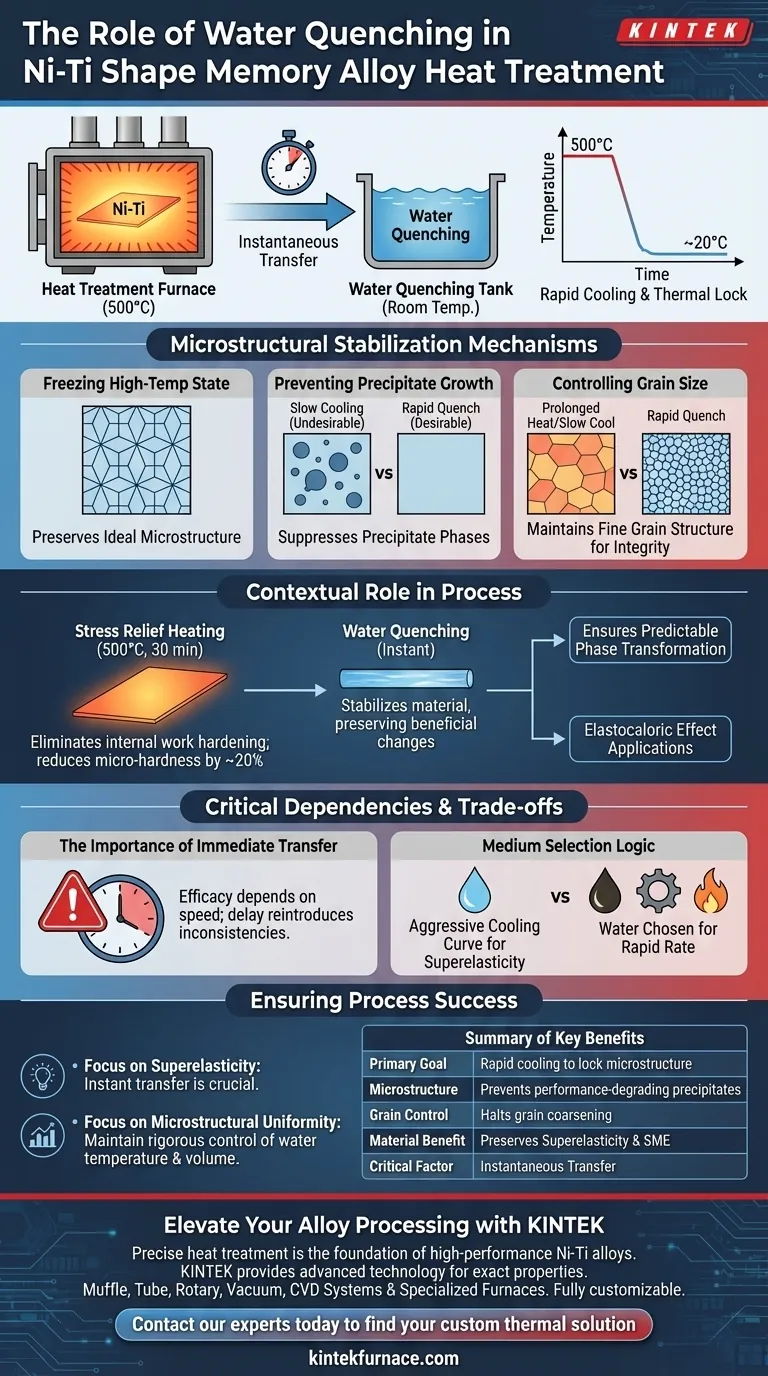
The primary function of a water quenching tank in this context is to rapidly cool Ni-Ti shape memory alloy sheets from a heat treatment temperature of 500 degrees Celsius down to room temperature. This immediate thermal drop is executed instantly following the heating phase to lock in specific material properties.
By effectively "freezing" the alloy's microstructure, water quenching prevents the material from degrading during the cooling phase. This ensures the preservation of the alloy's defining characteristics: superior superelasticity and the shape memory effect.
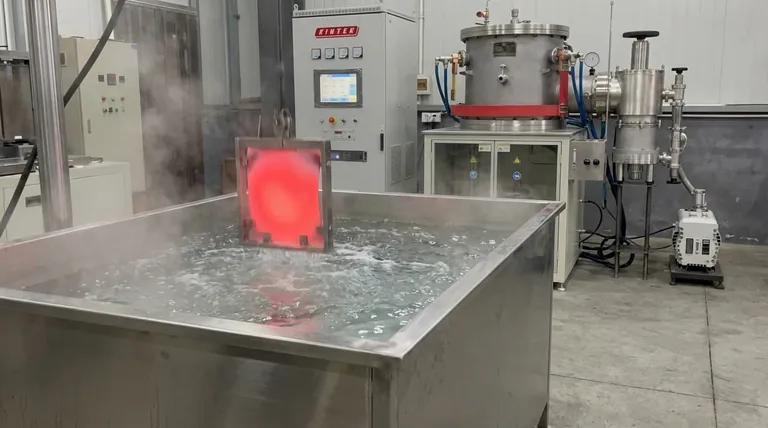

The Mechanism of Microstructural Stabilization
Freezing the High-Temperature State
The heat treatment process at 500 degrees Celsius induces a specific, ideal microstructural organization within the Ni-Ti alloy.
