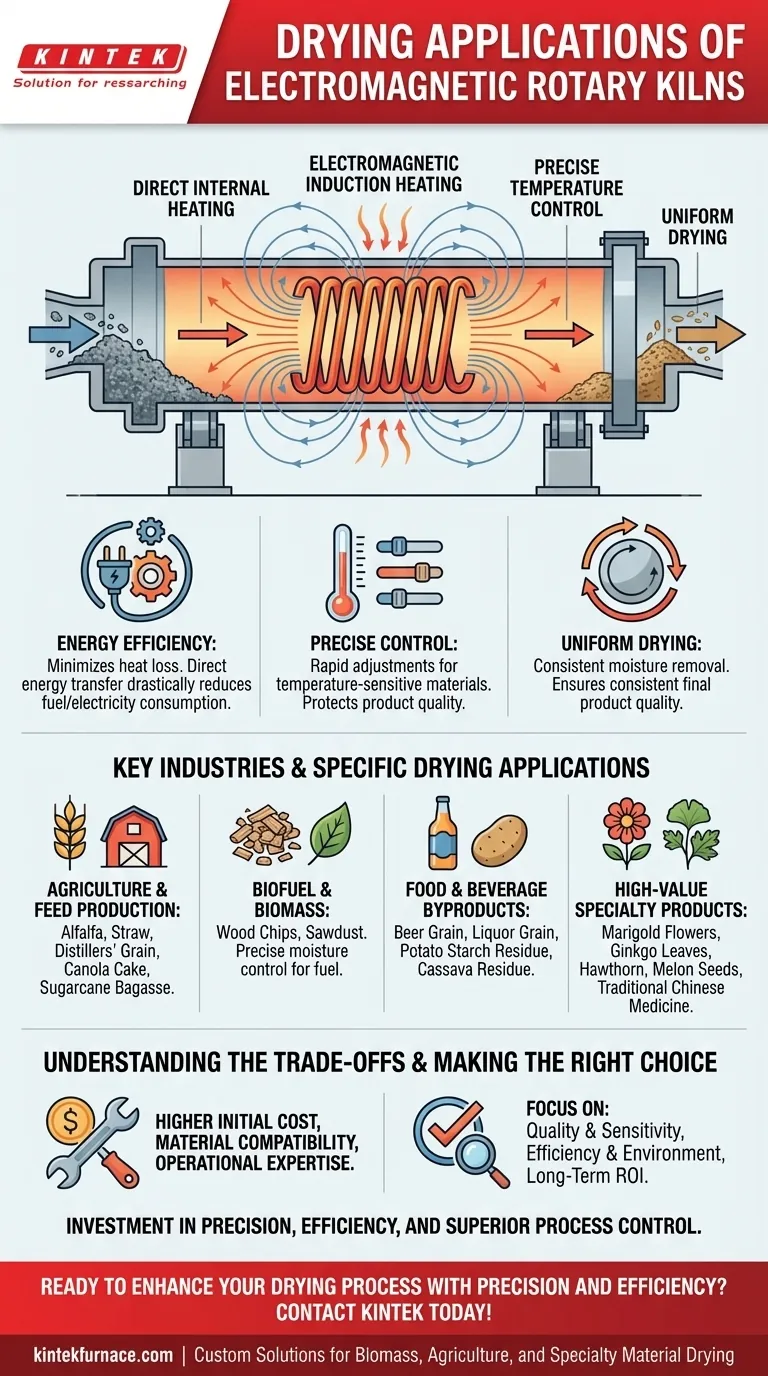
At their core, electromagnetic rotary kilns are versatile thermal processing units with a wide array of drying applications, particularly for biomass, agricultural byproducts, and temperature-sensitive materials. They are used for drying everything from alfalfa, sawdust, and wood chips to distillers' grains, cassava residue, and high-value products like marigold flowers and traditional Chinese medicine.
The key takeaway is not simply the list of materials an electromagnetic kiln can dry, but why it is chosen. This technology provides highly efficient and precisely controlled direct heating, making it a superior choice for applications where product quality, energy consumption, and uniform moisture removal are critical.
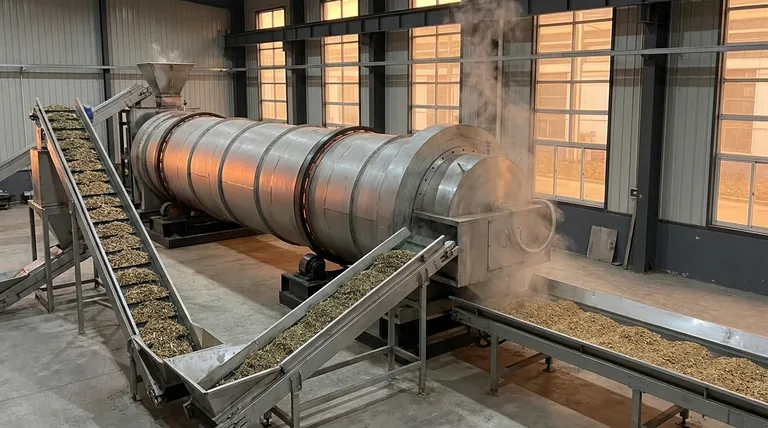

The Role of Rotary Kilns in Thermal Processing
Before focusing solely on drying, it's essential to understand that a rotary kiln is fundamentally a tool for high-temperature material processing. Drying is just one of its many capabilities.
