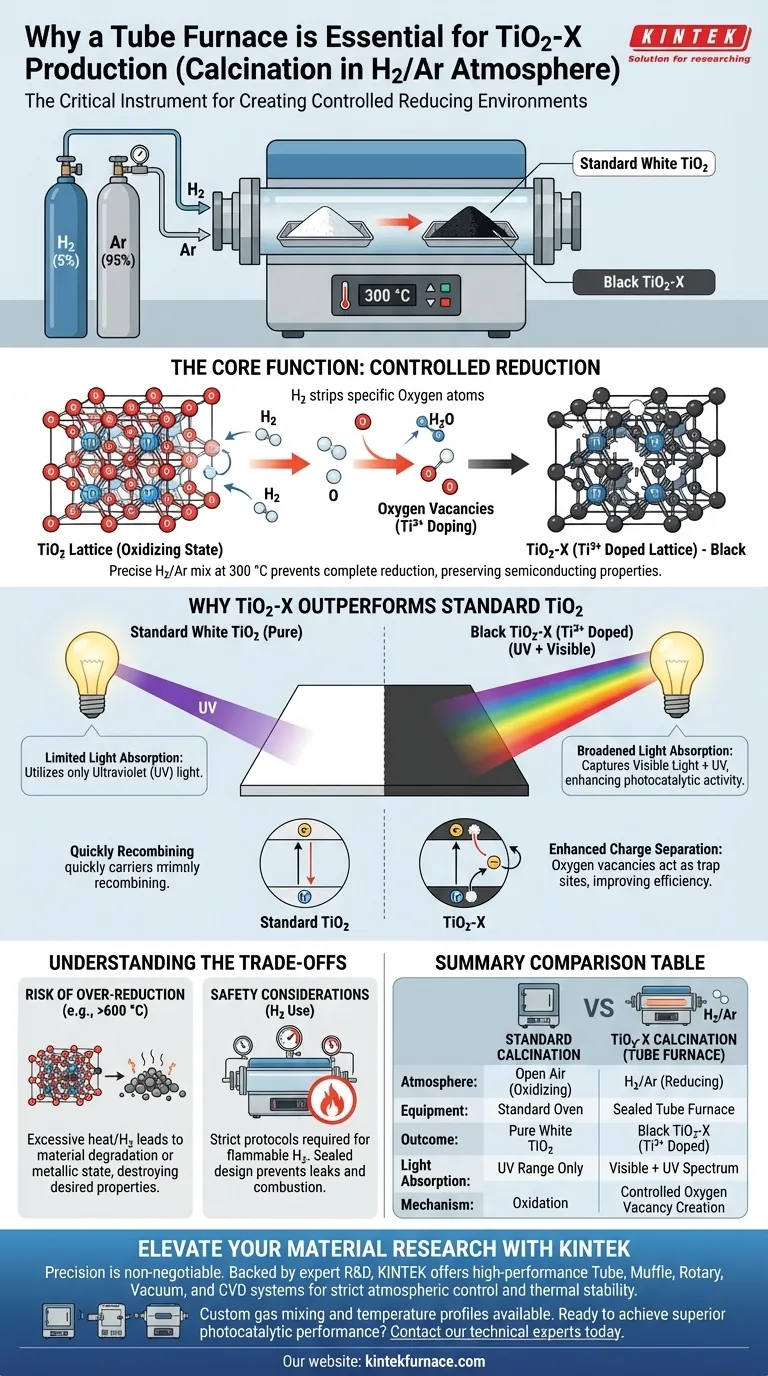
The tube furnace is a critical instrument because it creates a strictly controlled reducing environment necessary to alter the chemical structure of titanium dioxide (TiO2). By utilizing a specific mixture of hydrogen (H2) and argon (Ar), the furnace enables the precise introduction of defects into the material lattice—a process that is impossible in an open-air or standard oven environment.
The core function of the tube furnace in this process is "controlled reduction." It allows you to maintain a precise 300 °C temperature within a reducing atmosphere, converting standard white TiO2 into black TiO2-X by introducing oxygen vacancies (Ti3+ doping) without reducing the material completely to a metallic state.
The Mechanism of Controlled Reduction
To understand why this specific equipment is required, one must look beyond simple heating and examine the chemical engineering occurring at the atomic level.
Creating the Reducing Atmosphere
Standard calcination usually occurs in air (oxidizing). Producing TiO2-X requires the opposite: a reducing atmosphere.
