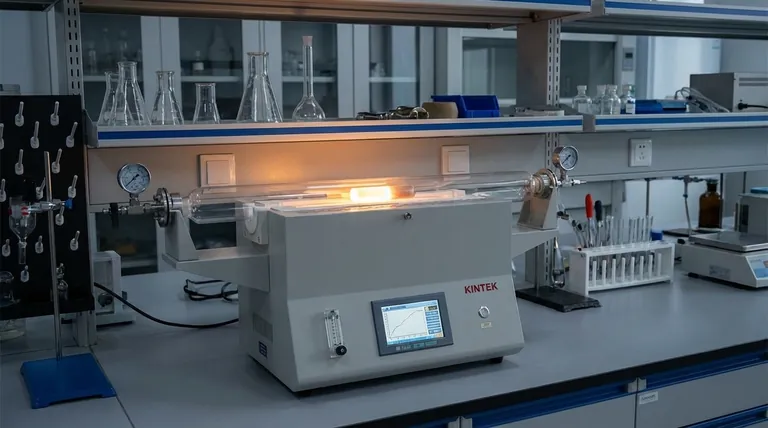
At their core, quartz tube furnaces are precision instruments for subjecting materials to a highly controlled, high-temperature environment. They are widely used across research and industry for tasks like heat-treating metals and ceramics, synthesizing new materials through chemical reactions, and preparing samples for analysis.
The decision to use a quartz tube furnace is not just about reaching a high temperature. It's about leveraging the unique combination of quartz's chemical purity, thermal stability, and optical transparency while respecting its inherent physical fragility and operational limits.

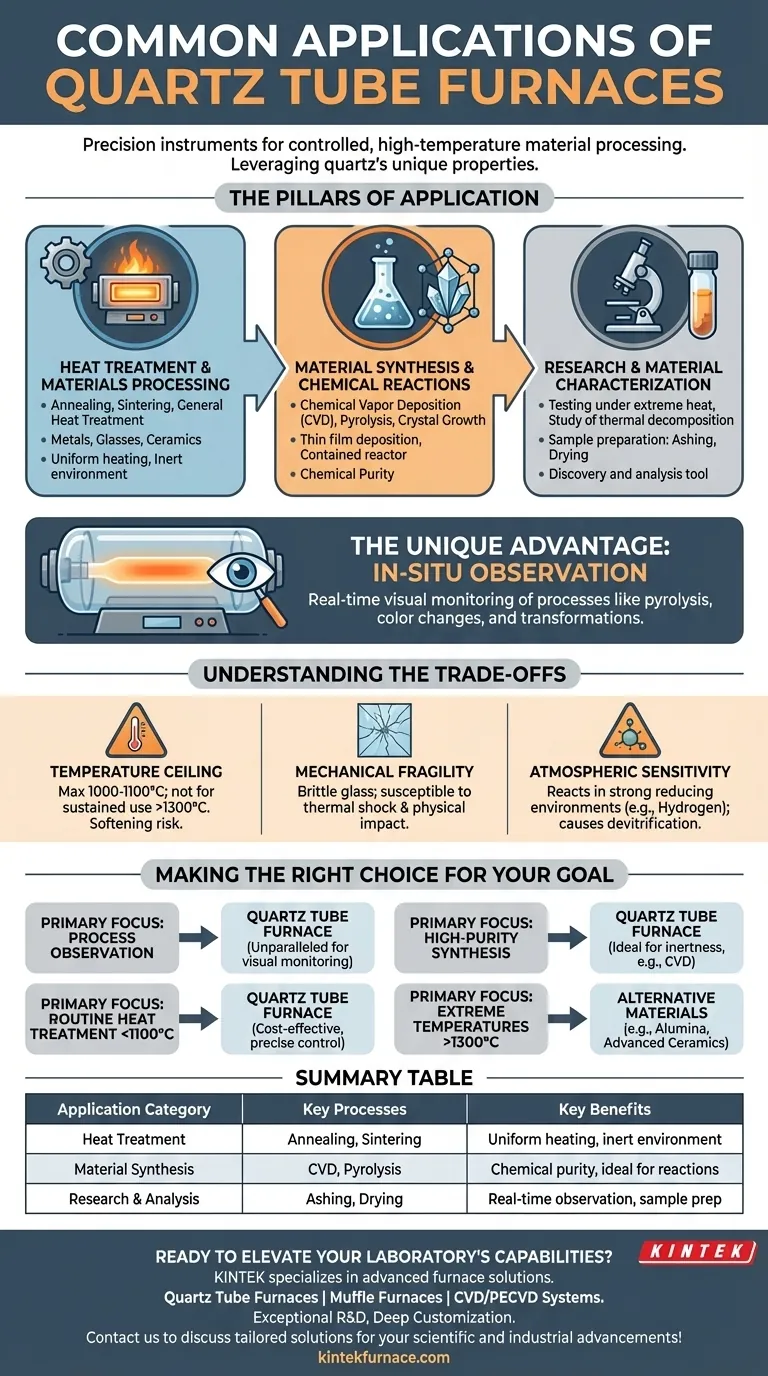
The Pillars of Application
The utility of a quartz tube furnace can be understood through its primary use cases, each of which leverages a specific set of its core properties.
