Phased high-temperature annealing in a tube furnace is the decisive mechanism for activating the electrochemical and structural potential of three-dimensional porous graphene (3D PG) cathodes. By subjecting the material to a staged heating profile—specifically targeting 350 °C and 900 °C under a protective argon atmosphere—this process systematically purifies the cathode and fundamentally restores its atomic structure. It transforms a precursor composite into a highly conductive, mechanically robust electrode capable of withstanding the rigors of battery cycling.
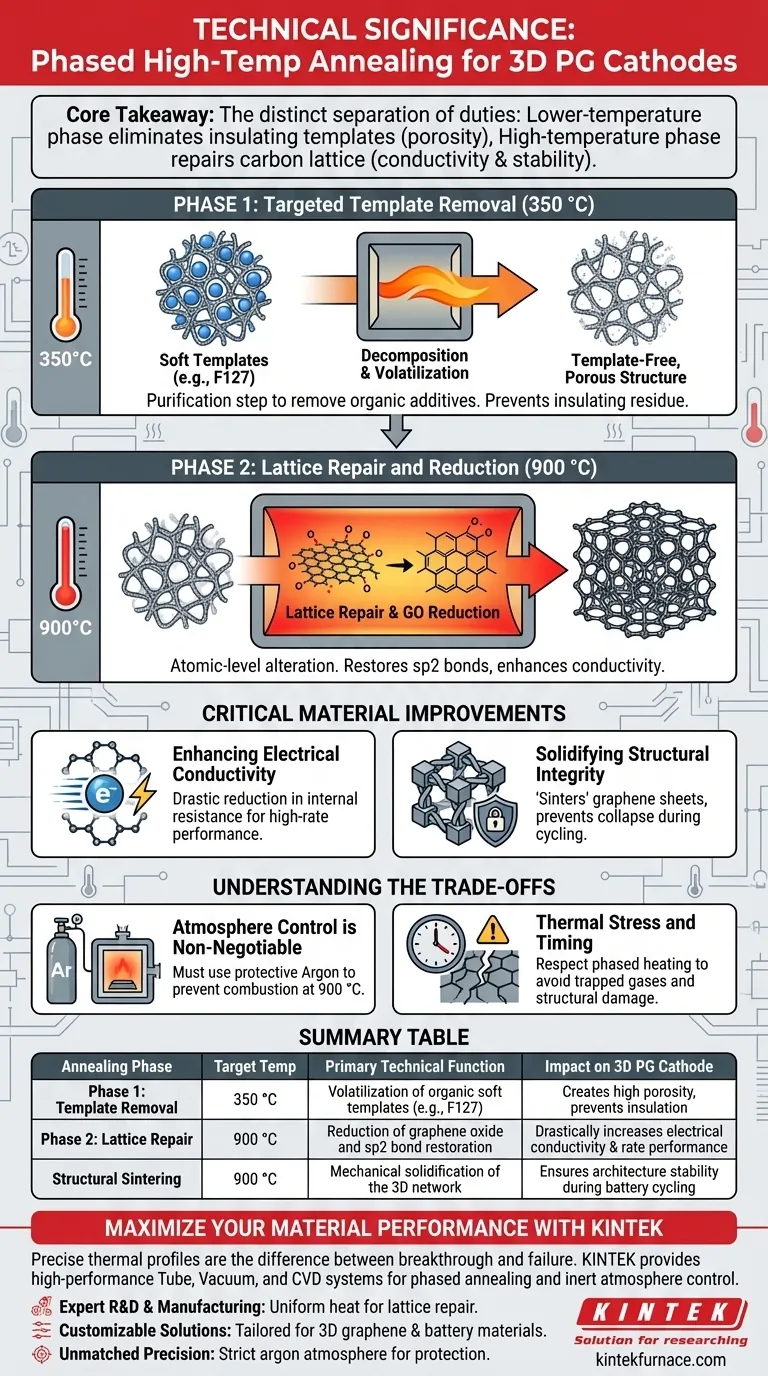
Core Takeaway: The technical significance lies in the distinct separation of duties: the lower-temperature phase eliminates insulating soft templates to create porosity, while the high-temperature phase repairs the carbon lattice to maximize conductivity and permanently lock in the 3D architecture.

