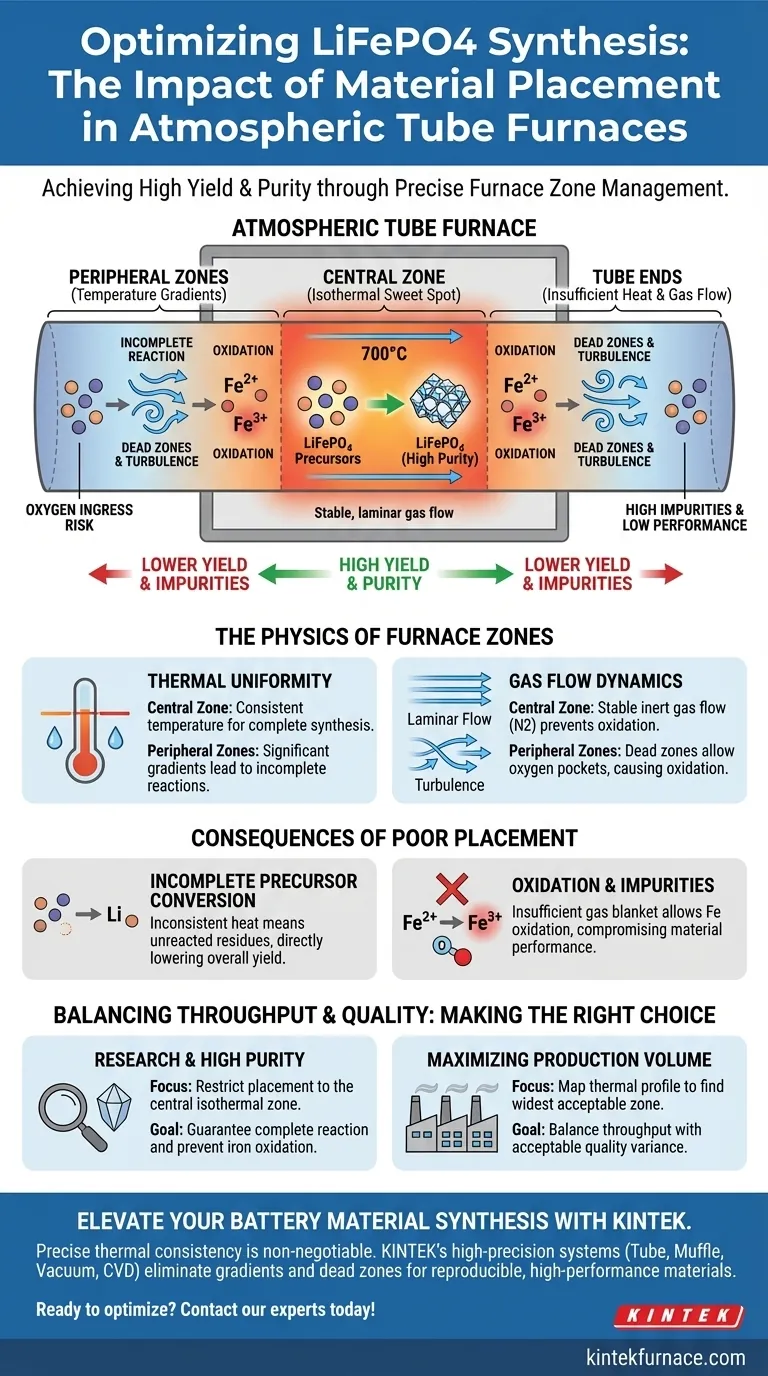
The placement of precursor materials within an atmospheric tube furnace is a decisive factor in the quality of synthesized lithium iron phosphate ($LiFePO_4$). Positioning materials in the furnace's central zone ensures they are exposed to the most uniform thermal field and stable gas flow, which are prerequisites for high yield and purity. Conversely, placing materials in the peripheral zones exposes them to temperature gradients and gas flow "dead zones," leading to incomplete reactions and lower-quality output.
Core Takeaway: Achieving high-purity lithium iron phosphate requires precise control over the reaction environment. By utilizing the central zone of the tube furnace, you maximize thermal consistency and gas flow stability, preventing the incomplete conversion and oxidation risks associated with peripheral placement.

