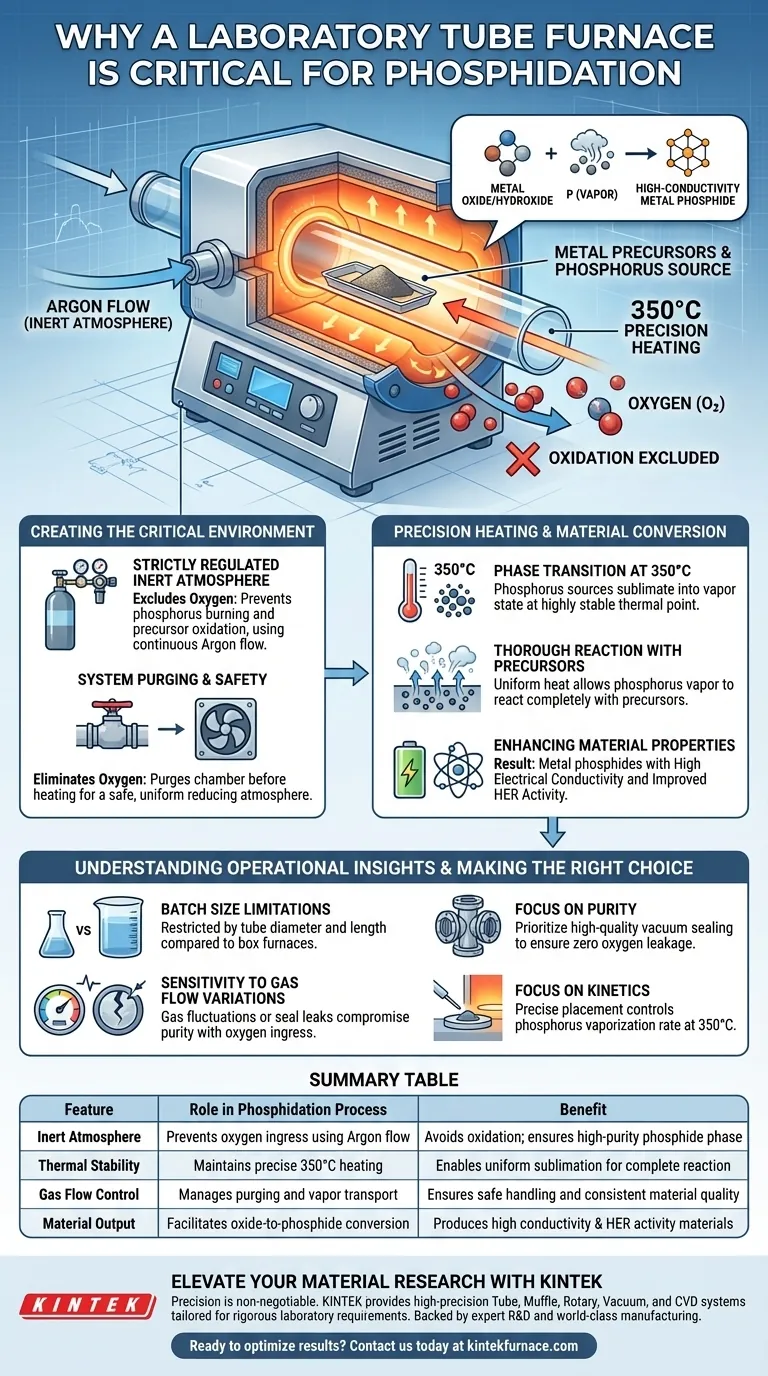
A laboratory tube furnace is required for phosphidation because it creates a strictly regulated, inert environment that allows phosphorus vapor to react with metal precursors without oxidizing. This specific apparatus simultaneously manages gas flow and precise heating, which are the two critical variables for successful conversion.
The tube furnace facilitates the conversion of metal oxides or hydroxides into high-conductivity metal phosphides by maintaining a strictly regulated argon atmosphere at 350°C. This ensures thorough reaction with phosphorus vapor while completely preventing oxidation.

