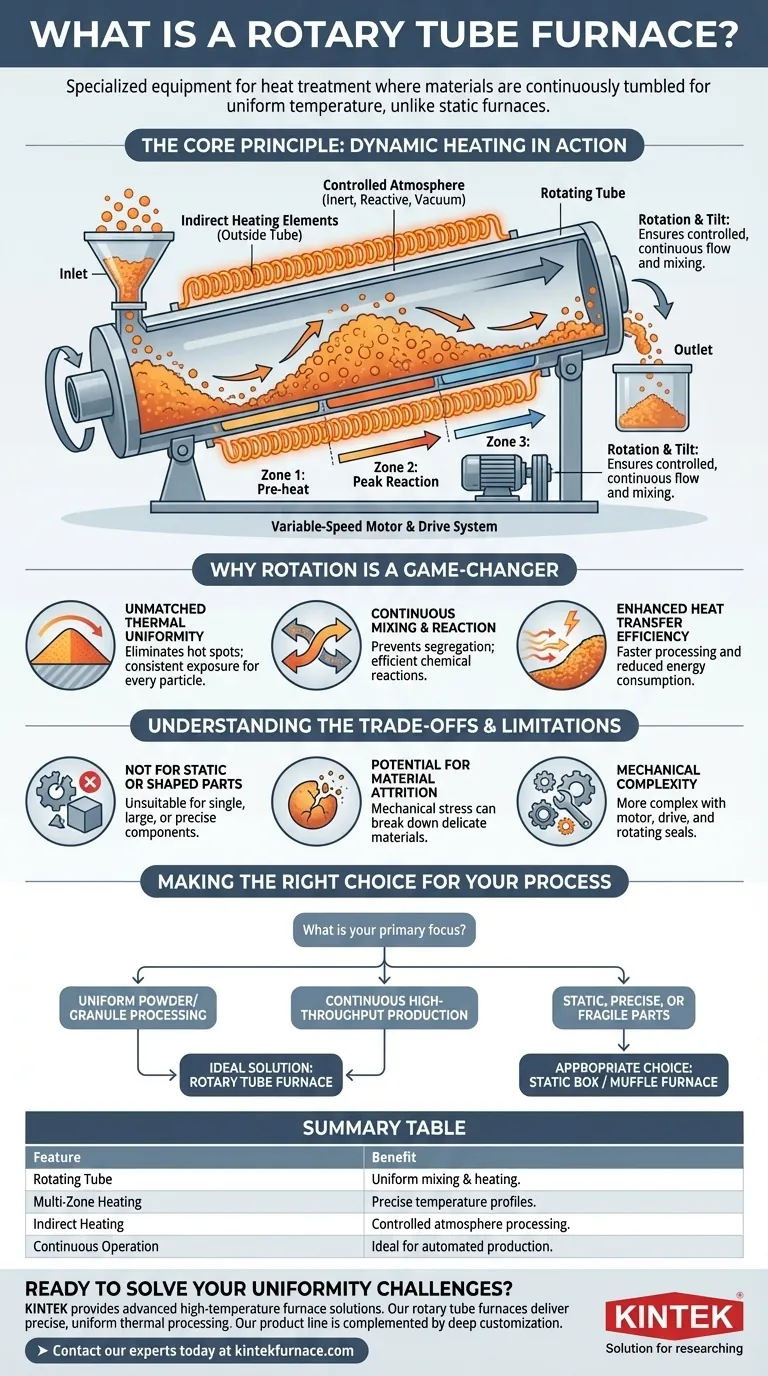
In materials science and industrial processing, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized piece of equipment designed for heat treatment where materials are continuously tumbled as they are heated. Unlike a static furnace, it uses a slowly rotating, often tilted, cylindrical tube to transport, mix, and ensure every part of the sample achieves a uniform temperature.
The core advantage of a rotary tube furnace is not just heating, but achieving exceptional thermal and compositional uniformity. Its continuous rotation is specifically engineered to solve the common problem of inconsistent processing in powders, granular materials, and slurries.
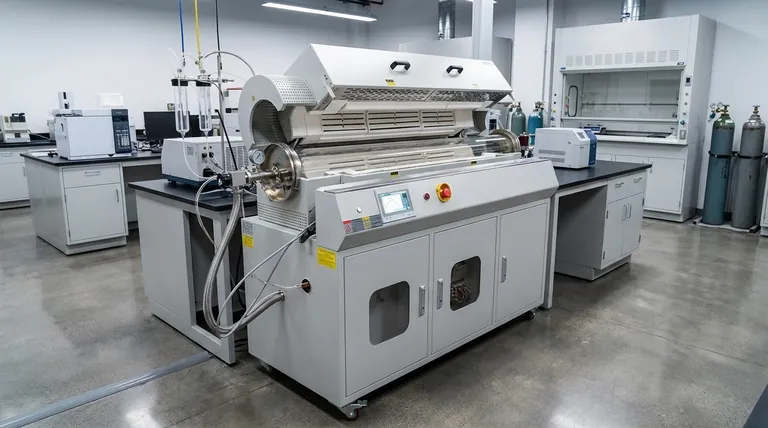

The Core Principle: Dynamic Heating in Action
A rotary tube furnace moves beyond simple static heating. Its design is centered on creating a dynamic environment that actively processes the material inside.
