At its core, the use of ceramic heating elements spans a vast range of sectors, from heavy industrial manufacturing to high-tech electronics and everyday consumer goods. Their adoption is driven by a unique set of properties that make them indispensable where traditional metallic elements would fail, contaminate a process, or prove inefficient.
The widespread use of ceramic heaters is not accidental; it's a direct result of their ability to provide stable, high-temperature, and contamination-free heat in environments where metal elements would corrode, short-circuit, or degrade.
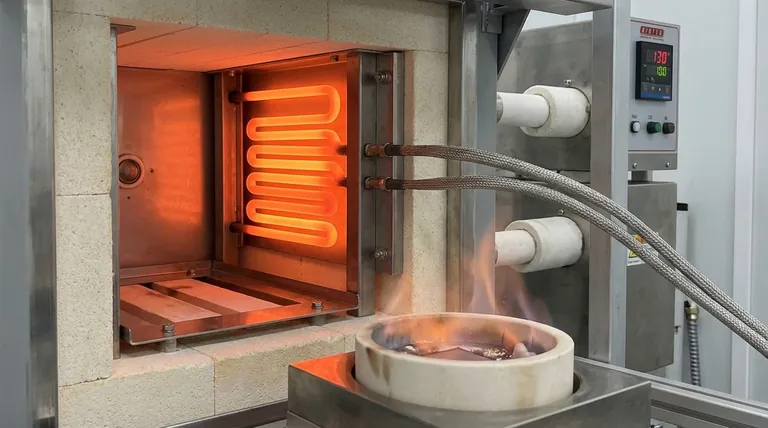

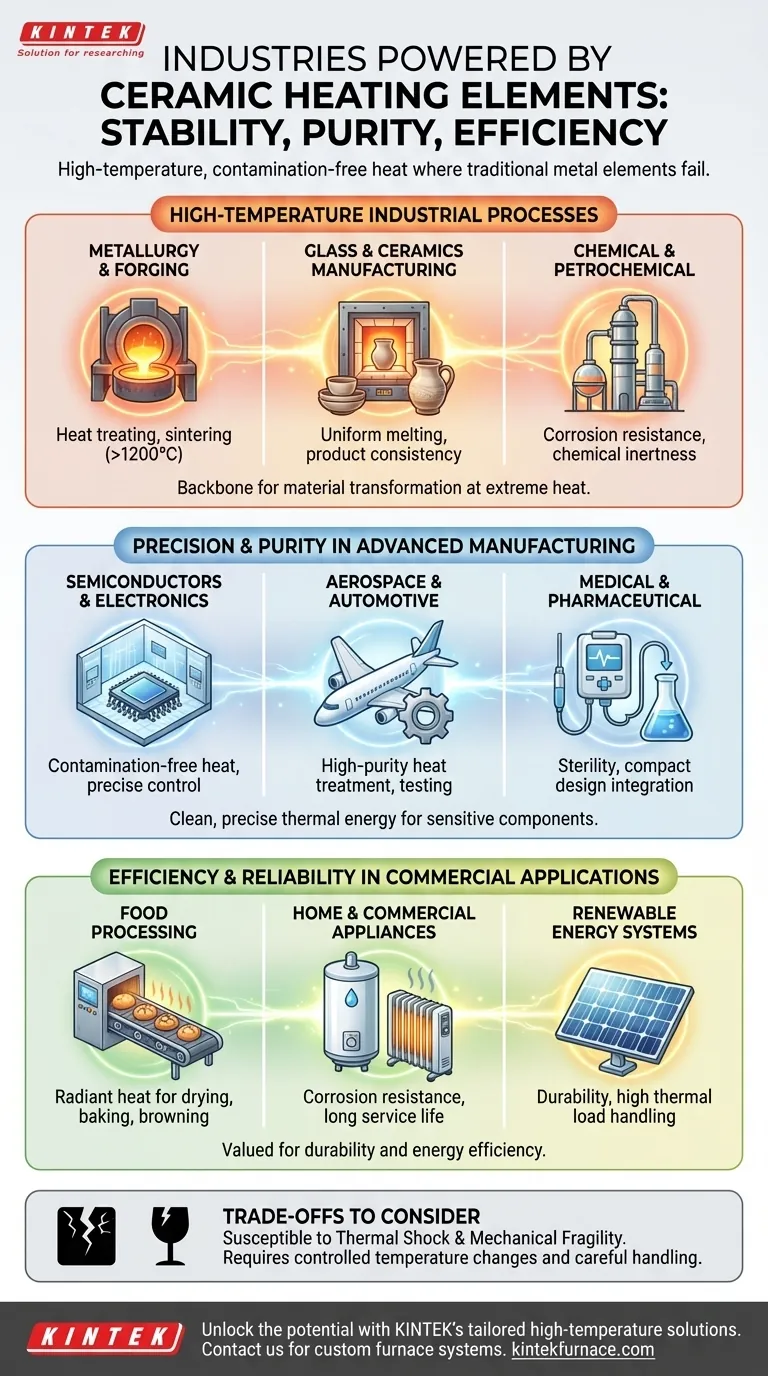
The Foundation: High-Temperature Industrial Processes
Ceramic heaters form the backbone of industries that rely on extreme heat for material transformation. Their ability to operate consistently at very high temperatures without melting or warping is their primary advantage here.
