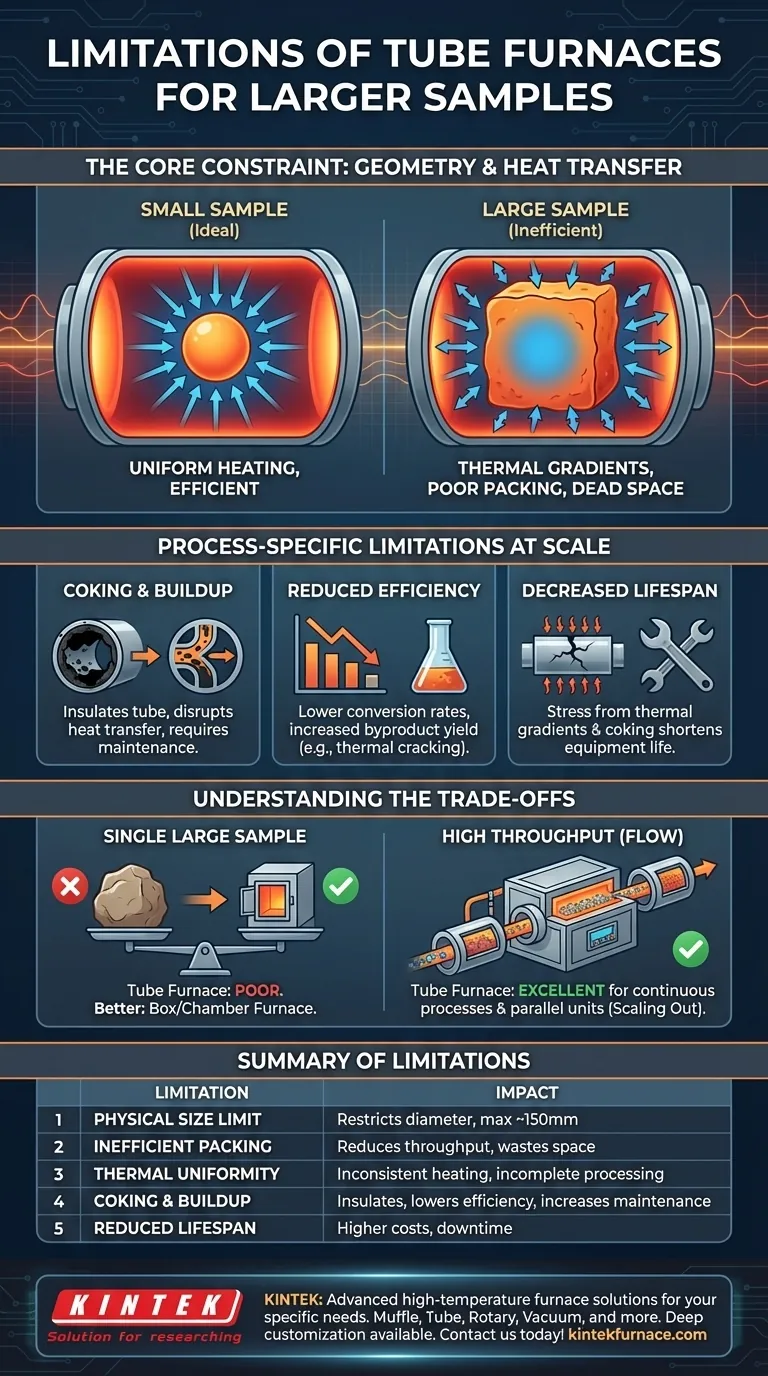
The fundamental limitation of a tube furnace for larger samples is its geometry. The cylindrical shape and fixed diameter impose a hard physical limit on sample size and create significant challenges in achieving uniform heat transfer, especially as you attempt to process bulkier materials or larger volumes.
While tube furnaces can be scaled for high-throughput industrial production, this is achieved by running continuous processes or using multiple units in parallel. They are inherently ill-suited for processing a single, physically large, or bulky solid sample due to geometric and thermal inefficiencies.
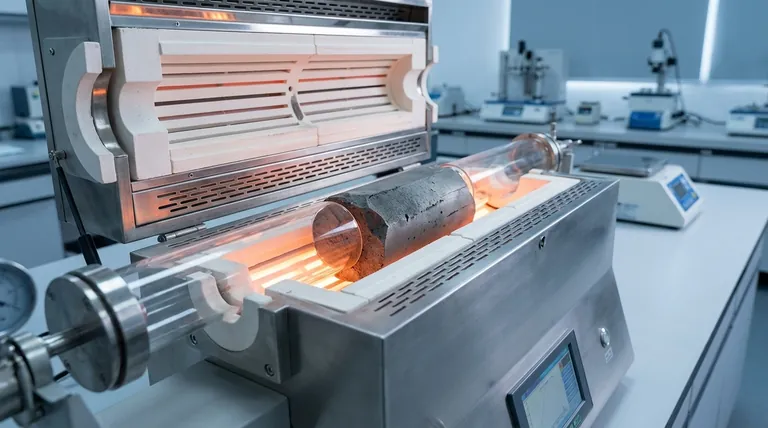

The Core Constraint: Geometry and Heat Transfer
The design that makes a tube furnace perfect for controlled atmospheres and uniform heating of small samples becomes its primary weakness when size increases.