Creating the Critical Reaction Environment
Strictly Regulated Inert Atmosphere
The primary function of the tube furnace in this context is atmosphere control. Phosphidation requires the exclusion of oxygen to prevent the phosphorus from burning or the metal from oxidizing further.
By utilizing a sealed tube design, the furnace allows for the continuous flow of inert gases, such as argon.
System Purging and Safety
Before the heating process begins, the tube furnace enables system purging. This step eliminates existing oxygen from the chamber using inert or reducing gases.
This creates a uniform reducing atmosphere, which is safer and chemically necessary when handling volatile components like phosphorus.
Precision Heating and Material Conversion
Enabling Phase Transition at 350°C
The primary reference indicates that the phosphidation process typically occurs at 350 degrees Celsius. The tube furnace maintains this temperature with high stability.
At this specific thermal point, solid phosphorus sources sublimate into phosphorus vapor.
Thorough Reaction with Precursors
Once the phosphorus is in a vapor state, it must permeate the metal precursor. The furnace ensures the heat is applied uniformly, allowing the vapor to react thoroughly with metal oxide or hydroxide precursors.
This complete reaction is vital for converting the precursors into metal phosphides.
Enhancing Material Properties
The goal of this conversion is to enhance the physical properties of the material. The controlled environment results in phosphides with high electrical conductivity.
Furthermore, these optimized materials demonstrate improved Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER) activity, a critical metric for catalytic applications.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Batch Size Limitations
While tube furnaces offer precision, they are inherently limited by the diameter and length of the tube. This restricts the volume of material you can process in a single batch compared to larger box furnaces.
Sensitivity to Gas Flow Variations
The success of the process relies heavily on the integrity of the gas flow. If the inert gas supply fluctuates or the tube seals leak, oxygen ingress will immediately compromise the purity of the phosphide phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a tube furnace for phosphidation, consider your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is material purity: Prioritize a furnace with high-quality vacuum sealing flanges to ensure zero oxygen leakage during the argon purge.
- If your primary focus is reaction kinetics: Focus on the precise placement of the phosphorus source relative to the heating zone to control the rate of vaporization at 350°C.
A tube furnace is not just a heater; it is a chemical reactor that precisely aligns thermodynamics and atmosphere to engineer high-performance metal phosphides.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Phosphidation Process | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents oxygen ingress using Argon flow | Avoids oxidation; ensures high-purity phosphide phase |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains precise 350°C heating | Enables uniform sublimation of phosphorus for complete reaction |
| Gas Flow Control | Manages purging and vapor transport | Ensures safe handling of phosphorus and consistent material quality |
| Material Output | Facilitates oxide-to-phosphide conversion | Produces materials with high conductivity and HER activity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing high-performance metal phosphides. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for rigorous laboratory requirements. Our customizable high-temperature furnaces ensure the strictly regulated environments necessary for your most sensitive chemical processes.
Ready to optimize your phosphidation results? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution and leverage our expertise in advanced thermal processing.
Visual Guide
References
- Yu Gao, Xiaoteng Liu. In situ growth of three-dimensional walnut-like nanostructures of W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for water decomposition. DOI: 10.1007/s42114-024-01176-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do three-zone furnaces offer? Achieve Superior Temperature Control and Efficiency
- In what ways is a vertical tube furnace flexible and diverse? Unlock Custom Solutions for Your Lab
- How are tubular furnaces utilized in semiconductor manufacturing? Precision Thermal Processing for High-Yield ICs
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace required during Fe-Mn catalyst synthesis? Control Morphology and CNF Quality
- Why is it necessary to integrate aluminum alloy plates into split tube furnace covers? Ensure Safety and Longevity
- What types of atmospheres can be controlled in a drop tube furnace? Master Precise Gas Control for Superior Materials
- How do advanced control systems enhance the operation of a tube furnace? Boost Precision and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What role does a tube furnace play within a fixed-bed adsorption system? Expert Se/PPS Performance Evaluation Guide



















