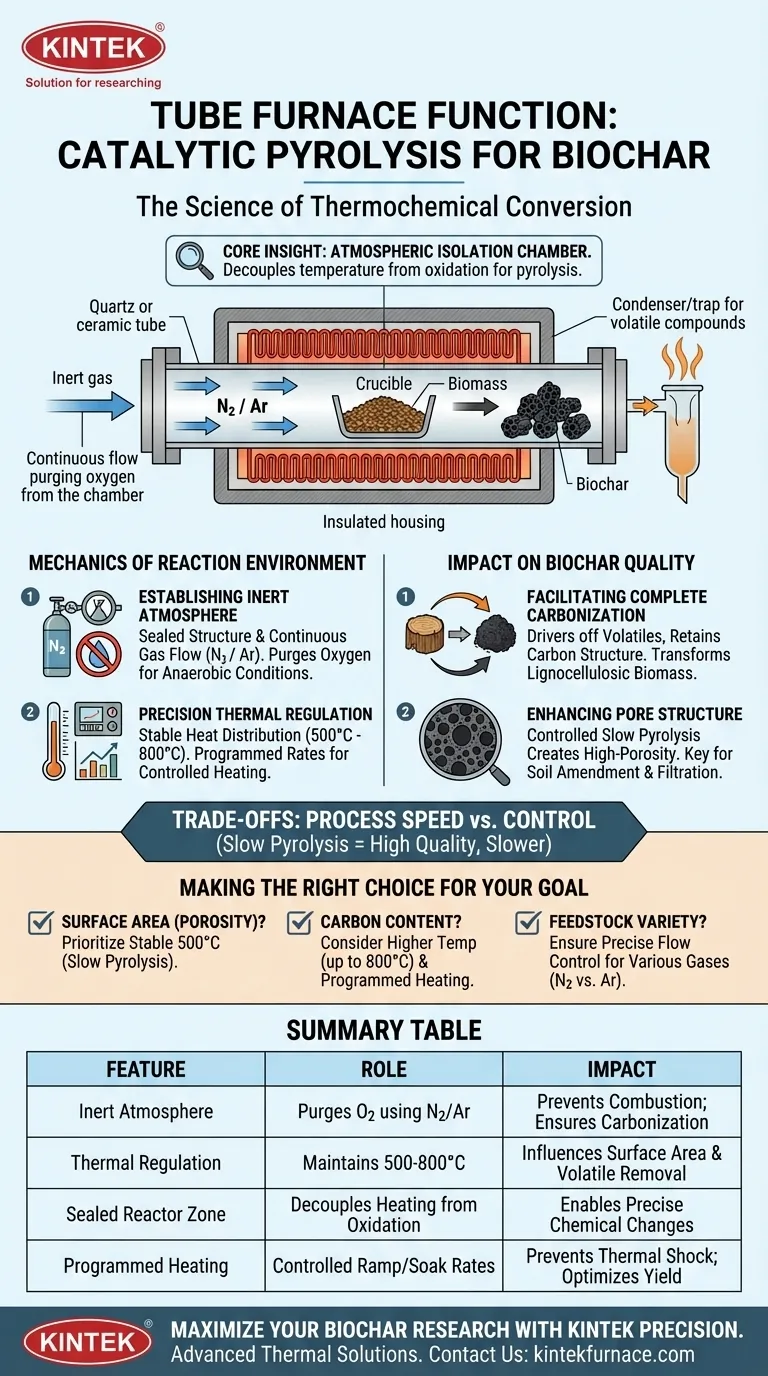
A Tube Furnace functions as a precision-controlled reactor that facilitates the thermochemical conversion of biomass into biochar. It creates a sealed, high-temperature environment where biomass is heated (typically around 500 °C) under a continuous flow of inert gas, preventing combustion and enabling the specific chemical changes required for carbonization.
Core Insight: The Tube Furnace is not merely a heater; it is an atmospheric isolation chamber. Its primary value lies in decoupling temperature application from oxidation, ensuring biomass undergoes pyrolysis (thermal decomposition) rather than combustion (burning), effectively fixing carbon into a solid, high-porosity structure.

The Mechanics of the Reaction Environment
Establishing an Inert Atmosphere
The fundamental requirement for producing biochar is the absence of oxygen. If oxygen is present during heating, the biomass will burn and turn to ash.
