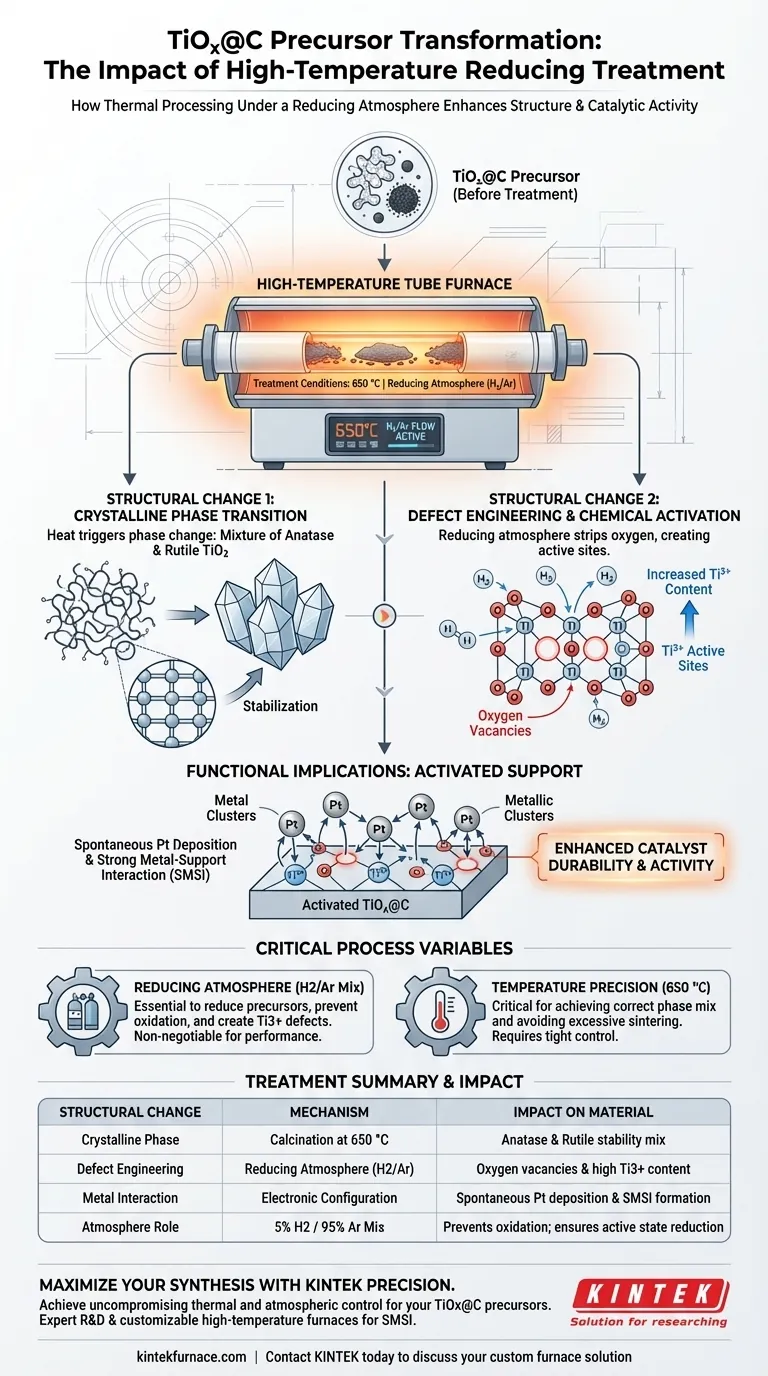
High-temperature thermal treatment under a reducing atmosphere fundamentally alters the crystalline and electronic structure of TiOx@C precursors. Specifically, calcining the material at 650 °C in a hydrogen-argon environment triggers a phase transition into a mixture of anatase and rutile TiO2 while simultaneously creating a high concentration of oxygen vacancy defects.
The primary value of this process is not just structural stabilization, but chemical activation. By generating oxygen vacancies and increasing Ti3+ content, the treatment creates the specific active sites required for the spontaneous deposition of Platinum (Pt) and the formation of Strong Metal-Support Interactions (SMSI).

Mechanisms of Structural Transformation
Crystalline Phase Transition
Under standard conditions, TiOx precursors may lack a defined or optimal crystalline structure.
