When selecting a high-temperature tube furnace, your primary consideration is its physical configuration, as this directly impacts how you interact with your sample. The four principal designs are horizontal, vertical, split-tube, and rotary. Each serves a distinct purpose, moving beyond simple heating to accommodate specific experimental setups, sample types, and process requirements.
Choosing the right furnace design is not about finding the "best" one, but about aligning the furnace's physical layout with the specific demands of your material and process. The core decision hinges on sample access, the physical state of your material, and whether your process benefits from gravity or rotation.
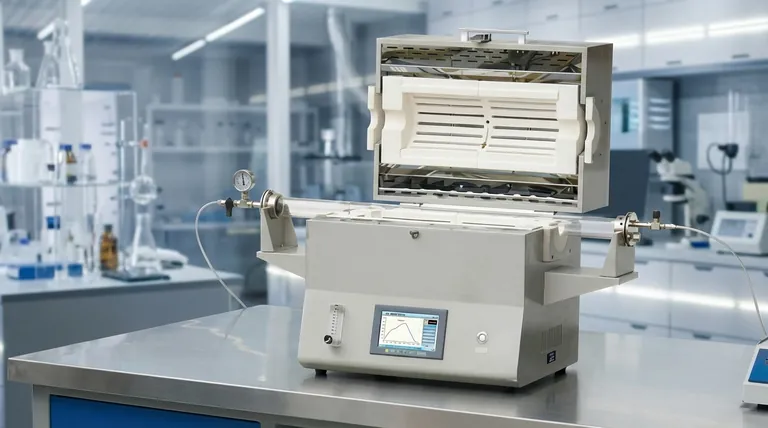

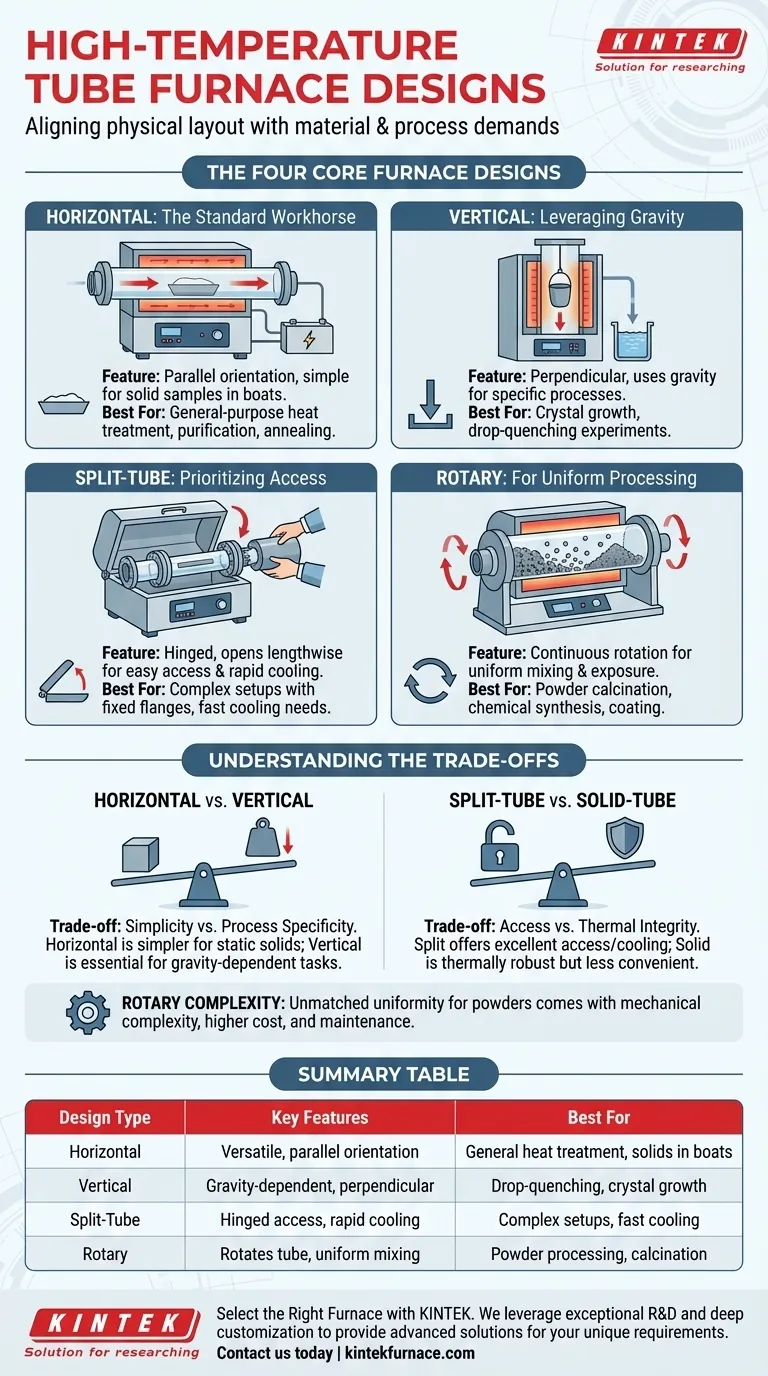
The Four Core Furnace Designs
Each furnace design offers a fundamental advantage tailored to different laboratory or production needs. Understanding these differences is the first step in selecting the correct tool for your work.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Standard Workhorse
A horizontal furnace is the most common and versatile design, with the process tube oriented parallel to the workbench. It is the standard for a wide range of applications.
