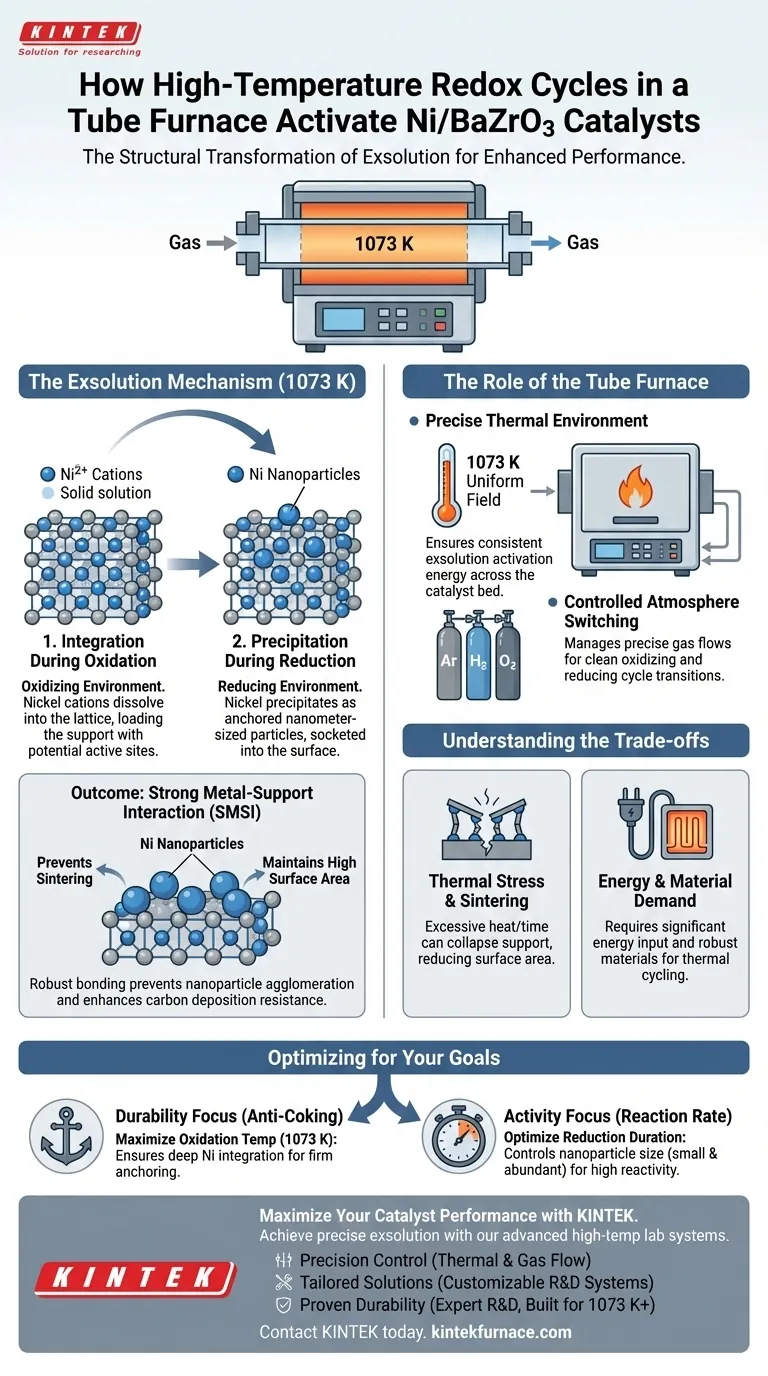
High-temperature redox cycles facilitate a structural transformation known as exsolution. When performed at 1073 K in a tube furnace, this process forces Nickel cations to integrate into the BaZrO3 lattice during oxidation and subsequently emerge as anchored nanoparticles during reduction. This creates a specific surface architecture that is critical for high catalytic performance.
The tube furnace environment enables a precise dissolution-precipitation mechanism, resulting in strong metal-support interactions that significantly enhance activity and resistance to carbon deposition.

The Exsolution Mechanism Explained
The core function of the redox cycle in this context is to manipulate the physical location and state of the Nickel atoms relative to the Barium Zirconate (BaZrO3) support.
Integration During Oxidation
In the oxidation phase, the high thermal energy provided by the tube furnace drives Nickel cations into the perovskite structure.
The Nickel effectively dissolves into the BaZrO3 lattice, creating a solid solution. This step "loads" the support with potential active sites.
