At its core, an electric heating rotary kiln is a specialized furnace that uses electrical resistance elements to generate heat. This inclined, rotating cylinder is designed for the high-temperature thermal processing of solid materials, most often powders or granules, in a highly controlled environment. It is a cornerstone technology in the non-ferrous metallurgy, chemical, and advanced materials industries.
The fundamental advantage of an electric rotary kiln is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity for exceptionally precise, uniform, and clean heating. This makes it essential for processing sensitive, high-value materials where contamination from combustion byproducts is unacceptable.
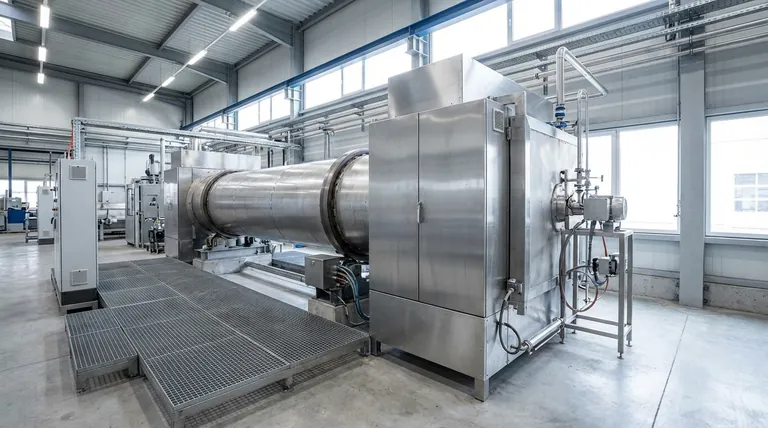

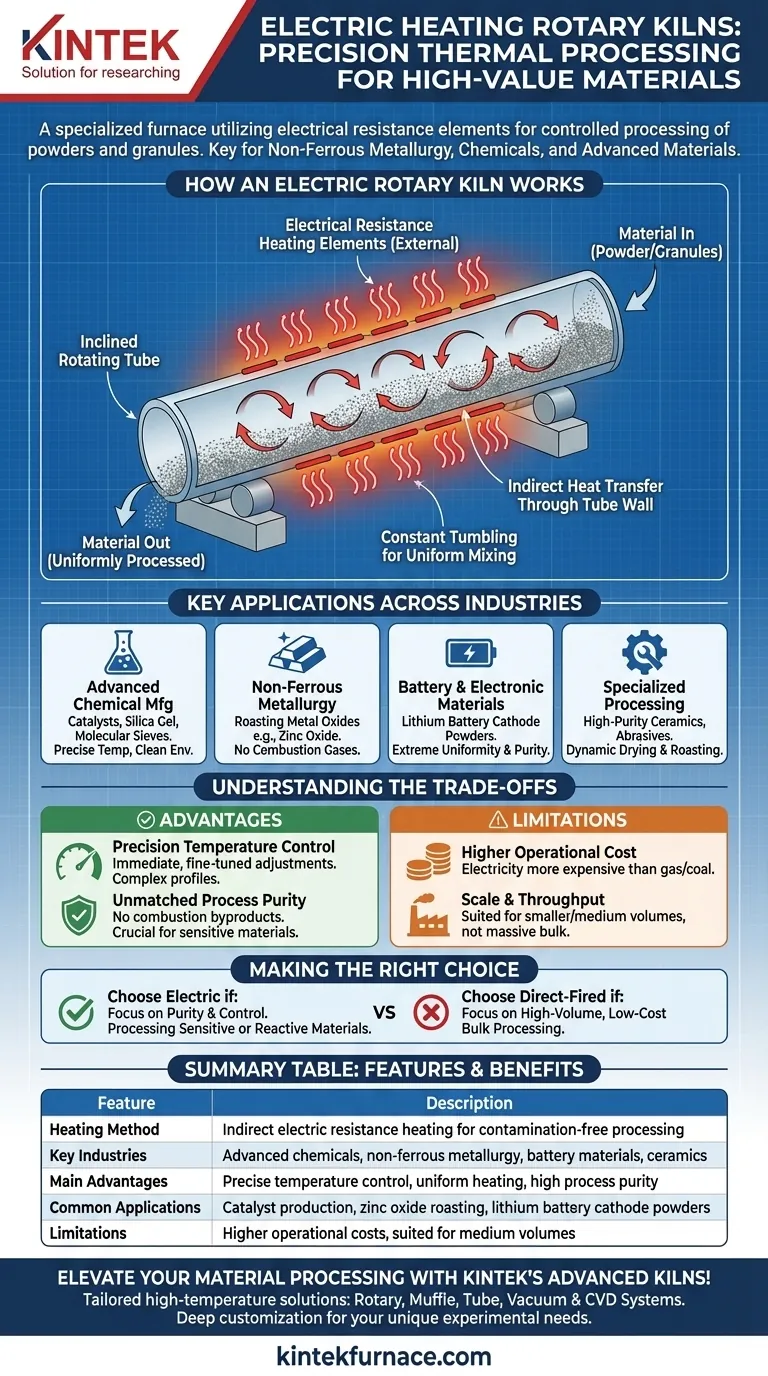
How an Electric Rotary Kiln Works
An electric rotary kiln's design is elegantly simple and effective. It leverages a few key principles to achieve uniform material processing.