The tube furnace solves this by utilizing a sealed structure and a continuous flow of inert gas, primarily Nitrogen (though Argon is also used). This flow purges air from the reaction zone, creating the strictly anaerobic conditions necessary for efficient devolatilization.
Precision Thermal Regulation
Consistency is critical for catalytic processes. The tube furnace employs a precise temperature control system to maintain a stable heat distribution within the reaction zone.
This allows for programmed heating rates, ensuring the biomass reaches specific target temperatures (ranging from 500 °C to 800 °C depending on the feedstock) without thermal shock or fluctuation. This stability is essential for the catalytic reactions to proceed predictably.
Impact on Biochar Quality
Facilitating Complete Carbonization
By maintaining a stable, oxygen-free environment, the furnace ensures the complete carbonization of the feedstock.
Whether processing wood, food waste, or sludge, the furnace allows organic matter to decompose thermally. This drives off volatile compounds while retaining the carbon structure, transforming lignocellulosic biomass into a stable biochar precursor.
Enhancing Pore Structure
The specific conditions maintained by the tube furnace directly influence the physical properties of the final product.
The primary reference notes that the controlled slow pyrolysis process results in biochar with a high-porosity structure. This porosity is a key indicator of biochar quality, determining its effectiveness in applications like soil amendment or filtration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Speed vs. Control
The tube furnace is primarily associated with slow pyrolysis. While this method yields high-quality biochar with excellent porosity, it is inherently slower than fast pyrolysis methods.
Dependency on Gas Flow stability
The integrity of the biochar is entirely dependent on the continuous flow of inert gas.
Any interruption or fluctuation in the Nitrogen or Argon supply can compromise the anaerobic environment. Even a small ingress of oxygen at high temperatures can lead to partial combustion, significantly altering the surface properties and yield of the biochar.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting or operating a tube furnace for biochar production, your operational parameters must align with your specific research or production targets.
- If your primary focus is Surface Area (Porosity): Prioritize a furnace with exceptional thermal stability to maintain 500 °C, as this creates the optimal high-porosity structure defined in slow pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is Carbon Content: Consider a furnace capable of higher temperature ranges (up to 800 °C) and programmed heating to drive off maximum volatiles and fix the carbon.
- If your primary focus is Feedstock Variety: Ensure the furnace offers precise flow control for different inert gases (Nitrogen vs. Argon) to accommodate the specific chemical sensitivities of materials like food waste or sludge.
Success in catalytic pyrolysis relies not just on the heat, but on the rigor of the atmospheric control that the tube furnace provides.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Biochar Production | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Purges oxygen using Nitrogen or Argon | Prevents combustion; ensures carbonization over ash formation |
| Thermal Regulation | Maintains stable 500°C - 800°C range | Influences surface area and volatile matter removal |
| Sealed Reactor Zone | Decouples heating from oxidation | Enables precise chemical changes for high-porosity structures |
| Programmed Heating | Controlled ramp and soak rates | Prevents thermal shock; optimizes carbon content and yield |
Maximize Your Biochar Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieve unparalleled control over your catalytic pyrolysis experiments with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific lab requirements. Whether you are optimizing pore structure or maximizing carbon yield, our high-temp furnaces provide the atmospheric integrity and thermal stability your research demands.
Ready to elevate your carbonization process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs with our technical specialists.
Visual Guide
References
- S. S. Ibrahim, Badr A. Mohamed. Catalyzed biochar from date palm waste for ammonium removal: potential application in poultry farms for ammonia mitigation. DOI: 10.1007/s43621-025-00817-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the uniform thermal field provided by a vertical tube resistance furnace impact phase equilibrium experiments?
- What conditions does a continuous flow fixed-bed quartz reactor provide? Master CO Oxidation Testing with Cobalt Oxide
- What are the benefits of a vertical tube furnace? Maximize Space and Purity in Your Lab
- What is a vertical furnace? A Guide to High-Purity, Uniform Thermal Processing
- What role does a tube high-temperature furnace play in the synthesis of nano carbon spheres? Unlock sp2 Hybridization
- Why is a tube furnace required for the calcination of TiO2 in an H2/Ar mixed atmosphere? Engineering TiO2-X Defects
- What are the main applications of a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Thermal Processing
- What are some common applications of tubular furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing



