Precipitation During Reduction
During the subsequent reduction phase, the environment changes to pull the Nickel back out of the lattice.
Nickel precipitates onto the surface in the form of nanometer-sized particles. Because these particles emerge from within the lattice structure, they are socketed firmly into the surface rather than merely sitting on top.
Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI)
The extreme heat (1073 K) ensures that the bond between the precipitating metal particles and the oxide support is robust.
This interaction, known as SMSI, prevents the nanoparticles from agglomerating (sintering) during operation, maintaining high surface area and reactivity.
The Role of the Tube Furnace
While the chemistry defines the reaction, the tube furnace provides the necessary engineering controls to execute it.
Precise Thermal Environment
The activation of Ni/BaZrO3 requires temperatures around 1073 K.
A tube furnace creates a uniform thermal field that ensures the entire catalyst bed reaches this activation energy simultaneously. This uniformity is vital for consistent exsolution across the entire batch.
Controlled Atmosphere Switching
The process requires alternating between oxidizing and reducing environments.
Tube furnaces are designed to manage gas flows (such as inert Argon, Hydrogen, or Oxygen) with precision. This control allows for the clean switching of atmospheres required to drive the integration and precipitation cycles without contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high-temperature redox cycling is effective, it introduces specific challenges that must be managed.
Thermal Stress and Sintering
While heat drives exsolution, excessive heat or prolonged holding times can lead to the sintering of the support material itself.
If the support structure collapses or grains grow too large, the surface area available for catalysis diminishes, counteracting the benefits of the Nickel activation.
Energy and Material Demand
Operating at 1073 K requires significant energy input and specialized furnace materials capable of withstanding thermal cycling.
Rapid heating and cooling rates can thermally shock ceramic components within the furnace or the catalyst support itself if not ramped strictly (e.g., controlled rates like 2°C/min are often used in similar reduction contexts).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of redox cycles should be tailored to the specific operational demands of your catalyst.
- If your primary focus is Durability (Anti-Coking): Ensure the oxidation temperature reaches the full 1073 K to maximize the depth of Nickel integration, which anchors particles firmly against carbon growth.
- If your primary focus is Activity (Reaction Rate): Optimize the reduction phase duration to control the size of the precipitated nanoparticles, ensuring they remain small and abundant rather than large and sparse.
By leveraging the precise thermal control of a tube furnace, you transform Ni/BaZrO3 from a simple mixture into a sophisticated, self-regenerating catalytic system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Integration (Oxidation) | Precipitation (Reduction) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1073 K | 1073 K |
| Mechanism | Nickel dissolves into BaZrO3 lattice | Nickel emerges as anchored nanoparticles |
| Outcome | Creates a solid solution | Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI) |
| Key Benefit | Uniform site loading | Resistance to sintering & carbon deposition |
| Atmosphere | Oxidizing environment | Reducing environment (e.g., Hydrogen) |
Maximize Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Achieving precise exsolution in Ni/BaZrO3 catalysts requires the rigorous thermal and atmospheric control found only in professional-grade equipment. KINTEK provides advanced lab high-temp systems specifically designed for researchers and manufacturers who demand excellence.
Why choose KINTEK for your catalyst research?
- Precision Control: Our tube furnaces offer the uniform thermal fields and gas flow management essential for complex redox cycles.
- Tailored Solutions: Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique R&D specifications.
- Proven Durability: Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are built to withstand repeated thermal cycling at 1073 K and beyond.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our specialized lab furnaces can optimize your activation processes.
Visual Guide
References
- Kai Shen, John M. Vohs. Enhanced Methane Steam Reforming Over Ni/BaZrO3. DOI: 10.1007/s10562-025-05087-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in the synthesis of one-dimensional silicon nanowires (SiNWs) using CVD?
- What is the role of a three-zone tube furnace in the synthesis of single-crystal V2O5 nanosheets? Expert Insights
- What is the primary function of a Drop Tube Furnace in iron ore beneficiation? Unlock High-Precision Thermal Shock.
- How does a vertical single-temperature zone tube furnace facilitate the growth of high-quality PdSe2 single crystals?
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace for the post-deposition annealing of ITO? Optimize Film Performance
- How does a Tube Furnace function in the catalytic pyrolysis process for producing biochar? Enhance Carbonization Quality
- What is the purpose of purging a tube furnace with argon for tellurium reduction? Ensuring Safety and Purity
- What are the advantages of using a tube furnace for small-volume samples or low-throughput operations? Achieve Precision and Control in Your Lab



