The application of 650 °C heat converts the titanium oxide into a distinct mixture of anatase and rutile phases.
This mixed-phase composition is often critical for optimizing the stability and electronic properties of the support material.
Creation of Oxygen Vacancies
The most significant structural change occurs at the atomic level through defect engineering.
The reducing atmosphere strips oxygen atoms from the lattice, resulting in a high concentration of oxygen vacancies.
These vacancies are not flaws; they are intentional features that dramatically alter the material's chemical behavior.
Elevation of Ti3+ Content
The removal of oxygen forces a reduction in the oxidation state of the titanium.
This process significantly increases the content of Ti3+ species within the structure.
These Ti3+ sites serve as the primary "hooks" for subsequent chemical reactions.
Functional Implications of the Structure
Enabling Spontaneous Metal Deposition
The structural changes directly dictate how the support interacts with other metals.
The Ti3+ defects act as active sites that facilitate the spontaneous deposition of Platinum (Pt).
Without this pre-treatment, the support would lack the necessary electronic configuration to effectively anchor the metal catalyst.
Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI)
The ultimate goal of this structural modification is to enhance catalyst durability and activity.
The interaction between the induced defects and the deposited platinum results in a Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI).
This interaction is essential for preventing metal sintering and ensuring long-term stability in electrochemical applications.
Critical Process Variables and Trade-offs
The Necessity of a Reducing Atmosphere
The presence of hydrogen (specifically a 5% H2/95% Ar mix) is non-negotiable for this outcome.
A reducing environment is required to reduce precursor salts to their metallic states or specific alloy structures.
Without this atmosphere, uncontrolled oxidation would occur at high temperatures, failing to produce the oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ sites required for high performance.
Temperature Precision
The process relies on a specific temperature setpoint (650 °C) to achieve the correct phase mix.
Deviating from this temperature could result in an incomplete phase transition or excessive sintering of the support.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Strategy
To ensure your TiOx@C precursors are correctly activated for catalytic applications, consider the following approach:
- If your primary focus is Enhancing Catalytic Activity: Ensure the atmosphere contains hydrogen to generate the Ti3+ defects necessary for spontaneous Platinum deposition and SMSI.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Strictly control the temperature at 650 °C to achieve the stable anatase/rutile phase mix without degrading the carbon framework.
The success of this treatment relies on the synergy between heat and the reducing gas; one triggers the phase change, while the other engineers the electronic defects that drive performance.
Summary Table:
| Structural Change | Mechanism | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Crystalline Phase | Calcination at 650 °C | Transition to anatase and rutile mixture for stability |
| Defect Engineering | Reducing Atmosphere (H2/Ar) | Creation of oxygen vacancies and high Ti3+ content |
| Metal Interaction | Electronic Configuration | Enables spontaneous Pt deposition and SMSI formation |
| Atmosphere Role | 5% H2 / 95% Ar Mix | Prevents oxidation; ensures precursor reduction to active states |
Maximize Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect balance of anatase/rutile phases and Ti3+ defect concentrations requires uncompromising thermal and atmospheric control. At KINTEK, we understand that the success of your TiOx@C precursors depends on precision.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs, providing the stable reducing environments and exact temperature profiles essential for Strong Metal-Support Interactions (SMSI).
Ready to elevate your catalyst performance?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution
Visual Guide
References
- Zihan Wei, Guisheng Li. Highly Dispersed Pt on TiOx Embedded in Porous Carbon as Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. DOI: 10.3390/catal15050487
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What temperature-related capabilities make multi zone tube furnaces valuable for research? Unlock Precision Thermal Control
- What are the primary applications of tubular furnaces? Precision Heat Treatment for Research and Industry
- What critical reaction conditions does a tube furnace provide during the synthesis of SFC5 materials?
- How do high-temperature redox cycles performed in a tube furnace contribute to the activation of Ni/BaZrO3 catalysts?
- How does the positioning of a quartz tube in a vertical tube furnace contribute to the stability of the synthesis reaction?
- What is the function of a laboratory tube furnace in Ti-5Al-4W-2Fe alloy forging? Enhance Thermoplasticity & Purity
- What is a tube furnace and how is it designed? Achieve Precise, Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace play in the heat treatment of NiTiCu alloys? Optimize Shape Memory Properties



