The Mechanics of Phased Heating
Phase 1: Targeted Template Removal
The initial heating stage, typically set at 350 °C, is a purification step designed to remove soft templates, such as Pluronic F127.
At this temperature, organic additives used to shape the 3D structure are decomposed and volatilized. This is critical because any remaining organic residue acts as an insulator, impeding electron flow and reducing the active surface area of the cathode.
Phase 2: Lattice Repair and Reduction
Once the template is removed, the temperature is ramped up to 900 °C to alter the material at the atomic level.
This high-temperature phase drives the further reduction of graphene oxide components. More importantly, it provides the thermal energy necessary to heal defects in the carbon lattice, restoring the conjugated sp2 bond structure that is essential for high performance.
Critical Material Improvements
Enhancing Electrical Conductivity
The primary technical benefit of the 900 °C treatment is a drastic reduction in internal resistance.
By repairing the carbon lattice and removing oxygen functional groups, the process restores the intrinsic high conductivity of graphene. This facilitates rapid electron transport throughout the electrode, which is vital for high-rate battery applications.
Solidifying Structural Integrity
Beyond chemistry, this process serves a mechanical function by solidifying the three-dimensional porous network.
The high thermal treatment effectively "sinters" the graphene sheets, locking the porous architecture in place. This ensures the cathode maintains its structural stability and prevents collapse during the expansion and contraction cycles of battery operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Atmosphere Control is Non-Negotiable
This process relies entirely on a protective argon atmosphere to prevent combustion.
At 900 °C, carbon is highly reactive with oxygen. Without a strictly controlled inert environment, the graphene lattice would simply burn away rather than repair itself, destroying the cathode.
Thermal Stress and Timing
The "phased" nature of the heating is a constraint that must be respected to avoid structural damage.
Ramping too quickly to the high-temperature phase without allowing sufficient time at 350 °C for template removal can trap gases inside the structure. This can lead to structural cracking or exfoliation, undermining the mechanical stability the process aims to create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the post-treatment of 3D PG cathodes, align your thermal profile with your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Prioritize the duration and stability of the 900 °C phase to ensure maximum lattice repair and graphitization.
- If your primary focus is Porosity and Surface Area: ensure the 350 °C phase is sufficiently long to allow for the complete, gentle off-gassing of the Pluronic F127 template without disrupting the pore structure.
Success depends on balancing thorough purification at low temperatures with rigorous structural restoration at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Annealing Phase | Target Temperature | Primary Technical Function | Impact on 3D PG Cathode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Template Removal | 350 °C | Volatilization of organic soft templates (e.g., F127) | Creates high porosity and prevents insulation from residues |
| Phase 2: Lattice Repair | 900 °C | Reduction of graphene oxide and sp2 bond restoration | Drastically increases electrical conductivity and rate performance |
| Structural Sintering | 900 °C | Mechanical solidification of the 3D network | Ensures architecture stability during battery cycling |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal profiles are the difference between breakthrough research and material failure. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered to handle the rigorous demands of phased annealing and inert atmosphere control.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our furnaces deliver the thermal uniformity required to repair carbon lattices without structural stress.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored high-temp systems designed for 3D graphene, CNTs, and advanced battery materials.
- Unmatched Precision: Maintain strict argon atmospheres to protect your delicate 3D architectures.
Ready to optimize your 3D PG cathode production? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your unique laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Yanna Liu, Xiao Liang. Binder-Free Three-Dimensional Porous Graphene Cathodes via Self-Assembly for High-Capacity Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. DOI: 10.3390/nano14090754
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