Metallurgy and Metal Forging
In metallurgy, furnaces for heat treating, sintering, and forging metals require temperatures that can easily exceed the limits of most metals. Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) ceramic elements are critical in these settings.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing
Producing glass and firing ceramic goods demands sustained, uniform high temperatures. Ceramic heaters provide the stable thermal environment needed for melting raw materials and for the kilning process, ensuring product quality and consistency.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
Many chemical processes, such as drying and distillation, require heating materials that may be corrosive. The chemical inertness of ceramic elements prevents them from reacting with the substances they are heating, ensuring both process purity and element longevity.
Precision and Purity in Advanced Manufacturing
In high-technology fields, the quality of heat is as important as the quantity. Ceramic elements deliver clean, precise thermal energy, which is essential for manufacturing sensitive components.
Semiconductors and Electronics
The manufacturing of semiconductors and electronic components occurs in ultra-clean environments where any metallic contamination could ruin an entire batch. Ceramic heaters provide contamination-free heat and the precise temperature control needed for processes like soldering.
Aerospace and Automotive
Components for aerospace and automotive applications must withstand extreme conditions. Ceramic heaters are used in furnaces for material testing and in the manufacturing of specialized parts that require high-purity heat treatment.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
Sterility and purity are non-negotiable in the medical field. Ceramic heaters are used in manufacturing medical devices and in laboratory equipment because they deliver clean heat and can be integrated into compact designs without risk of contamination.
Efficiency and Reliability in Commercial Applications
Beyond heavy industry, ceramic heaters are valued for their durability and energy efficiency in a variety of commercial and consumer-facing applications.
Food Processing
Ceramic infrared emitters are commonly used for drying, baking, and browning in the food industry. They provide even, radiant heat that cooks food efficiently without direct contact or risk of contamination from degrading metal parts.
Home and Commercial Appliances
In appliances like modern water heaters, the corrosion resistance of ceramic is a major advantage, leading to a longer service life. They are also used in high-efficiency space heaters, where they hold and radiate heat effectively.
Renewable Energy Systems
Ceramic elements play a role in systems like solar thermal collectors. Their durability and ability to handle high thermal loads contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of these renewable energy technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, ceramic heating elements are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
Susceptibility to Thermal Shock
Unlike metals, ceramics can be brittle. A sudden, drastic change in temperature—known as thermal shock—can cause them to crack. They perform best in applications where temperature changes are controlled and gradual.
Mechanical Fragility
Ceramic elements are harder than metal but also more brittle. They must be handled and installed with care to avoid physical impact, which can lead to fracture. This requires more careful design considerations for their mounting and support structures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating element requires matching its properties to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature processing (>1200°C): Specialized ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi2 are the standard for high-temperature furnaces in metallurgy and glass production.
- If your primary focus is purity and contamination control: Ceramic heaters are the definitive choice for semiconductor, medical, and high-purity chemical applications.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance in a liquid environment: A ceramic-sheathed element is ideal for industrial water heating and processing corrosive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and long life in a dry environment: Ceramic emitters are an excellent option for industrial drying ovens, space heating, and food processing.
By understanding these core properties and trade-offs, you can confidently determine where a ceramic heating element is the optimal technical solution.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Heat treating, sintering, forging | High-temperature stability (>1200°C) |
| Glass & Ceramics | Melting, kilning | Uniform heating, product consistency |
| Chemical Processing | Drying, distillation | Chemical inertness, corrosion resistance |
| Semiconductors | Soldering, manufacturing | Contamination-free heat, precise control |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Material testing, part manufacturing | High-purity heat treatment |
| Medical & Pharmaceutical | Device manufacturing, lab equipment | Sterility, compact design |
| Food Processing | Drying, baking, browning | Radiant heat, efficiency |
| Home & Commercial Appliances | Water heaters, space heaters | Corrosion resistance, long life |
| Renewable Energy | Solar thermal systems | Durability, high thermal load handling |
Unlock the full potential of ceramic heating elements for your industry! At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need extreme temperature processing, contamination control, or energy-efficient designs, we have the expertise to deliver. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















