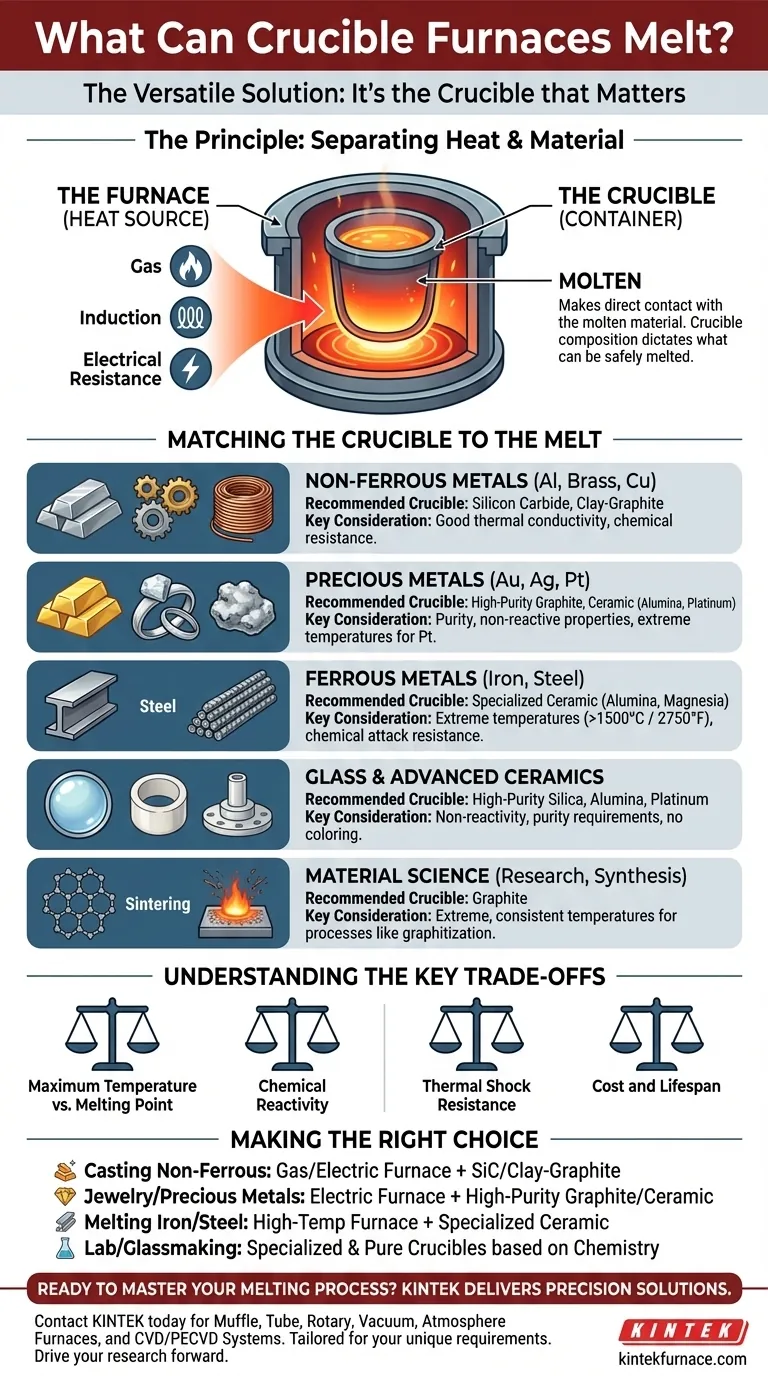
In short, a crucible furnace can melt an exceptionally wide range of materials. Its capabilities extend to most common metals and alloys, including aluminum, brass, bronze, gold, silver, iron, and steel. Beyond metals, these furnaces are also used for melting glass, certain ceramics, and even for processing advanced materials.
The true versatility of a crucible furnace comes not from the furnace itself, but from the crucible it holds. The furnace provides the heat, but the type of crucible you choose dictates the specific materials you can safely and effectively melt.
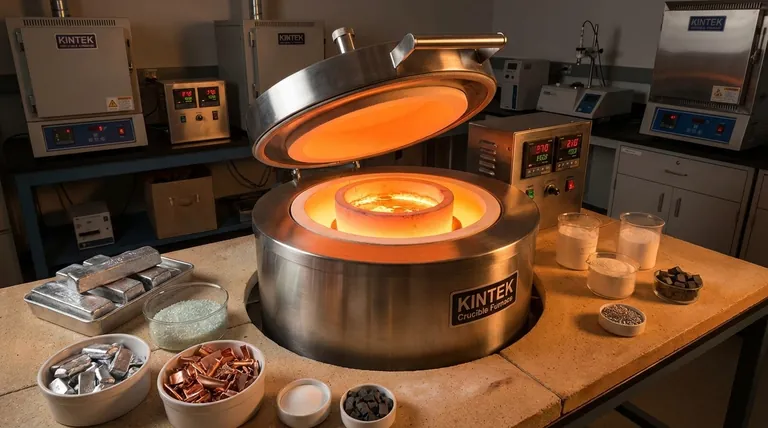

The Principle: Separating the Heat from the Material
To understand what a crucible furnace can melt, you must first understand its two core components. This simple design is the key to its flexibility.
