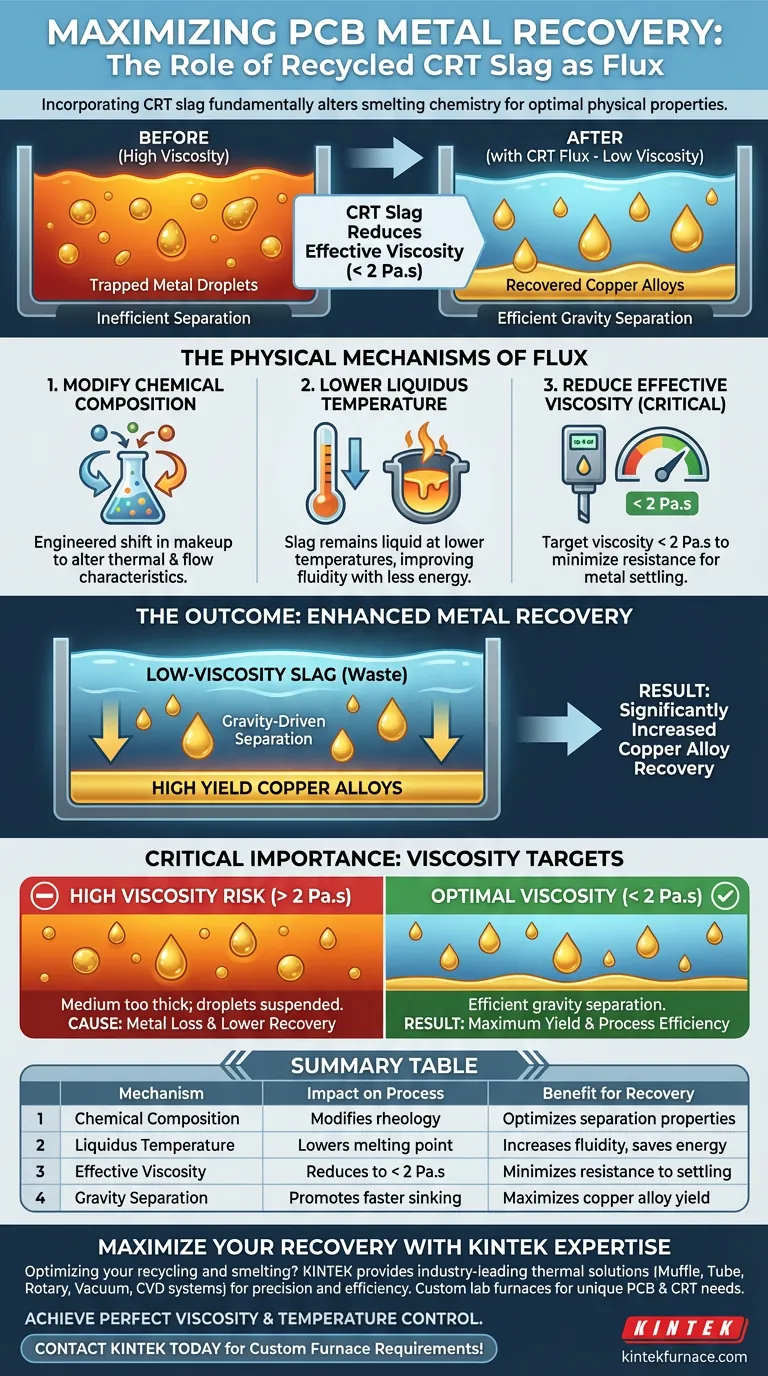
Incorporating recycled cathode ray tube (CRT) slag acts as a vital flux agent in the smelting of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This addition fundamentally alters the chemical composition of the smelting mixture to optimize its physical properties. By lowering the liquidus temperature and reducing the effective viscosity, CRT slag creates the ideal conditions for recovering valuable metals.
By modifying the rheology of the molten slag, CRT waste lowers the barrier to metal separation. This ensures that molten copper alloys can settle out of the waste material efficiently, preventing valuable resources from being lost in the slag.

The Physical Mechanisms of Flux
To understand why CRT slag is effective, one must look at how it alters the physical state of the molten material inside the furnace.
Modifying Chemical Composition
The primary function of adding CRT slag is to change the overall chemical makeup of the smelting slag.
