory high-temperature oven provide? Optimize Geopolymer Curing Results
- How does the recycling of CRT slag as a flux benefit PCB smelting? Boost Metal Recovery Efficiency
- Why is a precision temperature-controlled curing oven required for PIP? Ensure Integrity in Material Cross-Linking
- What is the primary function of a forced air oven in SnmCunOx-t synthesis? Master Chemical Foaming
- What is the function of planetary ball mills or industrial mixing granulators prior to RHF? Optimize FMDS Reactivity
- What is the technical purpose of the ball milling process for Ti12%Zr? Master Mechanical Activation & Alloying



















