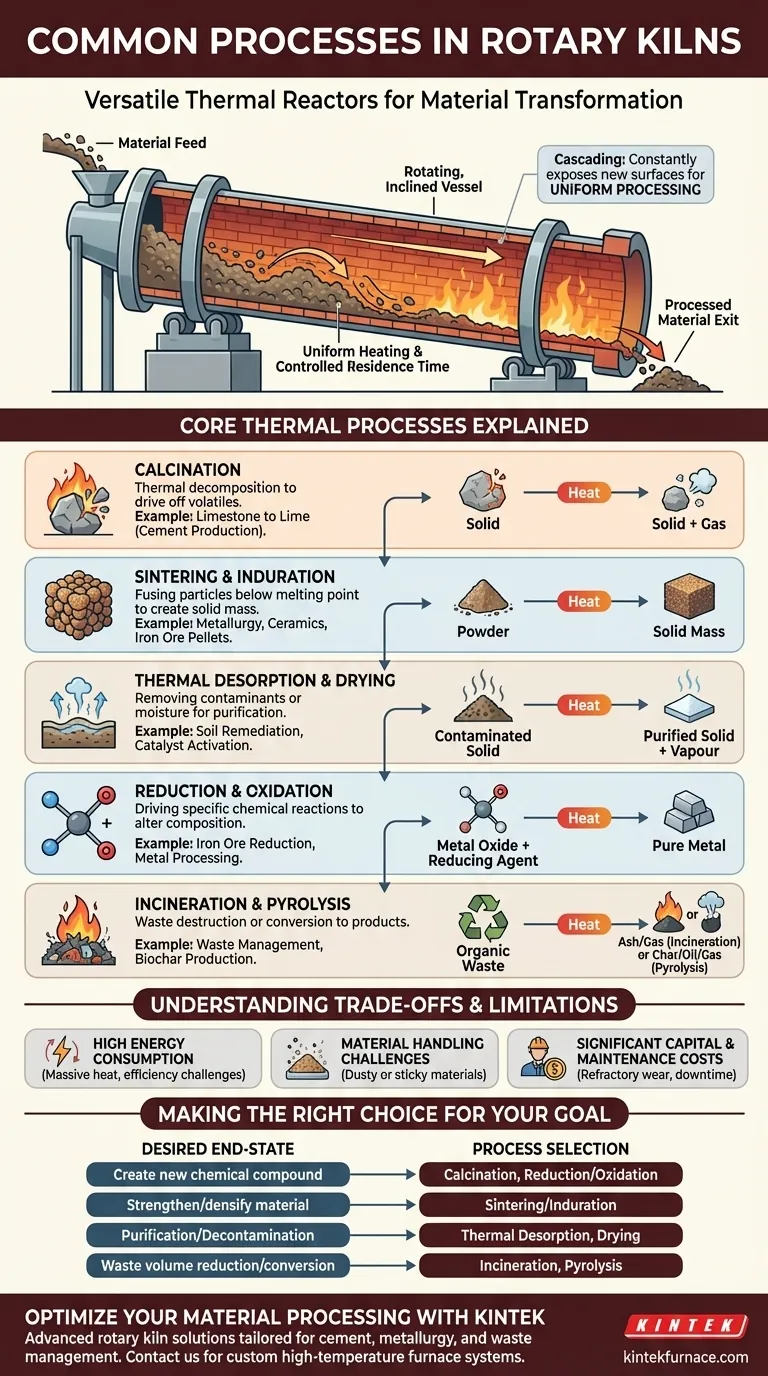
At their core, rotary kilns are highly versatile thermal reactors used to induce specific physical and chemical changes in solid materials. The most common processes they facilitate include calcination for chemical decomposition, sintering to create a solid mass, thermal desorption for purification, and reduction or oxidation for targeted chemical reactions. These processes leverage the kiln's unique ability to mix and uniformly heat materials to high temperatures.
A rotary kiln is not merely a furnace; it is a dynamic processing environment. Its value comes from its ability to use a combination of controlled heat, rotational mixing, and atmospheric conditions to precisely transform a material from one state to another.

The Fundamental Role of a Rotary Kiln
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical vessel, lined with heat-resistant brick, and mounted at a slight angle. Material is fed into the higher end, and the kiln's slow rotation and incline cause the material to tumble and gradually move toward the lower, hotter end.