Water quenching is employed to preserve this state. By dropping the temperature rapidly, the process denies the material the time necessary for the microstructure to alter or degrade as it cools.
Preventing Precipitate Growth
If the alloy were allowed to cool slowly, precipitate phases would have time to form and grow within the material matrix.
Large precipitate phases can interfere with the alloy's performance. Rapid quenching suppresses this growth, keeping the microstructure clean and uniform.
Controlling Grain Size
Prolonged exposure to high heat or slow cooling can lead to abnormal grain coarsening, where the grains in the metal become excessively large.
The water quenching tank halts this process immediately. This maintains a finer grain structure, which is essential for the mechanical integrity of the sheet.
Contextual Role in Heat Treatment
Post-Stress Relief Processing
Before quenching, the Ni-Ti sheets undergo a 30-minute heat treatment to eliminate internal work hardening and residual stresses.
This initial heating reduces the alloy's micro-hardness by approximately 20 percent. The quenching tank’s role is to stabilize the material after these beneficial changes have occurred, without reversing them.
Ensuring Predictable Phase Transformation
The uniformity achieved by the heat treatment and subsequent quench ensures the material behaves predictably.
This is vital for applications requiring the elastocaloric effect, as the phase transformation behavior must be stable and consistent across repeated cycles.
Critical Dependencies and Trade-offs
The Importance of Immediate Transfer
The efficacy of the water quenching tank is entirely dependent on speed. The transfer from the furnace to the water must be immediate.
Any delay allows the temperature to drop slowly in the air, which can reintroduce microstructural inconsistencies before the water cooling begins.
Medium Selection Logic
While other quenching media exist—such as polymers, oils, or gases like nitrogen and helium—water is specifically chosen here for its rapid cooling rate.
The choice of medium is dictated by the desired final properties. In this specific application, water provides the aggressive cooling curve necessary to maintain superelasticity in Ni-Ti sheets.
Ensuring Process Success
To maximize the effectiveness of your heat treatment process, consider the following regarding the quenching phase:
- If your primary focus is Superelasticity: Ensure the transfer to the water tank is instantaneous to prevent the formation of precipitates that impede elastic recovery.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Uniformity: Maintain rigorous control over the water temperature and volume to ensure the entire sheet cools at an identical rate, preventing internal variances.
The water quenching tank is not merely a cooling device; it is the final lock that secures the structural integrity and performance capability of the alloy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose in Ni-Ti Heat Treatment |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rapid cooling from 500°C to room temperature to lock microstructure |
| Microstructure | Prevents formation of performance-degrading precipitates |
| Grain Control | Halts grain coarsening to maintain mechanical integrity |
| Material Benefit | Preserves superelasticity and the shape memory effect (SME) |
| Critical Factor | Instantaneous transfer from furnace to water tank is essential |
Elevate Your Alloy Processing with KINTEK
Precise heat treatment is the foundation of high-performance Ni-Ti shape memory alloys. KINTEK provides the advanced technology needed to achieve exact material properties. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your specific research or production needs.
Don't let inconsistent cooling compromise your material's superelasticity. Partner with KINTEK to ensure every cycle delivers microstructural perfection.
Contact our experts today to find your custom thermal solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Gianmarco Bizzarri, Maria Elisa Tata. Mechanical Response and Elastocaloric Performance of Ni-Ti Shape Memory Alloy Sheets Under Varying Strain Rates. DOI: 10.3390/compounds5020013
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of placing a Nickel Mesh in a reactor? Maximizing Heat in Nickel-Hydrogen Systems
- Why is aluminum foil used during selenization and carbonization? Unlock Superior ZnSe Nanoparticle Synthesis
- How does high-precision temperature control impact the crystal growth of LaMg6Ga6S16? Precision Heating Strategies
- Why is Boron Nitride (BN) powder used as a diluent? Enhance Accuracy in Iron Oxidation Kinetics
- What necessary conditions does a vacuum drying oven provide for geopolymers? Optimize Your Curing and Molding Process
- What is the importance of cold traps and pump recovery systems in VTD? Boost Safety and Material Recycling
- What types of materials can crucible furnaces melt? Unlock the Power of Versatile Melting
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in catalyst supports? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Dispersion



















