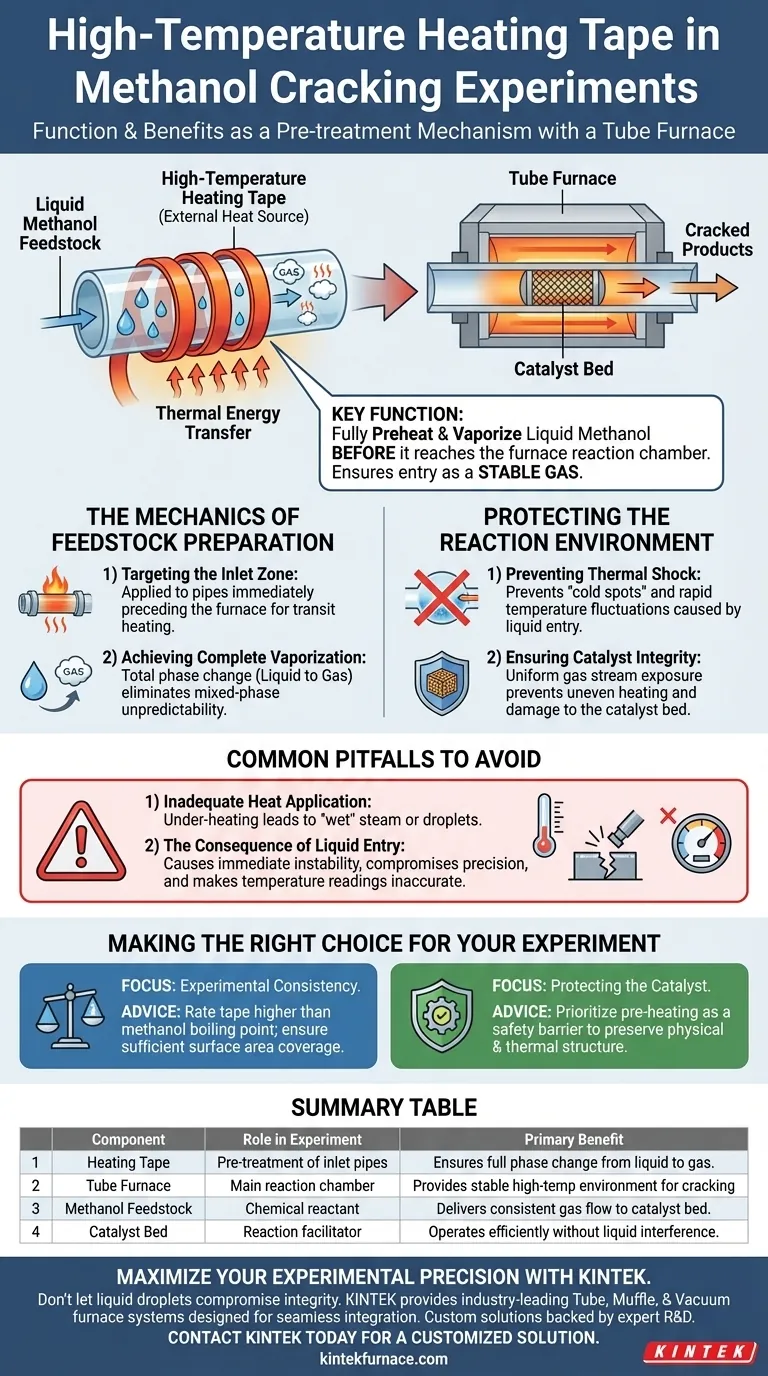
High-temperature heating tape functions as a critical pre-treatment mechanism for the methanol feedstock. It acts as an external heat source wrapped directly around the inlet pipes leading into the tube furnace. Its specific purpose is to fully preheat and vaporize liquid methanol before it ever reaches the main reaction chamber.
The heating tape guarantees that the feedstock enters the tube furnace as a stable gas rather than a liquid. This prevents liquid droplets from reaching the catalyst bed, which is essential for maintaining thermal stability and reaction uniformity.

The Mechanics of Feedstock Preparation
Targeting the Inlet Zone
The heating tape is applied to the piping immediately preceding the furnace. This allows the system to impart thermal energy to the methanol while it is still in transit.
Achieving Complete Vaporization
The primary objective is a total phase change. The methanol must transition from a liquid state to a gaseous state before entering the furnace.
This ensures that the material entering the high-temperature zone is consistent. It eliminates the unpredictability associated with mixed-phase flows (slugs of liquid mixed with gas).
Protecting the Reaction Environment
Preventing Thermal Shock
If liquid methanol enters the hot zone of a tube furnace, it absorbs a massive amount of heat instantly to vaporize.
This rapid absorption creates "cold spots" or local temperature fluctuations. The heating tape prevents this by ensuring the phase change energy is consumed outside the critical reaction zone.
Ensuring Catalyst Integrity
The tube furnace relies on a stable environment for the catalyst to function.
Liquid droplets hitting the catalyst bed can cause uneven heating. By vaporizing the feedstock externally, the tape ensures the catalyst is exposed only to a uniform gas stream, maximizing efficiency.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Inadequate Heat Application
The most significant risk is under-heating the inlet tape. If the tape does not generate enough thermal energy for the specific flow rate of methanol, "wet" steam or droplets may still pass through.
The Consequence of Liquid Entry
Failure to fully vaporize the methanol leads to immediate instability. The primary reference notes that liquid entry directly causes local temperature fluctuations.
This compromises the precision of the tube furnace, rendering the temperature controller's readings inaccurate for the specific localized area where the liquid hit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
If your primary focus is experimental consistency: Ensure the heating tape is rated for a temperature significantly higher than the boiling point of methanol and covers enough surface area of the inlet pipe to ensure total heat transfer.
If your primary focus is protecting the catalyst: Prioritize the pre-heating stage as a safety barrier; preventing liquid contact preserves the physical and thermal structure of your catalyst bed.
Proper utilization of heating tape transforms the feedstock from a variable liquid into a predictable gas, securing the baseline for a successful cracking experiment.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Experiment | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Tape | Pre-treatment of inlet pipes | Ensures full phase change from liquid to gas |
| Tube Furnace | Main reaction chamber | Provides stable high-temp environment for cracking |
| Methanol Feedstock | Chemical reactant | Delivers consistent gas flow to catalyst bed |
| Catalyst Bed | Reaction facilitator | Operates efficiently without liquid interference |
Maximize Your Experimental Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let liquid droplets compromise your catalyst integrity or thermal stability. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, and Vacuum furnace systems designed to integrate seamlessly with your pre-heating protocols. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our high-temp solutions are fully customizable to meet the unique demands of methanol cracking and other advanced chemical processes.
Ready to elevate your lab's performance? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yankun Jiang, Siqi Li. Sustainable Hydrogen from Methanol: NiCuCe Catalyst Design with CO2-Driven Regeneration for Carbon-Neutral Energy Systems. DOI: 10.3390/catal15050478
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What core physical conditions does a tube furnace provide in the two-step synthesis of WS2? Master Film Growth
- What are the options for zonal heating in horizontal tube furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Control
- How does a vacuum tube type experimental electric furnace work? Master Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- Why is a quartz tube fixed-bed reactor ideal for VOC/Hydrogen combustion? Unlock High-Temp Precision & Stability
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in biomass-derived carbon? Unlock Advanced Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What core functions does an argon atmosphere tube furnace perform? Optimize Al-PTFE FGM Sintering
- What steps are involved in the installation of a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety for Your Lab



















