At its core, a rotary kiln’s primary advantage is its ability to continuously and uniformly process materials at extremely high temperatures. Its design combines slow rotation with a slight inclination, ensuring that every particle of the material is mixed and exposed to heat in a consistent manner. This results in exceptional product homogeneity, high thermal efficiency, and the flexibility to handle a wide range of industrial processes.
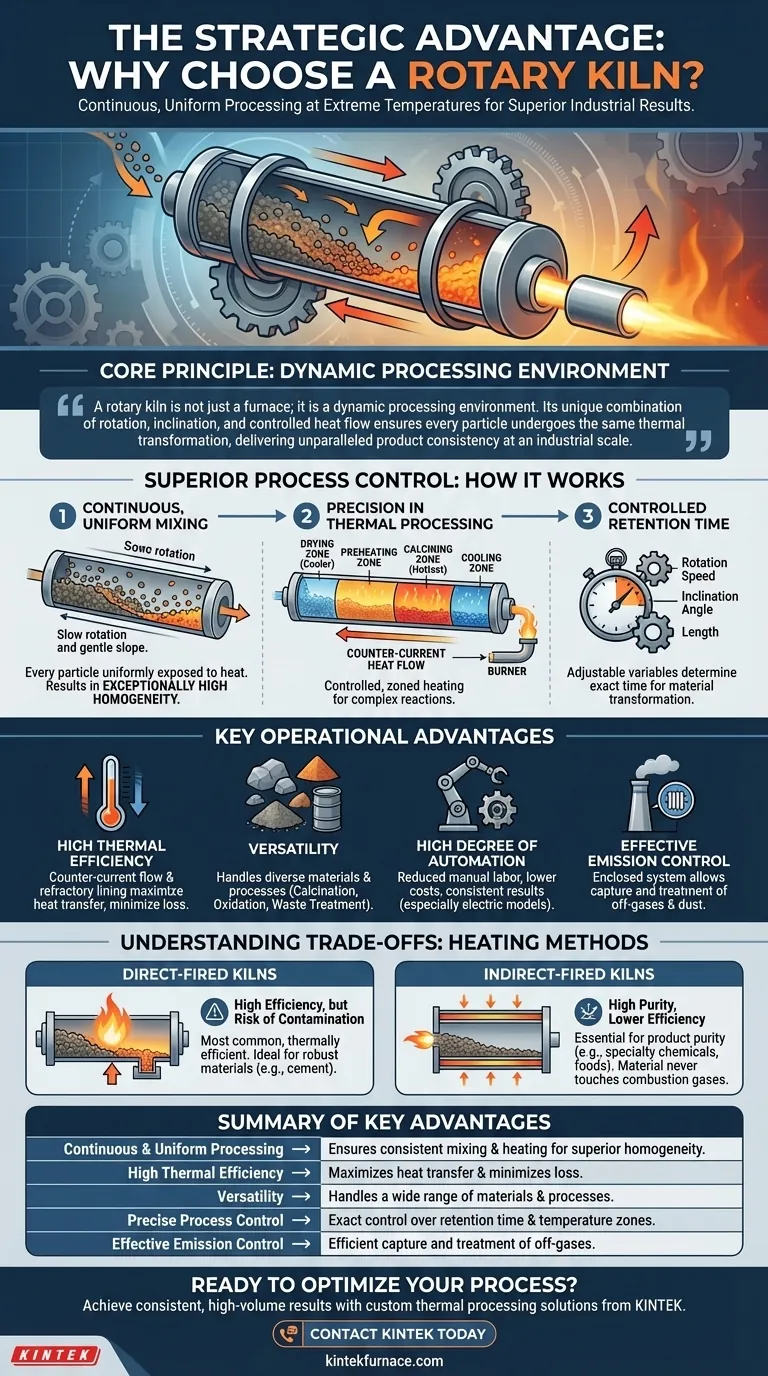
A rotary kiln is not just a furnace; it is a dynamic processing environment. Its unique combination of rotation, inclination, and controlled heat flow ensures every particle undergoes the same thermal transformation, delivering unparalleled product consistency at an industrial scale.
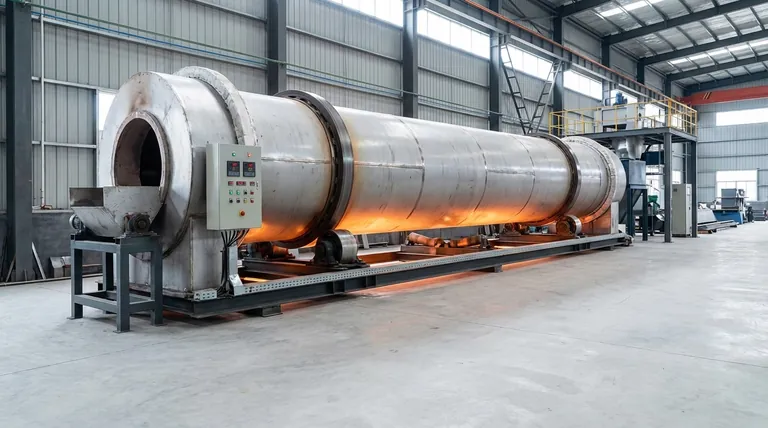

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Superior Process Control
The benefits of a rotary kiln are not accidental; they are the direct result of its fundamental mechanical and thermal design. Understanding this design is key to appreciating its capabilities.