Heat Treatment and Materials Processing
This is the most common application, focused on altering the physical properties of existing materials. The uniform heating and inert environment are critical.
Processes include annealing to increase ductility, sintering to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass, and general heat treatment of metals, specialty glasses, and ceramics to achieve desired characteristics.
Material Synthesis and Chemical Reactions
These furnaces provide an ideal, contained reactor for creating new materials from chemical precursors.
Applications like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) rely on the inert quartz surface to deposit thin films onto a substrate. It is also used for pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in an inert atmosphere) and growing high-purity crystals.
Research and Material Characterization
In a laboratory setting, a quartz tube furnace is an indispensable tool for discovery and analysis.
It is used to test a material's behavior under extreme heat, study thermal decomposition pathways, and prepare samples through processes like ashing (burning off organic matter) or drying.
The Unique Advantage: In-Situ Observation
Unlike opaque ceramic or metal furnaces, the transparency of quartz is a significant advantage.
This allows researchers and technicians to visually monitor the process in real-time. Observing color changes, melting, or transformations during pyrolysis provides invaluable qualitative data that would otherwise be impossible to capture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a quartz tube furnace is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is defined as much by its limitations as by its strengths. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for successful operation.
The Temperature Ceiling
Quartz begins to soften and can deform at very high temperatures. While it performs exceptionally well up to 1000-1100°C, it is generally not recommended for sustained use above 1300°C.
Exceeding this limit can compromise the structural integrity of the tube, affecting experimental accuracy and posing a safety risk.
Mechanical Fragility
Quartz is a glass, and as such, it is brittle. The tubes have low mechanical strength and are susceptible to cracking from thermal shock (rapid temperature changes) or physical impact.
Careful handling during installation, removal, and cleaning is non-negotiable to prevent breakage and ensure a long operational lifespan.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
While chemically inert in most situations, quartz can be affected by certain atmospheres at high temperatures.
Specifically, it can react in strong reducing environments (like hydrogen). This can cause the quartz to become brittle or devitrify over time, reducing its performance and lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right tool, align your primary goal with the furnace's core strengths and weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is process observation: A quartz tube furnace is unparalleled, allowing you to visually monitor reactions like pyrolysis or material transformations in real-time.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis: The chemical inertness of quartz makes it ideal for applications like CVD or crystal growth where contamination from the furnace tube itself must be avoided.
- If your primary focus is routine heat treatment below 1100°C: The combination of cost-effectiveness, precise temperature control, and chemical stability makes quartz an excellent choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (above 1300°C): You must consider alternative furnace tube materials like alumina or other advanced ceramics, as quartz will fail.
Understanding these capabilities and limitations empowers you to leverage the quartz tube furnace as a precise and powerful tool for scientific and industrial advancement.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Sintering | Uniform heating, inert environment |
| Material Synthesis | CVD, Pyrolysis | Chemical purity, ideal for reactions |
| Research & Analysis | Ashing, Drying | Real-time observation, sample prep |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Quartz Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—whether for heat treatment, material synthesis, or research. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your scientific and industrial advancements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