The Core Components
The kiln consists of a slightly inclined cylindrical tube, or barrel, that rotates slowly on its axis. The material is fed into the higher end and gradually moves toward the lower discharge end as the kiln turns.
The Indirect Heating Principle
Unlike traditional fuel-burning kilns, the heat source is not inside the processing chamber. Instead, electrical resistance heating elements are positioned outside the rotating tube.
These elements heat the tube's exterior wall, and the heat is then transferred through the wall to the material tumbling inside. This indirect heating method is critical, as it completely isolates the material from the heating source and any potential contaminants.
Material Flow and Uniform Mixing
The combination of the kiln's inclination and its slow rotation forces the material to tumble. This constant mixing ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heated surface of the tube wall. The result is exceptionally even calcination, roasting, or drying with no hot or cold spots.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique benefits of electric rotary kilns make them indispensable in several high-tech and specialty fields where process control is paramount.
Advanced Chemical Manufacturing
Electric kilns are widely used for producing catalysts, silica gel, and chemical molecular sieves. These processes demand precise temperature profiles and an absolutely clean environment to achieve the desired chemical properties.
Non-Ferrous Metallurgy
In metallurgy, these kilns are used for roasting metal oxides like zinc oxide. The absence of combustion gases from fuel prevents unwanted side reactions, ensuring the purity of the final metal product.
Battery and Electronic Materials
This is a critical, modern application. The production of lithium battery materials, such as cathode powders, relies on the extreme uniformity and purity that electric kilns provide. The performance of the final battery is directly tied to the quality of this thermal processing step.
Specialized Material Processing
The technology is also used for the dynamic drying and roasting of various powders, including high-purity ceramics and industrial abrasives, where consistent particle characteristics are essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an electric rotary kiln involves balancing its unique advantages against its operational limitations. It is not the right tool for every thermal processing job.
Advantage: Precision Temperature Control
Electricity allows for immediate, fine-tuned adjustments to the heat output. This enables operators to program complex temperature profiles with ramps and holds that are difficult to achieve with fuel-fired systems.
Advantage: Unmatched Process Purity
This is the kiln's defining benefit. Because no fuel is burned, there are no combustion byproducts (like sulfur, ash, or water vapor) to contaminate the material. This is non-negotiable for high-purity chemicals and electronic materials.
Limitation: Higher Operational Cost
On a pure energy basis, electricity is typically more expensive than natural gas or coal. The higher operating cost must be justified by the value added through superior product quality and purity.
Limitation: Scale and Throughput
Electric rotary kilns are generally used for processing high-value materials in smaller or medium volumes. For massive bulk processing, such as in the cement industry, large-scale direct-fired kilns are far more economical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision to use an electric rotary kiln should be guided by the specific requirements of your material and final product.
- If your primary focus is product purity and precise control: An electric rotary kiln is the superior choice, especially for sensitive chemical or battery materials where contamination is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost bulk processing: A traditional direct-fired kiln using gas or coal is almost always more economical for commodities like cement or bulk minerals.
- If you are processing materials that could react with combustion gases: The indirect electric heating method provides a crucially inert processing environment that a direct-fired kiln cannot.
Ultimately, selecting an electric rotary kiln is a strategic decision that prioritizes material quality and process control over raw energy cost.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect electric resistance heating for contamination-free processing |
| Key Industries | Advanced chemicals, non-ferrous metallurgy, battery materials, ceramics |
| Main Advantages | Precise temperature control, uniform heating, high process purity |
| Common Applications | Catalyst production, zinc oxide roasting, lithium battery cathode powders |
| Limitations | Higher operational costs, suited for medium volumes, not for bulk processing |
Elevate your material processing with KINTEK's advanced electric rotary kilns! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your product purity and process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















