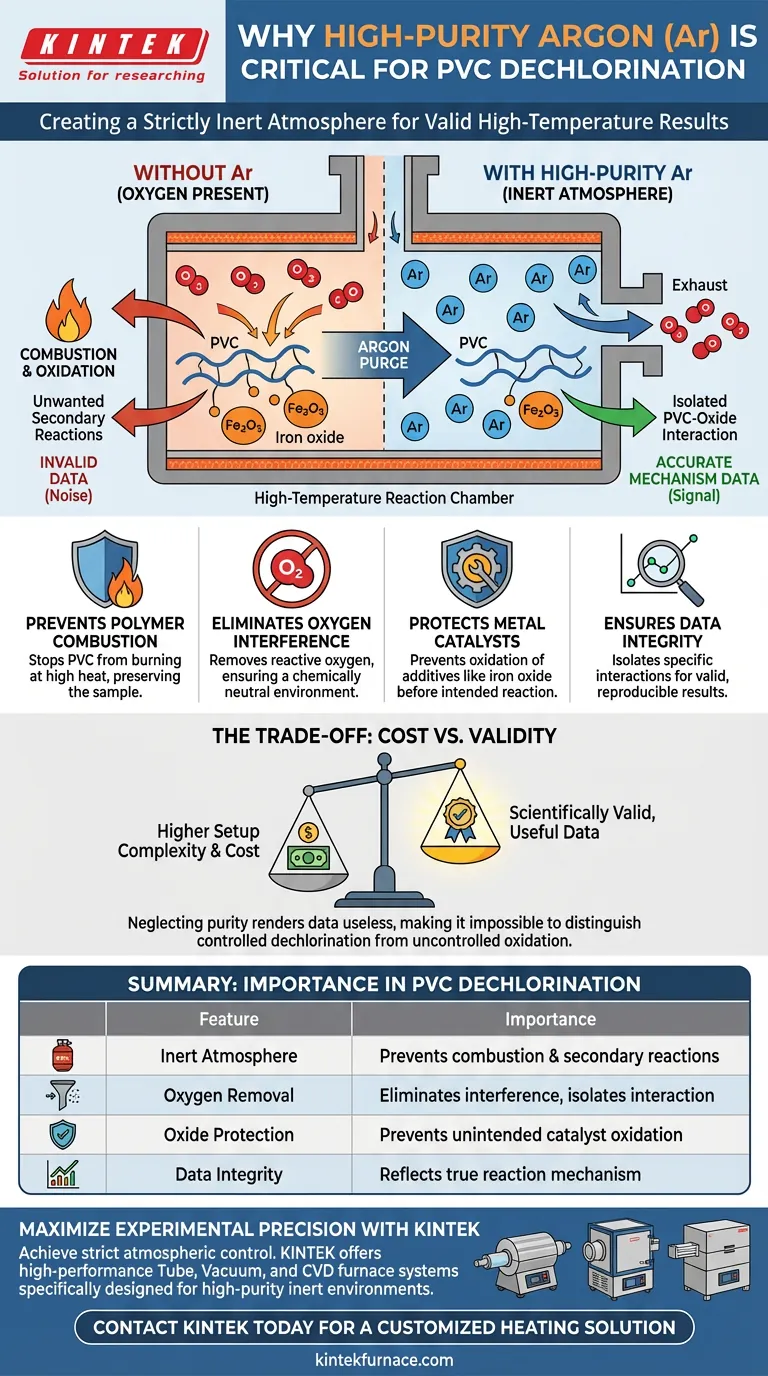
A high-purity argon (Ar) environment is essential for creating a strictly inert atmosphere. During the high-temperature dechlorination of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), argon acts as a purge gas to effectively strip oxygen from the reaction chamber. This prevents unwanted secondary reactions, specifically the oxidation of metal additives or the combustion of the polymer itself.
By eliminating oxygen, the argon environment ensures that the observed experimental results isolate the specific interaction between PVC and metal oxides, rather than reflecting artifacts of combustion or atmospheric oxidation.