The Inherent Size Limit of the Tube
The most obvious limitation is the physical boundary of the tube. While "large volume" models exist, they are still restrictive, with diameters often topping out around 6 inches (150 mm). This immediately disqualifies any sample that will not physically fit within these dimensions.
Inefficient Packing and "Dead Space"
For bulk solids or powders, a cylindrical shape is inefficient. It leads to poor packing density compared to a rectangular chamber, meaning less material can be processed per unit of heated volume. This "dead space" wastes energy and reduces overall throughput.
The Challenge of Thermal Uniformity
As the tube diameter increases, it becomes exponentially harder to heat the sample's core uniformly. Heat must radiate from the furnace walls inward, and a larger sample mass creates a significant thermal gradient. The center of the sample will lag in temperature, potentially leading to incomplete or inconsistent processing.
This issue is magnified by the tube material itself. Materials like stainless steel have lower thermal conductivity than quartz or ceramic, making it even more difficult to achieve a uniform temperature profile across a large-diameter sample.
Process-Specific Limitations at Scale
Pushing a tube furnace beyond its intended sample size doesn't just reduce efficiency; it can actively harm the process and the equipment. This is clearly seen in applications like the thermal cracking of heavy materials.
Coking and Material Buildup
When processing larger volumes of organic or heavy materials, side reactions and incomplete processing become more common. This can lead to coking, where carbonaceous deposits build up on the tube's inner walls. This buildup acts as an insulator, further disrupting heat transfer and shortening the effective work cycle.
Reduced Processing Efficiency
The direct consequence of poor heat transfer and coking is a less effective process. For thermal cracking, this means a lower cracking depth, resulting in lower utilization of the raw material and an increased yield of low-value byproducts like heavy oil. Your process becomes less productive and less profitable.
Decreased Equipment Lifespan
Coking and extreme thermal gradients place significant stress on the furnace tube. This can shorten the lifespan of the tube and even damage the heating elements of the furnace itself, leading to increased maintenance costs and operational downtime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use a tube furnace for larger-scale work involves navigating critical trade-offs, especially regarding the difference between sample size and overall throughput.
Throughput vs. Sample Size
It is crucial to distinguish between processing a single large sample and achieving high throughput. Tube furnaces are generally poor for the former but can be excellent for the latter. Their ability to operate continuously makes them ideal for processing steady flows of gases, liquids, or powders.
Scaling Out, Not Scaling Up
The references mentioning "large-scale industrial applications" are referring to scaling out. Instead of building one massive tube furnace, operations use multiple, modular tube furnaces running in parallel. This maintains the process control benefits of a small-diameter tube while achieving high total output.
Tube Material Constraints
The choice of tube material (e.g., quartz, alumina, stainless steel) becomes more critical with larger samples. A material that is chemically inert and has excellent thermal conductivity at your target temperature is essential for success. Using the wrong material, like stainless steel for very high-temperature pyrolysis, can lead to chemical reactions with the sample or poor temperature control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right equipment, you must be clear about what "larger" means for your specific process.
- If your primary focus is processing a single, large solid object: A tube furnace is the wrong tool. You should strongly consider a box or chamber furnace, which provides the necessary volume and more uniform heating for bulk items.
- If your primary focus is high throughput of flowing gases, liquids, or powders: A continuous-flow tube furnace system is an excellent choice that leverages the design's core strengths.
- If your primary focus is processing many small, discrete batches: A large-diameter tube furnace or a setup with multiple smaller furnaces running in parallel can be a highly effective solution.
- If your process involves materials prone to coking or off-gassing: Carefully evaluate the tube diameter and material, as a smaller diameter often provides better control and more efficient operation.
Understanding these constraints allows you to select the thermal processing tool that ensures the efficiency, accuracy, and reliability your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| Physical Size Limit | Restricts sample diameter, often max ~150mm |
| Inefficient Packing | Reduces throughput with wasted space |
| Thermal Uniformity Issues | Causes inconsistent heating and incomplete processing |
| Coking and Buildup | Insulates tube, lowers efficiency, increases maintenance |
| Reduced Equipment Lifespan | Leads to higher costs and downtime |
Struggling with tube furnace limitations for large samples? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















