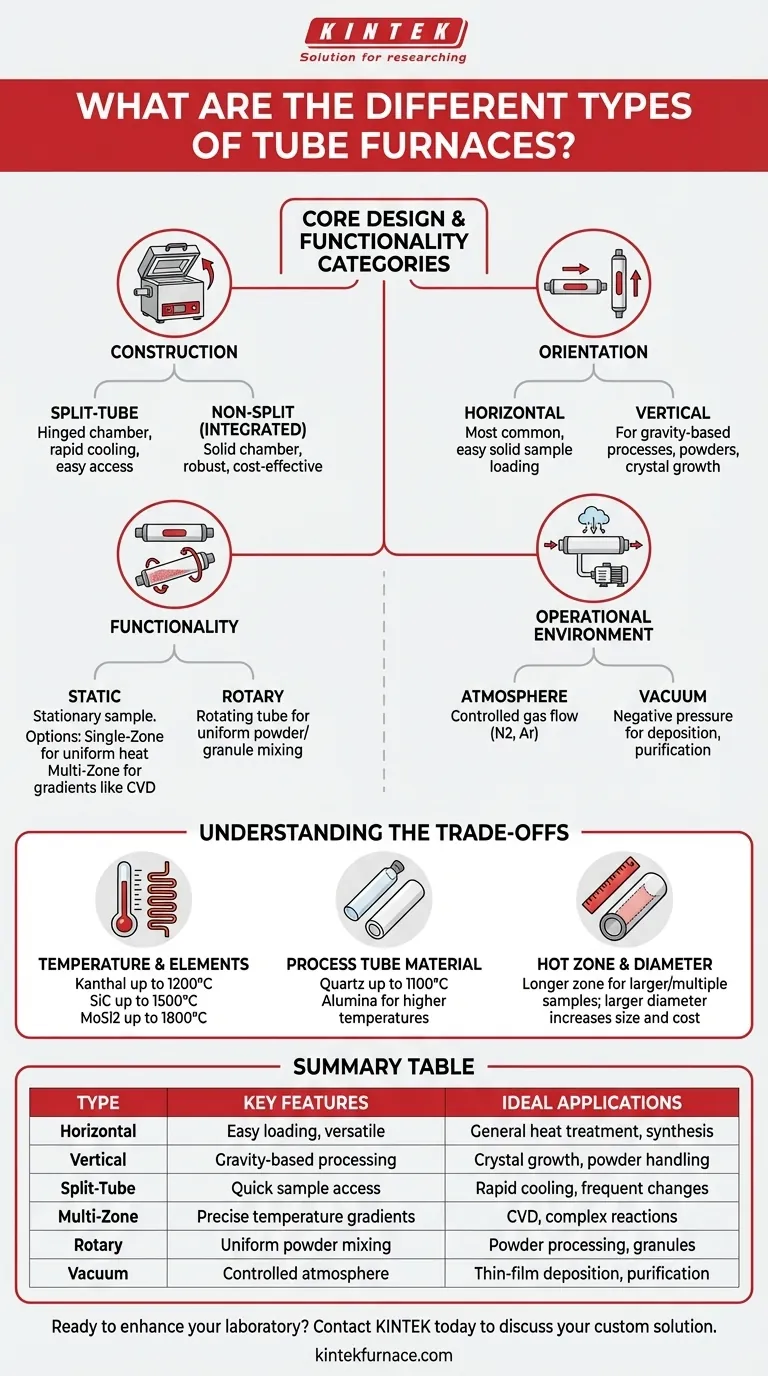
In essence, tube furnaces are categorized by their physical construction, sample handling capabilities, and the atmospheric environment they create. The main types are defined by their orientation (horizontal or vertical), construction (split-tube or non-split), functionality (static or rotary), and number of heating zones (single or multi-zone), each tailored for specific scientific processes.
The concept of a furnace "type" is a shorthand for a specific combination of design features. The critical task is not to choose a type, but to match the furnace's orientation, construction, thermal control, and atmospheric capabilities to the precise requirements of your application.

Core Design: How the Furnace is Built and Oriented
The most fundamental choice begins with the furnace's physical layout. This decision impacts how you interact with your sample and the types of processes you can run.
Split vs. Non-Split (Integrated) Construction
Split-tube furnaces feature a heating chamber that hinges open, splitting into two halves. This design allows the process tube to be placed or removed easily without disturbing the end seals and connected equipment. It is ideal for experiments requiring rapid cooling or frequent sample changes.
