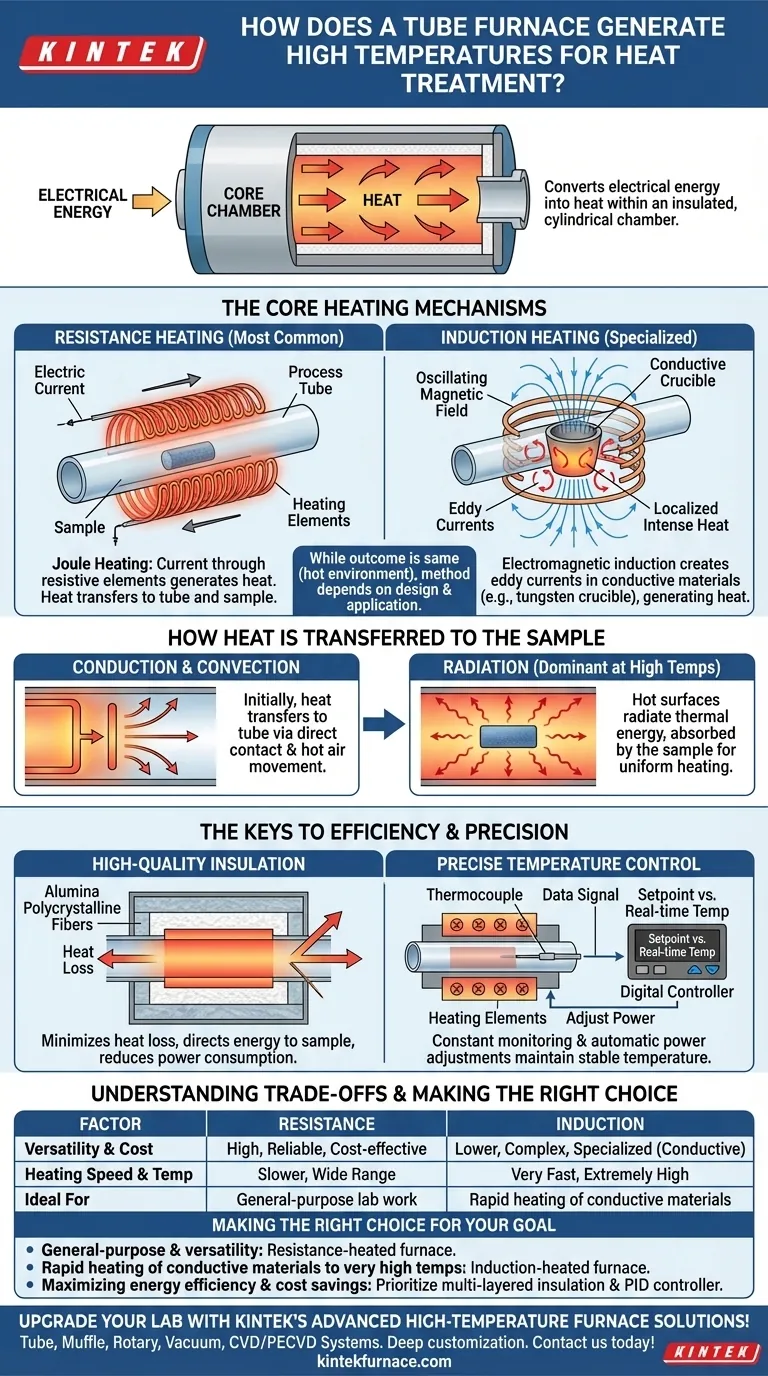
At its core, a tube furnace generates high temperatures by converting electrical energy into heat within a highly insulated, cylindrical chamber. This is achieved primarily through one of two methods: passing an electric current through a resistive heating element that encircles the tube, or using electromagnetic induction to directly heat a conductive crucible inside the tube.
The fundamental principle is not just about getting hot, but about doing so with extreme precision and efficiency. A tube furnace is a closed system designed to minimize heat loss and provide a stable, tightly controlled thermal environment for processing materials.

The Core Heating Mechanisms Explained
A tube furnace's ability to reach and maintain high temperatures hinges on its heating technology. While the outcome is the same—a hot processing environment—the method used depends on the furnace's design and intended application.
Resistance Heating: The Most Common Method
The vast majority of tube furnaces use resistance heating. This process works by passing a strong electrical current through heating elements strategically placed around the process tube.
These elements are made from materials with high electrical resistance. As current flows, the resistance causes the elements to heat up significantly—a principle known as Joule heating.
This generated heat is then transferred to the furnace tube and, ultimately, to the sample inside.
Induction Heating: For Specialized Applications
A more advanced method is medium-frequency induction heating. This is used for applications requiring very rapid heating or extremely high temperatures.
Instead of traditional heating elements, a high-frequency alternating current is passed through a coil. This creates a powerful, oscillating magnetic field.
When a conductive material, such as a tungsten crucible, is placed inside the coil, the magnetic field induces electrical currents (eddy currents) within it. These currents generate intense, localized heat directly in the crucible, which then radiates to the sample.
How Heat is Transferred to the Sample
Generating heat is only the first step. The furnace is engineered to transfer that heat to the sample efficiently and uniformly.
Conduction and Convection
Initially, the heat from the elements is transferred to the furnace tube wall through conduction (direct contact) and convection (movement of hot air in the space between the element and the tube).
Radiation
As the temperature climbs, thermal radiation becomes the dominant mode of heat transfer. The hot inner walls of the furnace tube (or the crucible in an induction furnace) radiate thermal energy, which is absorbed by the sample inside. This is a highly effective method for achieving uniform heating in a vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
The Keys to Efficiency and Precision
A tube furnace is more than just a heater; it's a precision instrument. Its efficiency comes from a combination of smart design and active control.
High-Quality Insulation
To prevent the generated heat from escaping, the heating zone is enclosed in layers of high-quality insulation. Materials like alumina polycrystalline fibers are used to minimize heat loss, ensuring that most of the energy is directed toward the sample. This dramatically reduces power consumption.
Precise Temperature Control
A thermocouple, a highly sensitive temperature sensor, constantly monitors the temperature inside the tube. It sends this data as an electrical signal to a digital controller.
The controller compares the real-time temperature to the user-defined setpoint. If there is a deviation, it instantly adjusts the power sent to the heating elements, maintaining the desired temperature with remarkable stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, different tube furnace designs present distinct advantages and limitations.
Resistance vs. Induction
Resistance heating is versatile, reliable, and cost-effective for a wide range of temperatures and materials. It is the workhorse of most research and production environments.
Induction heating is significantly faster and can reach higher temperatures, but it is more complex and is primarily effective for heating electrically conductive materials.
Thermal Mass vs. Responsiveness
A furnace with thick, heavy insulation will be extremely stable at temperature and highly energy-efficient. However, its high thermal mass means it will take longer to heat up and cool down.
Conversely, a lighter furnace may be more responsive but less stable and potentially less efficient at holding a setpoint for long durations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate furnace technology depends entirely on your specific processing needs.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work and versatility: A standard resistance-heated tube furnace is the ideal and most common choice.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating of conductive materials to very high temperatures: An induction-heated furnace will provide the speed and performance required for these specialized tasks.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and cost savings: Prioritize a furnace with multi-layered, high-grade insulation and a modern PID temperature controller.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select a tool that is perfectly matched to your technical objective.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Mechanism | Key Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Heating | Electric current through resistive elements | Versatile, reliable, cost-effective | General-purpose lab work, wide temperature range |
| Induction Heating | Electromagnetic induction in conductive materials | Rapid heating, very high temperatures | Specialized tasks with conductive materials |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