This design is highly effective for two reasons. First, the tumbling action, known as "cascading," constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the heat source, ensuring uniform processing. Second, the angle and rotation speed precisely control the residence time—how long the material spends inside the kiln—which is critical for achieving the desired transformation.
Core Thermal Processes Explained
While the applications are diverse, they can be grouped into a handful of fundamental thermal processes. Understanding these core functions is key to understanding the kiln's capabilities.
Phase and Chemical Change (Calcination)
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material to a high temperature to drive off a volatile component and induce a chemical change. This is one of the most common uses for rotary kilns.
A classic example is in cement production, where limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated to produce lime (calcium oxide) by driving off carbon dioxide. It is a process of thermal decomposition.
Creating a Solid Mass (Sintering & Induration)
Sintering involves heating a powdered or granular material to a temperature just below its melting point. At this temperature, the particles fuse, creating a single, solid, or porous mass.
This process increases the material's strength and density without liquefying it. It is widely used in metallurgy to process ore fines and in the production of ceramics. Induration is a similar process often applied to iron ore pellets.
Removing Unwanted Substances (Thermal Desorption & Drying)
These processes focus on purification by removing volatile substances from a solid base material.
Drying is the simplest form, used specifically to remove water or moisture. Thermal desorption, a more advanced process, uses heat to vaporize and remove other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or contaminants, such as cleaning contaminated soils or activating catalysts.
Driving Chemical Reactions (Reduction & Oxidation)
Beyond just heating, a rotary kiln can control the chemical atmosphere to drive specific reactions.
Reduction is a chemical process that removes oxygen from a compound, often by introducing a reducing agent like carbon monoxide. This is fundamental in metallurgy for converting metal oxides into pure metals, such as in iron ore reduction. Oxidation is the opposite, where the goal is to add oxygen to a material.
Destruction and Conversion (Incineration & Pyrolysis)
Rotary kilns are also effective tools for waste treatment and material conversion.
Incineration uses high temperatures and excess oxygen to achieve complete combustion of organic materials. This is primarily used for waste destruction and volume reduction. Pyrolysis involves heating organic materials in the absence of oxygen, causing them to decompose into valuable gas and charcoal products rather than burn away.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly versatile, rotary kilns are not the universal solution for all thermal processing needs. Understanding their inherent trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
High Energy Consumption
Operating at temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (1800°F), rotary kilns are massive energy consumers. Significant heat loss can occur through the kiln shell and exhaust gases, making energy efficiency a primary operational challenge.
Material Handling Challenges
The tumbling action that makes kilns effective can also create problems. Very fine or dusty materials can become entrained in the exhaust gas, requiring complex and expensive gas-handling systems. Conversely, sticky or agglomerating materials can build up on the refractory lining, requiring periodic shutdowns for cleaning.
Significant Capital and Maintenance Costs
Rotary kilns are large, heavy-duty pieces of equipment representing a major capital investment. Furthermore, the harsh internal environment causes wear on the refractory brick lining, which requires regular inspection and eventual replacement, leading to significant maintenance costs and operational downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln depends entirely on the transformation you need to achieve. By focusing on the end-state of your material, you can identify the correct process.
- If your primary focus is creating a new chemical compound: You are likely looking at calcination for decomposition or a reduction/oxidation process for chemical conversion.
- If your primary focus is strengthening or densifying a material: Sintering or induration is the key process needed to fuse particles together.
- If your primary focus is purification or decontamination: Thermal desorption, drying, or roasting will be your primary methods to drive off volatile components.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction or conversion: Incineration for destruction or pyrolysis for chemical conversion are the most direct applications.
Understanding these core processes allows you to leverage the rotary kiln not just as a furnace, but as a precise tool for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition to drive off volatiles | Cement production, lime manufacturing |
| Sintering & Induration | Fusing particles to create solid mass | Metallurgy, ceramics production |
| Thermal Desorption & Drying | Removing contaminants or moisture | Soil remediation, catalyst activation |
| Reduction & Oxidation | Chemical reactions to alter composition | Iron ore reduction, metal processing |
| Incineration & Pyrolysis | Waste destruction or conversion to products | Waste management, biochar production |
Ready to optimize your material processing with advanced rotary kiln solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace systems tailored for industries like cement, metallurgy, and waste management. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise performance for calcination, sintering, and more. Contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems can enhance your efficiency and meet your unique experimental needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