Non-split (or integrated) furnaces have a single, solid heating chamber. The process tube is inserted from one end. This design is generally simpler, more robust, and can be more cost-effective for standard, long-duration heating tasks.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Orientation
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration. Their primary advantage is ease of use for loading solid samples in boats or trays. They are versatile and suitable for a wide range of general-purpose heat treatment and synthesis applications.
Vertical furnaces are oriented upright. This design is superior for processes where gravity is a factor, such as preventing the "sagging" of materials at high temperatures, processing powders or liquids, or specific growth methods like the Bridgman technique for crystals.
Functional Types: How the Furnace Processes Samples
Beyond the basic structure, furnaces are differentiated by how they apply heat and handle the sample during the process.
Static Furnaces (Single and Multi-Zone)
This is the standard furnace where the sample remains stationary during heating. A single-zone furnace has one set of heating elements and one controller, providing a uniform hot zone in the center of the tube.
A multi-zone furnace has two, three, or more independent heating zones along the length of the tube, each with its own controller. This allows you to either create a longer, more precise uniform temperature zone or establish a controlled temperature gradient, which is essential for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Rotary and Oscillating Furnaces
Rotary furnaces continuously rotate the entire process tube. This tumbling action is critical for processing powders and granules, ensuring every particle is uniformly heated and exposed to the process atmosphere.
Oscillating furnaces provide a similar mixing function but do so by rocking back and forth rather than full rotation. This can be beneficial for more delicate materials or specific reaction kinetics.
Operational Environment: Controlling Atmosphere and Pressure
The final major classification relates to the environment inside the process tube, which is often the most critical variable in modern materials science.
Atmosphere Furnaces
This is the baseline capability for most tube furnaces. It involves flowing a controlled gas—such as nitrogen, argon, or a reactive gas mixture—through the tube to create a specific, non-oxidizing, or reactive environment for the sample.
Vacuum Furnaces
Vacuum furnaces are designed to operate under negative pressure. They use vacuum-tight seals and flanges to pump out the atmospheric air before heating. This is crucial for preventing unwanted reactions with oxygen or nitrogen and is a prerequisite for many thin-film deposition and purification processes. They can achieve different vacuum levels, from low vacuum to high vacuum (e.g., 10⁻⁵ torr).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with cost. The key specifications below are the primary drivers of this trade-off.
Temperature Range and Heating Elements
The maximum operating temperature dictates the heating element material. Kanthal (FeCrAl) elements are used for temperatures up to 1200°C. Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements reach up to 1500°C. For the highest temperatures, up to 1800°C, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are required. Higher temperature capability significantly increases cost.
Process Tube Material
The tube itself must withstand your process conditions. Quartz tubes are common, relatively inexpensive, and allow visual monitoring of the sample, but they are typically limited to about 1100°C. For higher temperatures, opaque ceramic tubes made of alumina are necessary.
Hot Zone and Tube Diameter
The hot zone is the length of the tube that maintains the set temperature. A longer hot zone allows for processing larger samples or multiple smaller samples at once. The tube diameter dictates the maximum size of your sample. Larger dimensions increase furnace size, power consumption, and overall cost.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be driven entirely by your experimental or production goals.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose material annealing or synthesis: A standard single-zone horizontal furnace with the appropriate temperature rating is your most versatile and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A multi-zone horizontal furnace is essential for creating the precise temperature gradients required for precursor decomposition and film growth.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of powders or granules: A rotary tube furnace is non-negotiable for ensuring process consistency and complete reaction.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample access or using complex, sealed apparatus: The convenience of a split-tube furnace will save significant time and effort.
Ultimately, the right tube furnace is the one whose features directly enable and control the critical variables of your process.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Furnace | Easy loading, versatile | General heat treatment, synthesis |
| Vertical Furnace | Gravity-based processing | Crystal growth, powder handling |
| Split-Tube Furnace | Quick sample access | Rapid cooling, frequent changes |
| Multi-Zone Furnace | Precise temperature gradients | CVD, complex reactions |
| Rotary Furnace | Uniform powder mixing | Powder processing, granules |
| Vacuum Furnace | Controlled atmosphere | Thin-film deposition, purification |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a tailored tube furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries



















