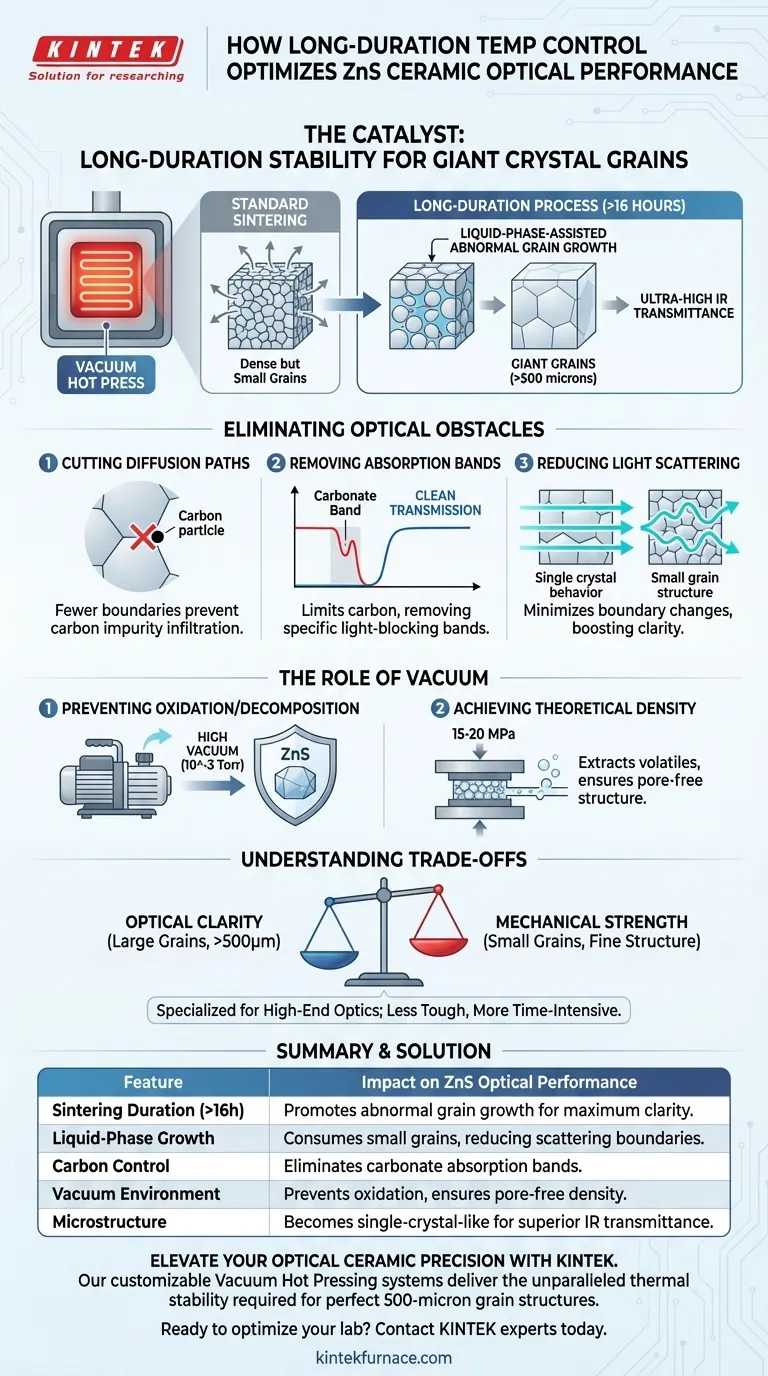
Long-duration temperature control acts as the catalyst for creating exceptionally large crystal grains, which is the defining factor in high-performance optical ceramics. By maintaining precise, stable heat for extended periods (often exceeding 16 hours), a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitates "liquid-phase-assisted abnormal grain growth." This process expands the grains to sizes greater than 500 microns, drastically reducing the density of grain boundaries that typically act as barriers to light and pathways for impurities.
The superior optical clarity of Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) ceramics is not just about density; it is about microstructure architecture. Extended thermal stability eliminates the grain boundaries that trap carbon impurities, directly removing absorption bands and maximizing infrared transmittance.

The Physics of Optical Enhancement
Liquid-Phase-Assisted Growth
To achieve optical-grade transparency, the ceramic microstructure must evolve beyond the standard sintered state. Long-duration heating triggers a specific phenomenon known as liquid-phase-assisted abnormal grain growth. This mechanism allows individual grains to consume their neighbors, growing significantly larger than they would under standard sintering schedules.
Reaching the 500-Micron Threshold
The primary goal of this extended cycle is to push grain size beyond 500 microns. Standard sintering might yield dense materials, but they often retain smaller grain structures. The vacuum hot press must possess high stability to hold temperatures constant long enough for this massive microstructural shift to occur without thermal fluctuation.