This layout is ideal for processing solid samples held in ceramic or quartz "boats." Its simplicity makes it a robust and cost-effective choice for general-purpose heat treatment, purification, and annealing.
Vertical Furnaces: Leveraging Gravity
Vertical furnaces orient the process tube perpendicularly. This design uses gravity to its advantage for specific, often more advanced, applications.
It is essential for processes where the sample should not touch the tube walls, such as certain crystal growth methods. It is also used for drop-quenching experiments, where a sample is released from the hot zone into a quenching medium below.
Split-Tube Furnaces: Prioritizing Access
Often called "clamshell" furnaces, split-tube furnaces are hinged and can be opened along their length. This feature grants unparalleled access to the process tube.
This design is invaluable when working with process tubes that have complex or fixed flanges, making them difficult to slide into a solid furnace. It also allows for rapid cooling of the sample, as the furnace body can be opened to expose the tube to ambient air.
Rotary Furnaces: For Uniform Processing
A rotary furnace is a specialized design that slowly rotates the entire process tube during heating. This continuous motion is critical for applications involving powders or granular materials.
The rotation ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to both the heat and the process atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon). This makes it the superior choice for calcination, chemical synthesis, and coating applications where mixing is essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single design is perfect for every task. Your choice will involve balancing accessibility, process requirements, and complexity.
Horizontal vs. Vertical
The trade-off here is between simplicity and process specificity. Horizontal furnaces are simpler to operate and more broadly applicable for static solid samples.
Vertical furnaces are more complex to set up but are indispensable for gravity-dependent processes like drop testing or specific types of material synthesis where contact with the tube must be avoided.
Split-Tube vs. Solid-Tube
The primary trade-off is between access and thermal integrity. A split-tube furnace offers excellent access for loading complex setups and allows for faster cooling.
However, the seam where the furnace opens can be a point of minor heat loss, potentially creating a less uniform thermal zone compared to a one-piece solid-tube design. Solid-tube furnaces are thermally robust but offer far less convenience for sample placement.
The Complexity of Rotary Furnaces
While rotary furnaces provide unmatched processing uniformity for powders, they introduce mechanical complexity. The rotating seals required for atmosphere control and the motor system demand more maintenance than static furnace designs. This specialization comes at a higher initial cost and operational overhead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment of solid samples: A standard horizontal furnace is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is easy sample loading or rapid cooling: A split-tube furnace provides the necessary access and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is uniform processing of powders or granules: A rotary furnace is the only design that ensures consistent mixing and exposure.
- If your primary focus is a gravity-dependent process like drop-quenching: A vertical furnace is specifically designed to meet this need.
By matching the furnace's fundamental design to your application, you ensure your equipment becomes an asset to your research, not a limitation.
Summary Table:
| Design Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Versatile, cost-effective, parallel tube orientation | General-purpose heat treatment, solid samples in boats |
| Vertical | Gravity-dependent, perpendicular tube orientation | Drop-quenching, crystal growth, avoiding tube contact |
| Split-Tube | Hinged access, rapid cooling, easy loading | Complex setups, fixed flanges, fast sample cooling |
| Rotary | Rotates tube, uniform mixing, atmosphere control | Powder processing, calcination, chemical synthesis |
Struggling to select the right high-temperature tube furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're processing powders, need gravity-dependent setups, or require easy access for complex samples, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















