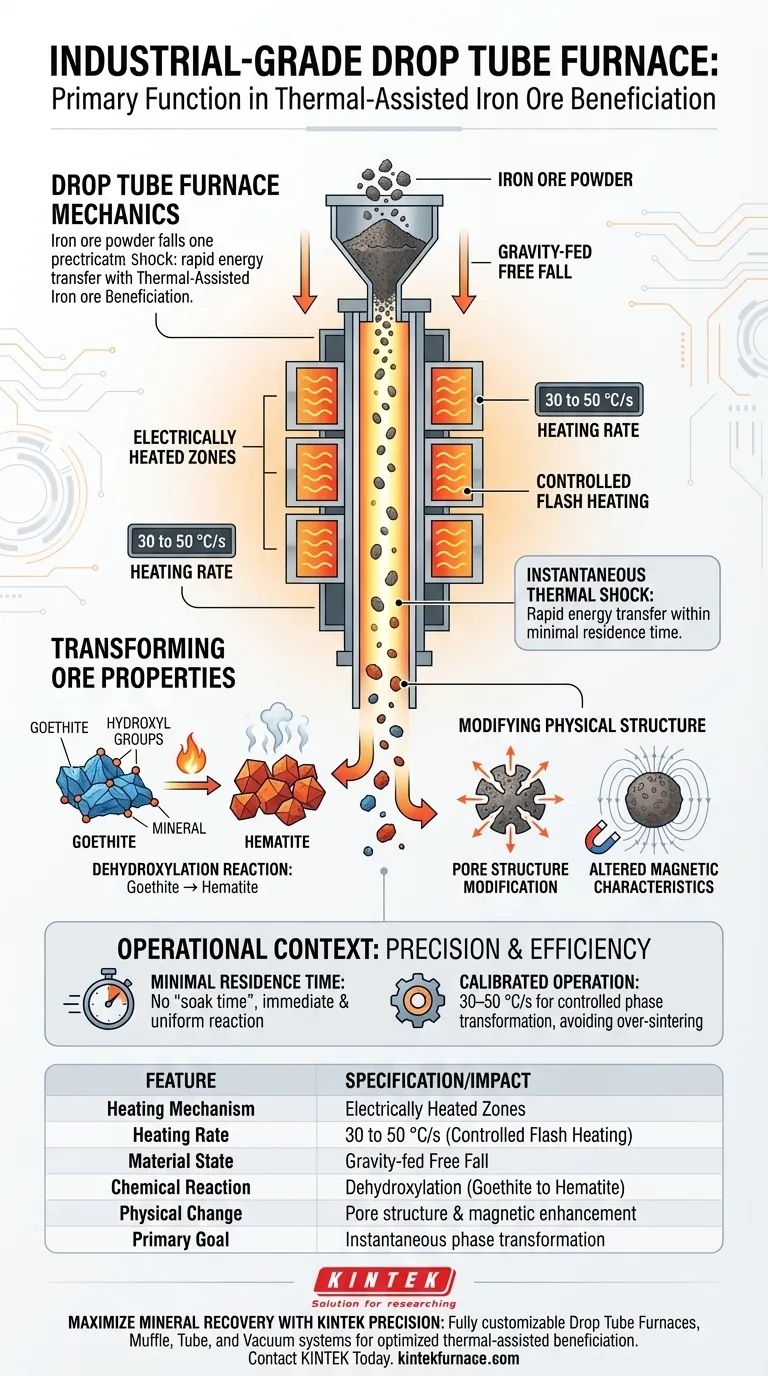
The primary function of an industrial-grade Drop Tube Furnace in this specific context is to act as high-precision flash heating equipment. By utilizing electrically heated zones, the furnace exposes falling iron ore particles to a controlled high-temperature environment, achieving rapid heating rates of 30 to 50 °C/s to induce immediate material transformation.
Core Takeaway The furnace leverages gravity-fed free fall to deliver an instantaneous thermal shock. This rapid energy transfer is the catalyst for converting goethite into hematite and modifying magnetic properties within a minimal residence time, thereby creating the essential conditions for effective mineral separation.

The Mechanics of Thermal-Assisted Beneficiation
Controlled Flash Heating
The Drop Tube Furnace differs from conventional roasting methods by prioritizing speed and intensity.