The Furnace's Role: The Heat Source
The furnace is the insulated housing that generates extreme heat. It acts as an oven, using sources like gas, induction, or electrical resistance to raise the temperature in its chamber. Its main job is to deliver controlled, consistent heat.
The Crucible's Role: The Container
The crucible is the removable pot that sits inside the furnace. This is where the material is actually placed to be melted. Because the crucible is the only component that makes direct contact with the molten material, its composition is the single most important factor.
Matching the Crucible to the Melt
The question is not "what can the furnace melt?" but "what material is my crucible made of?" Choosing the wrong crucible can lead to a failed melt, contamination of your material, or dangerous equipment failure.
For Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Brass, Copper)
These are the most common metals melted in small foundries and by hobbyists. Silicon carbide or clay-graphite crucibles are the standard choice. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and good resistance to the chemical wear from these metals.
For Precious Metals (Gold, Silver, Platinum)
Purity is the primary concern when melting precious metals. High-purity graphite crucibles are often used for gold and silver, as they are non-reactive and reduce the risk of contamination. For platinum group metals, which have extremely high melting points, specialized ceramic or even pure platinum crucibles may be required.
For Ferrous Metals (Iron, Steel)
Melting iron and steel requires significantly higher temperatures (above 1500°C / 2750°F). This pushes beyond the limits of many standard crucibles. Specialized ceramic crucibles, such as those made from alumina or magnesia, are necessary to withstand the heat and chemical attack from molten steel.
For Glass and Advanced Ceramics
Melting glass and technical ceramics demands crucibles that can handle high temperatures without reacting with or coloring the melt. Depending on the specific chemistry, this can involve high-purity silica, alumina, or even costly platinum crucibles for optical-grade glass.
For Material Science and Research
As noted in material science applications, graphite crucibles are essential. Their ability to handle extreme, consistent temperatures makes them ideal for processes like graphitization, sintering, and the synthesis of new materials like graphene.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible involves balancing performance, cost, and safety. There is no single crucible that is perfect for all applications.
Maximum Temperature vs. Melting Point
This is the most basic check. The crucible's maximum service temperature must be safely above the melting point of the material you intend to melt. Pushing a crucible past its limit will cause it to fail.
Chemical Reactivity
Molten materials are highly reactive. For example, molten aluminum is very aggressive and can degrade certain types of crucibles, leading to contamination of the aluminum and a shortened crucible lifespan. You must ensure the crucible material is chemically compatible with the molten charge.
Thermal Shock Resistance
A crucible undergoes immense stress when it is heated quickly or when cold material is added to a hot crucible. Poor thermal shock resistance will cause the crucible to crack. Silicon carbide, for instance, has excellent resistance to this.
Cost and Lifespan
High-performance ceramic or platinum crucibles can be exceptionally expensive. For industrial use or hobbyists, a less expensive clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers a practical balance of performance and cost for melting common non-ferrous metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the correct furnace and crucible combination.
- If your primary focus is casting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A standard gas or electric furnace with a silicon carbide or clay-graphite crucible is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is jewelry or small-scale precious metals: An electric furnace with a high-purity graphite or ceramic crucible will ensure the purity of your melt.
- If your primary focus is melting iron or steel: You need a high-temperature furnace (often induction or high-power gas) and a specialized ceramic crucible rated for the extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research or glassmaking: Your choice depends entirely on the specific material's chemistry, often requiring highly specialized and pure crucibles to prevent any contamination.
Ultimately, the crucible furnace is a versatile tool whose full potential is unlocked by choosing the correct crucible for the job.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Recommended Crucible Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Aluminum, Brass, Copper | Silicon Carbide, Clay-Graphite | Good thermal conductivity, chemical resistance |
| Precious Metals | Gold, Silver, Platinum | High-Purity Graphite, Ceramic | Purity, non-reactive properties |
| Ferrous Metals | Iron, Steel | Specialized Ceramic (Alumina, Magnesia) | Extreme temperatures (>1500°C) |
| Glass & Ceramics | Optical Glass, Technical Ceramics | High-Purity Silica, Alumina, Platinum | Non-reactivity, purity requirements |
| Material Science | Graphene Synthesis, Sintering | Graphite | Extreme, consistent temperatures |
Ready to Master Your Melting Process?
Whether you're working with common alloys, precious metals, or advanced materials, the right furnace and crucible combination is critical to your success.
KINTEK delivers precision high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities, we provide:
- Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces for diverse thermal processing needs
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces for controlled environment applications
- CVD/PECVD Systems for advanced material synthesis
- Strong deep customization capability to precisely match your experimental specifications
Our expertise ensures you get the perfect crucible furnace system for your specific materials and processes.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced furnace solutions can enhance your melting operations and drive your research or production forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