The Principle of Continuous, Uniform Mixing
A rotary kiln is a long, cylindrical shell mounted on bearings and inclined at a slight angle (typically 1-4%). This entire cylinder rotates slowly, generally between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute.
This slow rotation and gentle slope cause the material inside to tumble and mix as it gradually moves from the higher feed end to the lower discharge end. This constant tumbling action ensures homogeneity, as every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source.
Precision in Thermal Processing
For maximum efficiency, most rotary kilns use a counter-current heat flow. A burner at the lower discharge end generates hot gases that travel up the kiln, directly against the flow of the material moving down.
This design creates distinct temperature zones within the kiln:
- Drying Zone: Removes moisture at the cooler feed end.
- Preheating Zone: Begins raising the material temperature.
- Calcining Zone: The hottest zone where the primary chemical reaction or phase change occurs.
- Cooling Zone: Begins to lower the temperature before discharge.
This controlled, zoned heating allows for highly precise thermal treatment, which is critical for complex chemical reactions.
Controlled Retention Time
The amount of time the material spends inside the kiln is a critical process parameter. This retention time is precisely determined by the kiln's rotation speed, its angle of inclination, and its length. By adjusting these variables, operators can ensure the material is heated for the exact duration needed to complete its transformation.
Key Operational and Design Advantages
The unique operating principles of a rotary kiln translate into several tangible benefits that make it indispensable in many heavy industries.
High Thermal Efficiency
The counter-current flow of heat and material is inherently efficient, ensuring the maximum amount of heat is transferred from the gases to the material before the gases exit the kiln. Furthermore, the kiln's steel shell is protected by an internal refractory lining, which insulates the structure and minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment.
Versatility Across Materials and Processes
Rotary kilns are remarkably versatile. They are a cornerstone of the cement, metallurgy, and chemical processing industries, capable of handling materials ranging from powders to large granules. They can be designed for numerous processes, including calcination, oxidation, reduction reactions, and waste treatment.
High Degree of Automation
Modern rotary kilns, especially electric models, are designed for a high degree of automation. The continuous nature of the process, combined with precise control over temperature and retention time, reduces the need for manual labor and intervention. This leads to lower operational costs and more consistent results.
Effective Emission and Pollution Control
Because a rotary kiln is an enclosed system, it allows for the effective capture and treatment of off-gases and dust. This is crucial for meeting modern environmental regulations. Filtration systems and gas control technologies can be integrated to manage emissions effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heating Methods
The choice of heating method is a critical design decision that directly impacts product quality and process efficiency.
Direct-Fired Kilns
In a direct-fired kiln, the combustion gases from the burner are in direct contact with the material being processed.
This is the most common and thermally efficient design. However, it carries the risk of the product being contaminated by the fuel or byproducts of combustion. It is ideal for robust materials like cement clinker, where this interaction is not a concern.
Indirect-Fired Kilns
In an indirect-fired kiln, the outer shell of the cylinder is heated, and that heat is transferred through the shell wall to the material inside. The material never comes into contact with the combustion gases.
This method is essential when product purity is the highest priority, such as in the processing of specialty chemicals, foods, or some mineral oxides. The trade-off is typically lower thermal efficiency and a lower maximum operating temperature compared to direct-fired designs. Electric kilns are a form of indirect heating that offers exceptionally precise temperature control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate rotary kiln design depends entirely on your material, your desired output, and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a bulk material (like cement): A large, direct-fired, counter-current kiln is the most thermally and economically efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute product purity (like specialty chemicals): An indirect-fired or electric rotary kiln is necessary to prevent contamination from combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is precise process control for sensitive reactions: An electric rotary kiln offers the highest degree of temperature regulation and simplifies integration into fully automated systems.
Understanding these core principles allows you to leverage the rotary kiln not just as a piece of equipment, but as a strategic tool for achieving specific industrial outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous & Uniform Processing | Ensures every particle is mixed and heated consistently for superior product homogeneity. |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Counter-current heat flow and refractory lining maximize heat transfer and minimize loss. |
| Versatility | Handles a wide range of materials and processes like calcination, oxidation, and waste treatment. |
| Precise Process Control | Adjustable rotation speed and inclination allow for exact control over retention time and temperature zones. |
| Effective Emission Control | Enclosed system enables efficient capture and treatment of off-gases and dust. |
Ready to leverage a rotary kiln for your industrial process?
At KINTEK, we understand that achieving consistent, high-volume results requires equipment tailored to your specific needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced thermal processing solutions, including high-performance rotary kilns.
Our expertise ensures you get a system designed for maximum efficiency, precise control, and the versatility to handle your unique materials—whether for cement, metallurgy, chemical processing, or specialized applications requiring absolute purity.
Contact KINTOOL today to discuss how our custom rotary kiln solutions can optimize your production, improve product quality, and meet your operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