Minimizing Grain Boundaries
The geometric result of larger grains is a massive reduction in the total area of grain boundaries per volume. Grain boundaries are essentially defects where the crystal lattice is interrupted. Fewer boundaries mean the material behaves more like a single crystal, providing a clearer path for light waves.
Eliminating Optical Obstacles
Cutting Off Diffusion Paths
Grain boundaries act as highways for impurities, specifically allowing carbon to diffuse through the material. By reducing the number of boundaries, you effectively cut off these diffusion paths. This prevents carbon from settling within the ceramic structure, which is critical for optical purity.
Removing Carbonate Absorption Bands
When carbon infiltrates the ceramic, it creates "carbonate absorption bands" that block specific wavelengths of light. The long-duration heat treatment, by limiting carbon diffusion, eliminates these specific absorption bands. This results in a "cleaner" transmission spectrum, particularly in the infrared range.
Reducing Light Scattering
Every grain boundary represents a change in refractive index that can scatter light. By growing grains to >500 microns, the frequency of these scattering events drops precipitously. This reduction in scattering is the primary driver for the substantial enhancement in overall infrared transmittance.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Preventing Oxidation and Decomposition
While temperature controls the grain structure, the vacuum environment protects the chemistry. High vacuum (e.g., 10^-3 Torr) is mandatory to prevent ZnS from oxidizing or decomposing at these sustained high temperatures. Without this vacuum protection, the long duration required for grain growth would simply destroy the material.
Achieving Theoretical Density
Vacuum hot pressing applies simultaneous pressure (e.g., 15-20 MPa) to rearrange particles and induce plastic flow. The vacuum assists this by extracting volatiles and trapped gases from the powder interstices. This ensures that the final "large grain" structure is free of micro-pores, which are another major source of light scattering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optical vs. Mechanical Properties
There is often an inverse relationship between grain size and mechanical strength. While abnormal grain growth (>500 microns) is excellent for optical transmission, large grains can make the ceramic mechanically weaker or more brittle compared to fine-grained structures. You are essentially trading structural toughness for optical perfection.
Process Efficiency
The requirement for constant temperature sintering over 16+ hours represents a significant increase in cycle time and energy consumption. This process is specialized for high-end optical applications and is less efficient than standard densification cycles used for structural ceramics. Standard VHP cycles typically aim to suppress excessive grain growth to save time and boost strength; this long-duration process deliberately reverses that logic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your Zinc Sulfide ceramic production, you must align your furnace parameters with your specific performance criteria:
- If your primary focus is Infrared Transmittance: Prioritize long-duration stability (>16 hours) to encourage abnormal grain growth and eliminate carbon diffusion paths.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Utilize standard, shorter VHP cycles that suppress grain growth to maintain a fine, tough microstructure.
- If your primary focus is Defect Elimination: Ensure your vacuum levels remain high (10^-3 Torr) throughout the cycle to extract volatiles and prevent oxidation.
The ultimate quality of an optical window is determined not just by the material, but by the precise thermal history you impose upon it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on ZnS Optical Performance |
|---|---|
| Sintering Duration (>16h) | Promotes abnormal grain growth (>500 microns) for maximum clarity. |
| Liquid-Phase Growth | Consumes small grains to reduce light-scattering boundaries. |
| Carbon Control | Limits diffusion paths to eliminate carbonate absorption bands. |
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and extracts volatiles to reach theoretical density. |
| Microstructure | Transforms ceramic to behave like a single crystal for IR transmittance. |
Elevate Your Optical Ceramic Precision with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect 500-micron grain structure for high-performance ZnS optics requires more than just heat—it requires unparalleled thermal stability and vacuum integrity.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including advanced Vacuum Hot Pressing furnaces. Our systems are fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of long-duration sintering, ensuring you can eliminate carbon impurities and maximize infrared transmittance without compromise.
Ready to optimize your lab’s high-temperature processes? Contact our technical experts today to discuss your unique needs and discover the KINTEK advantage.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the heating mechanism of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) function? Enhance TiC/SiC Composite Fabrication
- What are the advantages of using a HIP sintering system over conventional sintering for Bismuth Telluride composites?
- What is the core advantage of using a Hot Pressing Sintering (HPS) furnace? Enhance SiC/YAG Ceramic Density & Strength
- How does vacuum hot pressing compare to vacuum brazing and sintering? Choose the Right Process for Your Materials
- What role does SPS equipment play in half-Heusler fabrication? Mastering Density and Microstructure for Thermoelectrics
- What are the benefits of the high vacuum environment in a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Gain Maximum Density
- What is a hot press machine used for? From custom apparel to aerospace components
- What is the difference between hot pressing and sintering? Choose the Right Process for Your Materials



