It uses electrically heated zones to maintain a precise temperature profile. This allows the equipment to deliver a specific thermal load—heating the particles at a rate of 30 to 50 °C/s—which is critical for the specific beneficiation of iron ore.
The Free Fall Advantage
The defining feature of this equipment is the free fall mechanism.
Ore powder is dropped through the vertical tube, ensuring that every particle is exposed to the heat source from all sides. This eliminates the need for mechanical agitation and ensures the thermal treatment occurs within a minimal residence time.
Transforming Low-Grade Ore Properties
Dehydroxylation Reaction
The thermal shock generated by the furnace triggers a specific chemical reaction known as dehydroxylation.
During the fall, the heat removes hydroxyl groups from the mineral structure. This effectively transforms goethite (a common component in low-grade ore) into hematite.
Modifying Physical Structure
Beyond chemical changes, the furnace alters the physical architecture of the ore particles.
The rapid heating modifies the pore structure of the material. Simultaneously, it alters the magnetic characteristics of the ore. These physical changes are the "deep need" of the process, as they render the low-grade powder suitable for subsequent magnetic separation techniques.
Understanding Operational Context
Precision vs. Power
While Drop Tube Furnaces are capable of extreme heating rates (often used in combustion research for coal at rates up to $10^5$ K/s), this application requires restraint.
For iron ore beneficiation, the goal is not combustion or ignition, but controlled phase transformation. Therefore, the specific range of 30 to 50 °C/s is the operational sweet spot tailored to this material, avoiding over-sintering or vitrification.
The Importance of Residence Time
The efficiency of this system relies on the short duration of the treatment.
Because the process occurs during free fall, the reaction is instantaneous. This high throughput makes it efficient, but it also means the temperature zones must be perfectly calibrated. There is no "soak time" to correct for temperature fluctuations; the thermal shock must be immediate and uniform.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a Drop Tube Furnace for beneficiation, align your parameters with your specific separation targets.
- If your primary focus is Phase Transformation: Ensure the heating zones are calibrated strictly to the 30–50 °C/s rate to guarantee the complete conversion of goethite to hematite without degrading the material.
- If your primary focus is Separation Efficiency: Analyze the resulting pore structure and magnetic susceptibility to confirm that the "thermal shock" was sufficient to liberate the iron minerals from the gangue.
The Drop Tube Furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision reactor that uses gravity and thermal shock to upgrade the fundamental quality of low-grade ore resources.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification/Impact |
|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | High-precision Electrically Heated Zones |
| Heating Rate | 30 to 50 °C/s (Controlled Flash Heating) |
| Material State | Gravity-fed Free Fall |
| Chemical Reaction | Dehydroxylation (Goethite to Hematite) |
| Physical Change | Pore structure modification & magnetic enhancement |
| Primary Goal | Instantaneous phase transformation for separation |
Maximize Your Mineral Recovery with KINTEK Precision
Are you looking to optimize your low-grade ore processing? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Drop Tube Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific thermal-assisted beneficiation needs.
Our industrial-grade furnaces deliver the precise heating rates and uniform thermal shock required to transform goethite into hematite efficiently. Let our experts help you calibrate the perfect residence time and temperature profile for your unique materials.
Contact KINTEK Today to Upgrade Your Lab
Visual Guide
References
- Rebecca O’Hara, Alfonso Chinnici. Thermally Assisted Beneficiation of a Low-Grade Iron Ore Powder in a Pilot-Scale Drop Tube Reactor: Effects on Ore Upgrading, Mineralogy and Chemical-Physical Characteristics. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-025-03634-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using an Entrained Flow Reactor (EFR)? Achieve Industrial Scale Char Simulation
- What are the advantages of atmosphere control and high-temperature capabilities in a tube furnace? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the different types of tube furnaces available? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab's Needs
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the primary function of a Tube Furnace in converting PET to activated carbon? Achieve Precision Carbonization
- What is the mechanism of the drive-in process in a tube furnace? Master Dopant Redistribution with Nitrogen Shielding
- What are the common features of the heating chamber in a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What are some examples of applications for three-zone tube furnaces in advanced materials processing? Unlock Precision Thermal Control for Your Lab



