How It Works: Rotation and Tilt
A powerful, variable-speed motor drives the rotation of the central processing tube. This tube is typically mounted at a slight downward angle.
This combination of rotation and tilt causes the material—such as a powder or granule—to gently tumble and advance from the furnace's inlet to its outlet, ensuring a controlled and continuous flow.
The Role of Indirect Heating
The heating elements, often high-temperature coils, are positioned outside the rotating tube. This is known as an indirect-fired design.
This separation is critical because it allows the atmosphere inside the tube (e.g., inert gas, reactive gas, or a vacuum) to be precisely controlled without being contaminated by the heating source.
Precision Through Multi-Zone Control
Advanced rotary tube furnaces feature multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube.
This allows engineers to create a precise temperature profile. A material can be pre-heated, brought to a peak reaction temperature, and then cooled in a highly controlled sequence, all within the same continuous process.
Why Rotation Is a Game-Changer
The defining feature of this furnace—its rotation—directly addresses the inherent challenges of heating bulk materials.
Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
In a static furnace, a pile of powder will heat unevenly; the outside becomes much hotter than the insulated core.
The tumbling action of a rotary furnace constantly exposes new surfaces, ensuring every particle receives consistent exposure to the heat. This eliminates hot spots and temperature gradients, leading to a highly uniform final product.
Continuous Mixing and Reaction
For processes like powder metallurgy, coating, or chemical synthesis, constant mixing is essential.
Rotation prevents segregation of different materials and ensures that reactants are in continuous contact, driving chemical reactions to completion more efficiently.
Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency
The constant movement of the material bed significantly improves the efficiency of heat transfer from the tube wall into the material itself. This can result in faster processing times and reduced energy consumption compared to static batch processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized tool and not universally applicable. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Not for Static or Shaped Parts
This furnace is fundamentally designed for loose, flowable materials like powders, pellets, or granules. It is unsuitable for heat-treating single, large, or precisely shaped components that cannot be tumbled.
Potential for Material Attrition
The continuous tumbling action can be abrasive. For delicate, brittle, or friable materials, this mechanical stress can cause particles to break down, creating unwanted fines or dust.
Mechanical Complexity
The addition of a motor, drive system, and rotating seals introduces more mechanical complexity and maintenance requirements compared to a simple, static box furnace. These seals are critical for maintaining atmosphere integrity and are a key point of wear.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the nature of your material and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is processing powders, granules, or slurries uniformly: A rotary tube furnace is likely the ideal solution due to its superior mixing and heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-throughput production: The feed-through nature of these furnaces makes them highly effective for integrating into an automated industrial line.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating static, precisely shaped, or fragile parts: A static box, muffle, or standard (non-rotating) tube furnace is the appropriate choice.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary tube furnace is a decision to prioritize process uniformity and consistency for materials that benefit from dynamic heating.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Ensures uniform mixing and heating of powders/granules. |
| Multi-Zone Heating | Allows precise temperature profiles (pre-heat, react, cool). |
| Indirect Heating | Enables controlled atmosphere (inert, reactive, vacuum) processing. |
| Continuous Operation | Ideal for high-throughput, automated industrial production lines. |
Ready to Solve Your Uniformity Challenges?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our rotary tube furnaces are engineered to deliver the precise, uniform thermal processing your powders, granules, or slurries require.
Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental or production requirements.
➤ Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary tube furnace can enhance your process consistency and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the CVD of Si-SiO2 composites? Achieve Precise Nanostructure Control
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials
- Why is a secondary high-temperature activation in a tubular furnace required? Unlock Peak Catalyst Performance
- What are the limitations of tube furnaces when handling larger samples? Overcome Size and Heat Transfer Challenges
- How does high-temperature tube furnace programmed control influence porous carbon? Expert Pore Geometry Insights
- What accessories are typically included with a three-zone split tube furnace? Essential Tools for Safe Operation
- Why is a continuous nitrogen flow required in a closed tube furnace during the solid-phase synthesis of LiMnO2 precursors?



