The tube furnace allows for the flow of a specific gas mixture, typically 5% H2 and 95% Ar. The Hydrogen acts as the active reducing agent, while the Argon serves as an inert carrier to maintain pressure and safety.
Introducing Oxygen Vacancies
The goal is not to melt the material, but to modify its lattice. The reducing H2 gas strips specific oxygen atoms from the TiO2 structure.
This creates "oxygen vacancies," effectively doping the material with Ti3+ ions. This chemical shift is what creates the "X" in TiO2-X, fundamentally changing the material's electronic properties.
Precise Temperature Regulation
According to your primary data, this reaction requires a stable environment at 300 °C.
A tube furnace provides the thermal stability needed to sustain this temperature uniformly across the sample. This ensures the reduction is consistent throughout the batch, preventing uneven doping which would degrade performance.
Why TiO2-X Outperforms Standard TiO2
The necessity of the tube furnace is justified by the significant performance gains of the resulting material.
Broadening Light Absorption
Standard TiO2 is white, meaning it reflects visible light and only utilizes ultraviolet (UV) light.
The Ti3+ doping turns the material black (TiO2-X). This dark color indicates that the material can now absorb a significantly broader range of the spectrum, specifically capturing visible light energy that standard TiO2 misses.
Enhancing Charge Separation
The oxygen vacancies created in the tube furnace act as trap sites that improve the separation of electrical charges.
By preventing charge carriers (electrons and holes) from recombining too quickly, the material becomes much more efficient at photocatalytic or photovoltaic applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace is essential for this synthesis, the process requires careful management of specific risks.
The Risk of Over-Reduction
Control is paramount. If the temperature is too high (e.g., approaching 600 °C) or the hydrogen concentration is too high, you risk "over-reducing" the material.
Instead of creating a doped semiconductor (TiO2-X), you might strip away too much oxygen, degrading the oxide structure or pushing it toward a metallic state, which destroys the desired photocatalytic properties.
Safety Considerations
Using hydrogen, even at 5%, requires strict safety protocols.
The tube furnace design is specifically sealed to manage flammable gases safely, preventing leaks and ensuring that the reducing atmosphere does not mix with ambient oxygen at high temperatures, which could lead to combustion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters you choose for your tube furnace depend entirely on the final material properties you require.
- If your primary focus is Photocatalytic Efficiency (TiO2-X): Adhere strictly to the 300 °C target to achieve partial reduction (Ti3+ doping) and broaden visible light absorption.
- If your primary focus is Metallic Precursors or Alloys: You would likely need higher temperatures (e.g., 600 °C) to achieve complete reduction to a metallic state, but this is not applicable for producing semiconducting TiO2-X.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is a chemical reactor that precisely balances thermal energy and gas composition to engineer atomic defects for superior material performance.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Standard Calcination | TiO2-X Calcination (Tube Furnace) |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Open Air (Oxidizing) | H2/Ar Mixture (Reducing) |
| Equipment | Standard Muffle Oven | Sealed Tube Furnace |
| Key Outcome | Pure White TiO2 | Black TiO2-X (Ti3+ Doped) |
| Light Absorption | UV Range Only | Visible + UV Light Spectrum |
| Core Mechanism | Oxidation | Controlled Oxygen Vacancy Creation |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when engineering advanced materials like TiO2-X. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to provide the strict atmospheric control and thermal stability your synthesis requires.
Whether you need custom gas mixing capabilities for hydrogen reduction or specialized temperature profiles for delicate doping, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable for your unique needs.
Ready to achieve superior photocatalytic performance? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Bingke Zhang, Ergang Wang. Facile Synthesis of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Heterojunctions of Glycolated Conjugated Polymer‐TiO<sub>2−X</sub> for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202402649
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different designs of High Temperature Tube Furnaces? Choose the Right Design for Your Lab
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the preparation of biomimetic composite skeletons?
- Why is a specialized tube furnace with a steam inlet required for the steam activation of carbon materials?
- How does a tube furnace generate high temperatures for heat treatment? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- Why is vacuum sealing of a reaction tube necessary during the in-situ solvothermal growth of BiVO4/COF?
- What role does a scissor lift play in the thermogravimetric analysis system of a tube furnace? Precision Alignment Guide
- What is the function of a tube furnace in pRF preparation? Optimize Carbonization & Conductivity



