Calcination and Sintering
Rotary kilns are foundational in industries like cement manufacturing, where they heat raw materials to create clinker. They are also used for calcining (thermally decomposing) materials like lime and for sintering (fusing without melting) small, granular solids.
Reduction and Oxidation
In metallurgy, rotary kilns are used for critical chemical reactions. This includes reducing metallic ores to extract metals or performing controlled oxidation processes on various compounds.
Pyrolysis and Waste Treatment
For environmental applications, these kilns are used for pyrolysis (decomposition in an oxygen-starved environment) and the incineration of both hazardous and non-hazardous waste, such as sewage sludge and scrap tires.
Why Electromagnetic Heating is a Game Changer for Drying
The "electromagnetic" aspect is what differentiates these modern kilns. Instead of relying on external burners and hot gas, electromagnetic induction generates heat directly, which fundamentally changes the drying process.
The Principle of Induction Heating
Electromagnetic induction uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly within the kiln's conductive shell or, in some cases, the material itself. This method is exceptionally efficient as it minimizes the heat lost to the surrounding environment.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
Traditional kilns lose significant energy heating the air and the kiln's structure from the outside in. By generating heat internally, electromagnetic kilns transfer energy far more effectively, drastically reducing fuel or electricity consumption.
Precise Temperature Control
This direct heating allows for rapid adjustments and extremely precise temperature control. This is critical for drying sensitive organic materials like ginkgo leaves, botanicals, or food products that could be damaged or scorched by the temperature fluctuations common in conventional kilns.
Uniform Drying
The slow rotation of the kiln continually tumbles the material, exposing all particles to the heated surface. Combined with the consistent heat from induction, this ensures highly uniform moisture removal and a consistent final product, which is vital for quality control.
Key Industries and Specific Drying Applications
With this understanding, we can see why electromagnetic kilns are so effective for specific drying tasks across various industries.
Agriculture and Feed Production
This is a primary application area. The kiln's efficiency is ideal for drying high-moisture, high-volume materials like alfalfa, straw, distillers’ grain, canola cake, and sugarcane bagasse.
Biofuel and Biomass
For the production of biofuels, uniformly drying materials like wood chips and sawdust to a specific moisture content is essential. The control offered by electromagnetic kilns excels here.
Food and Beverage Byproducts
The precise, gentle heat is perfect for drying byproducts without degrading their nutritional value. Applications include drying beer grain, liquor grain, potato starch residue, and cassava residue.
High-Value Specialty Products
For materials where quality and integrity are paramount, this technology is invaluable. It is used for drying marigold flowers, ginkgo leaves, hawthorn, melon seeds, and various forms of traditional Chinese medicine.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the potential downsides.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
The advanced technology and control systems of an electromagnetic induction kiln typically mean a higher upfront investment compared to a simple, direct-fired conventional kiln.
Material Compatibility
The efficiency of induction heating can be influenced by the electrical and magnetic properties of the material being processed. While the kiln shell is the primary heating element, process optimization may be required for certain materials.
Operational Expertise
While highly automated, these advanced systems require a different skill set for maintenance and troubleshooting compared to older, mechanically simpler kiln designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be driven by your specific product, operational goals, and long-term financial strategy.
- If your primary focus is drying high-value, temperature-sensitive products: The precise control and uniform heating of an electromagnetic kiln are critical advantages that protect product quality and justify the investment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and environmental compliance: An electromagnetic kiln offers significant operational savings and a smaller carbon footprint by eliminating direct fuel combustion and improving energy transfer.
- If your primary focus is processing low-margin, robust bulk materials: While a traditional kiln may have a lower initial cost, the long-term energy savings from an electromagnetic model can deliver a compelling return on investment.
Ultimately, choosing an electromagnetic rotary kiln is an investment in precision, efficiency, and superior process control.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Materials Dried | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Feed Production | Alfalfa, Distillers' Grain, Sugarcane Bagasse | High efficiency, uniform moisture removal |
| Biofuel & Biomass | Wood Chips, Sawdust | Precise moisture control, energy savings |
| Food & Beverage Byproducts | Beer Grain, Cassava Residue | Gentle drying, preserves nutritional value |
| High-Value Specialty Products | Marigold Flowers, Traditional Chinese Medicine | Superior quality, precise temperature control |
Ready to enhance your drying process with precision and efficiency? Contact KINTEK today to learn how our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces and more, can be customized to meet your unique needs. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we deliver tailored systems for biomass, agriculture, and specialty material drying. Get in touch now to discuss your requirements and discover the benefits of our technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials



