This chemical shift is not arbitrary; it is specifically engineered to alter the thermal and flow characteristics of the melt.
Lowering Liquidus Temperature
The addition of CRT slag lowers the liquidus temperature of the mixture.
This means the slag remains in a fully liquid state at lower temperatures, or flows more freely at standard operating temperatures. This improves the overall fluidity of the bath without requiring excessive thermal energy inputs.
Reducing Effective Viscosity
The most critical impact of this flux is the reduction of effective viscosity.
For optimal processing, the viscosity is typically targeted to drop below 2 Pa.s.
The Outcome: Enhanced Metal Recovery
The physical changes described above are means to an end. The ultimate goal is the physical separation of materials based on density.
Promoting Gravity-Driven Separation
Smelting produces a mixture of molten metal droplets and waste slag.
Because the CRT slag reduces the viscosity (thickness) of the melt, it reduces the resistance these droplets face.
This promotes gravity-driven separation, allowing the heavier metal droplets to sink through the slag layer more easily.
Increasing Copper Alloy Yield
The direct result of improved separation is a higher recovery rate.
Fewer metal droplets remain trapped or suspended in the viscous slag phase.
Consequently, the overall recovery of copper alloys from the PCBs is significantly increased.
The Critical Importance of Viscosity Targets
While the benefits are clear, the process relies heavily on achieving specific physical parameters.
The Consequence of High Viscosity
If the slag viscosity remains above the 2 Pa.s threshold, the medium remains too thick.
In this scenario, gravity cannot effectively pull the metal droplets down through the slag.
Risk of Metal Loss
When separation is inefficient, metal droplets remain suspended in the waste slag.
This leads to lower recovery rates and the loss of valuable copper alloys, negating the efficiency of the recycling process.
Optimizing Your Smelting Strategy
To maximize the benefits of integrated recycling, focus on the specific physical parameters of your melt.
- If your primary focus is Metal Recovery: Ensure your flux addition is sufficient to drive the slag viscosity specifically below 2 Pa.s to prevent metal entrapment.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Utilize CRT slag to lower the liquidus temperature, maintaining fluidity without excessive thermal demands.
By strictly controlling the viscosity of the slag, you transform a waste product into a critical tool for maximizing yield.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Impact on Smelting Process | Benefit for Metal Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Modifies the rheology of the molten mixture | Optimizes physical properties for separation |
| Liquidus Temperature | Lowers the melting point of the slag | Increases fluidity at lower energy inputs |
| Effective Viscosity | Reduces viscosity to below 2 Pa.s | Minimizes resistance for metal droplet settling |
| Gravity Separation | Promotes faster sinking of heavy alloys | Maximizes yield of recovered copper alloys |
Maximize Your Metal Recovery with KINTEK Expertise
Are you looking to optimize your recycling and smelting operations? KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions designed for precision and efficiency. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique PCB and CRT recycling needs.
Don't let valuable copper alloys go to waste. Let our specialized equipment help you achieve the perfect viscosity and temperature control for maximum yield. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Sello Tsebe, J.D. Steenkamp. Development of an Integrated Process Flowsheet to Recover Valuable Metals from Waste Cathode Ray Tubes and Printed Circuit Boards. DOI: 10.1007/s40831-023-00775-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
People Also Ask
- Why is high-purity argon necessary for PVC dechlorination? Ensure Precise Reaction Control & Safety
- What are the advantages of using a high-pressure oxygen annealing furnace for La1-xSrxMnO3 thin films?
- What core processing conditions does a laboratory high-temperature oven provide? Optimize Geopolymer Curing Results
- Why is a laboratory oven required for drying samples at 80°C for MoO3/Ti-Felt? Ensure Electrode Structural Integrity
- What is the function of a high-pressure hydrothermal reactor in graphene aerogel synthesis? Key to 3D Carbon Frameworks
- What are the benefits of applying secondary artificial aging heat treatment to aluminum alloy parts? Boost Yield Strength
- Why is a final drying step necessary when restructuring adsorbents? Ensure Chemical Bonding & Industrial Safety
- Why is vacuum impregnation necessary for PAN-GF electrodes? Ensure Peak Fiber Conductivity and Slurry Integration