The Physics of Furnace Zones
To understand why placement dictates yield, we must examine the internal environment of the furnace.
Thermal Uniformity
The central zone of the tube typically functions as the isothermal "sweet spot."
Here, the temperature remains consistent, reaching the necessary levels (often around 700°C) to drive the synthesis reaction.
Peripheral zones, located closer to the tube ends, suffer from significant temperature gradients. Materials placed here may not reach the target temperature required for the reaction to initiate or complete.
Gas Flow Dynamics
Atmospheric tube furnaces rely on a continuous flow of inert gas, typically Nitrogen.
This flow is necessary to exclude oxygen and create the specific atmospheric conditions required for synthesis.
The central zone generally benefits from stable, laminar gas flow. This ensures the precursors are constantly blanketed in the protective inert atmosphere, preventing unwanted side reactions.
Consequences of Poor Placement
Deviating from the central zone introduces variables that degrade the final product.
Incomplete Precursor Conversion
When materials sit in the peripheral zones, they often experience inconsistent heat energy.
This lack of thermal energy results in incomplete reactions.
Consequently, the final product will contain unreacted residues, directly lowering the overall yield of the desired lithium iron phosphate.
Oxidation and Impurities
The synthesis of $LiFePO_4$ is highly sensitive to oxidation.
You must prevent divalent iron ($Fe^{2+}$) from oxidizing to trivalent iron ($Fe^{3+}$) to maintain correct stoichiometry and electrochemical activity.
Peripheral zones are prone to gas flow dead zones where the nitrogen blanket may be insufficient. This allows oxygen pockets to linger, oxidizing the iron and introducing impurity phases that compromise the material's performance.
Balancing Throughput and Quality
While the central zone offers the best results, it presents a practical trade-off regarding production volume.
The Volume Constraint
Strictly limiting material placement to the center significantly reduces the usable volume of the furnace.
This restricts the batch size you can process in a single run.
Managing Uniformity Risks
Attempting to increase throughput by using the full length of the tube inevitably increases quality variance.
If you extend into the peripheral zones, you accept a higher probability of impurities and lower electrochemical performance in the outer edges of the batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your synthesis process, align your placement strategy with your specific output requirements.
- If your primary focus is research and high purity: Restrict sample placement strictly to the central isothermal zone to guarantee complete reaction and prevent iron oxidation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production volume: Map the thermal profile of your specific furnace to identify the widest possible zone that maintains acceptable temperature tolerances before loading.
Ultimately, treating the furnace geometry as a critical process variable is essential for producing reproducible, high-performance battery materials.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Zone | Thermal Field | Gas Flow Dynamics | Product Quality Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Zone | Uniform & Isothermal | Stable Laminar Flow | High Purity & Maximum Yield |
| Peripheral Zone | High Temp Gradients | Dead Zones/Turbulence | Incomplete Reaction & Oxidation |
| Tube Ends | Insufficient Heat | Oxygen Ingress Risk | High Impurities & Low Performance |
Elevate Your Battery Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal consistency is non-negotiable for high-performance lithium iron phosphate. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to eliminate temperature gradients and gas flow dead zones. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable furnace for unique research needs, our systems ensure reproducible results and superior material purity.
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency and output? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your synthesis goals.
Visual Guide
References
- Tengshu Chen, Liyao Chen. Research on the synthesis of lithium iron phosphate using vivianite prepared from municipal sludge. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-16378-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory tube furnace required for the phosphidation process? Master Precision Material Synthesis
- What types of heating elements are commonly used in drop tube furnaces? Find the Right Element for Your Temperature Needs
- What factors determine the selection of a three-zone split tube furnace? Key Specs for Precision Thermal Processing
- What is a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity for Powders & Granules
- How is the atmosphere controlled in a vacuum tube furnace? Achieve Precise Gas Environments for Your Experiments
- What are the common applications of quartz tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the technical significance of phased high-temperature annealing in a tube furnace for 3D Porous Graphene?
- What is a horizontal electric furnace designed for? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing in Controlled Environments



