The Critical Role of an Inert Atmosphere
Eliminating Oxygen Interference
The presence of oxygen during high-temperature thermal treatment fundamentally alters the chemical pathway.
Oxygen is highly reactive and will compete with the intended dechlorination reaction. A high-purity argon purge removes this variable, ensuring the environment remains chemically neutral.
Preventing Polymer Combustion
PVC is an organic polymer that is susceptible to burning when exposed to heat and oxygen.
Without an inert argon blanket, the high temperatures required for dechlorination would trigger the combustion of the PVC matrix. This destroys the sample and creates byproducts that obscure the actual thermal degradation process.
Protecting Reaction Integrity
Preventing Iron Oxide Oxidation
Many PVC dechlorination studies involve metal oxides, such as iron oxide, to act as scavengers or catalysts.
If oxygen is present in the chamber, the iron oxide can undergo unintended oxidation. This alters the valence state of the metal before it has a chance to interact with the PVC, invalidating the study of the catalyst's original properties.
Ensuring Accurate Mechanism Data
The goal of these processes is often to understand the specific reaction mechanism between PVC and metal oxides.
Secondary reactions caused by impurities create "noise" in the data. An argon environment ensures that the mass loss or chemical changes observed are strictly due to the interaction between the polymer and the oxide.
Understanding the Constraints
The Cost of Purity vs. Data Validity
Achieving a high-purity argon environment adds complexity to the experimental setup.
It requires a sealed reaction chamber and a continuous supply of expensive technical-grade gas. However, neglecting this requirement renders the data scientifically useless, as it becomes impossible to distinguish between controlled dechlorination and uncontrolled oxidation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your high-temperature process yields valid results, consider the following specific applications:
- If your primary focus is experimental validity: rigorous argon purging is mandatory to prevent the oxidation of iron oxides and ensure the reaction mechanism is isolated.
- If your primary focus is safety: the argon environment is critical to prevent the risk of igniting the polymer during high-temperature heating.
Control the atmosphere, and you control the accuracy of your results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Importance in PVC Dechlorination |
|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents polymer combustion and unwanted secondary reactions. |
| Oxygen Removal | Eliminates interference to isolate interaction between PVC and metal oxides. |
| Oxide Protection | Prevents unintended oxidation of catalysts like iron oxide. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures mass loss and chemical changes reflect the true reaction mechanism. |
Maximize Experimental Precision with KINTEK
Achieve the strict atmospheric control your research demands. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems specifically designed for high-temperature applications requiring high-purity inert environments. Whether you are conducting PVC dechlorination or complex material synthesis, our customizable lab furnaces provide the stability and purity needed for valid, reproducible results.
Ready to upgrade your lab capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a customized heating solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Lan Hong, Lin-hai Ye. De-chlorination of poly(vinyl) chloride using Fe <sub>2</sub> O <sub>3</sub> and the improvement of chlorine fixing ratio in FeCl <sub>2</sub> by SiO <sub>2</sub> addition. DOI: 10.1515/htmp-2022-0299
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why a 1:4 KOH Ratio and 1000 °C are Essential for Chemical Activation? Achieving Ultra-High Surface Area
- What are the characteristics of a Batch Reactor for plastic pyrolysis? A Guide to Versatile Waste Processing
- What thermochemical environment does an entrained flow reactor provide? Simulate Industrial Biomass Combustion
- How does a vacuum thermal evaporation system ensure the quality of Bismuth Telluride thin films? Expert Insights
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace ensure structural integrity? Expert Thermal Management Guide
- What function does a water quenching tank serve in Ni-Ti alloy heat treatment? Lock in Superelasticity & Shape Memory
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum oven for drying porous carbon? Protect Microstructures & Prevent Oxidation
- What are the technological advantages of using a Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) system? Precision for Semiconductors
















