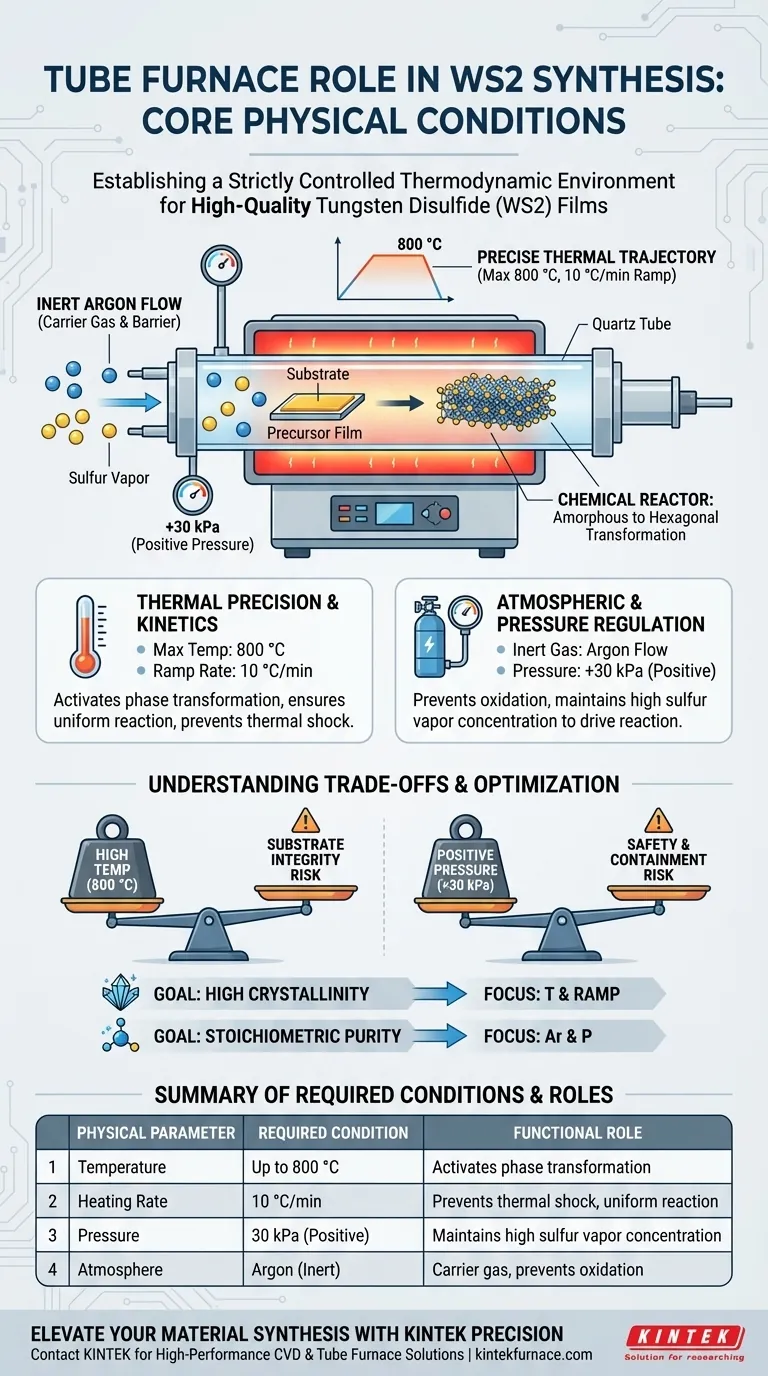
The tube furnace establishes a strictly controlled thermodynamic environment essential for converting precursor films into high-quality Tungsten Disulfide (WS2). It provides three specific physical conditions: a precise thermal trajectory reaching temperatures up to 800 °C, a regulated positive pressure environment (typically 30 kPa above atmospheric), and a consistent inert gas flow (argon) to drive the sulfurization reaction.
Core Insight The tube furnace does not merely heat the material; it acts as a chemical reactor that forces the phase transformation of amorphous precursors. By strictly controlling pressure and temperature, it facilitates the growth of hexagonal WS2 with a specific (00L) crystalline orientation.

Thermal Precision and Reaction Kinetics
Precise Temperature Control
The primary function of the furnace is to reach and maintain high temperatures, specifically around 800 °C for this synthesis.
This high thermal energy is required to activate the chemical reaction between the solid precursor films and the sulfur vapor. Without achieving this specific threshold, the activation energy for the phase transformation cannot be met.
Programmed Heating Rates
It is not enough to simply reach the target temperature; the rate of heating is equally critical.
The equipment utilizes programmed ramping, such as 10 °C/min. This controlled rise prevents thermal shock to the substrate and ensures the precursor reacts uniformly with the sulfur vapor as the temperature climbs.
Atmospheric and Pressure Regulation
Controlled Inert Atmosphere
The furnace maintains a constant flow of argon gas throughout the process.
This inert atmosphere serves a dual purpose: it acts as a carrier transport for the sulfur vapor and creates a barrier against external contaminants. By excluding oxygen and moisture, the system prevents the oxidation of the tungsten, ensuring the final product is pure sulfide.
Positive Pressure Maintenance
Distinct from vacuum annealing processes used for other materials, this WS2 synthesis relies on maintaining a pressure 30 kPa above atmospheric pressure.
Operating at slight overpressure ensures that the sulfur vapor concentration remains sufficiently high near the precursor surface to drive the reaction forward. It also prevents the ingress of outside air should a minor leak occur.
Understanding the Trade-offs
High Temperature vs. Substrate Integrity
While 800 °C is necessary for high-quality crystallization, it limits the types of substrates you can use.
Materials with low melting points or high thermal expansion coefficients may degrade or delaminate at these temperatures. You must ensure your substrate is thermally compatible with the processing window required for hexagonal WS2 formation.
Pressure Management Risks
maintaining positive pressure (overpressure) is effective for driving reactions, but it presents safety and containment challenges.
Unlike vacuum systems that pull gases out, a positive pressure system pushes gases out. If the furnace seals are compromised, hazardous sulfur vapors can escape into the laboratory environment. Rigorous leak checking and exhaust management are required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your WS2 synthesis, align your furnace parameters with your specific structural requirements:
- If your primary focus is High Crystallinity: Prioritize reaching the full 800 °C and strictly adhering to the 10 °C/min ramp rate to ensure the amorphous-to-hexagonal phase transformation is complete.
- If your primary focus is Stoichiometric Purity: Focus on the Argon flow and Positive Pressure (30 kPa) to ensure an oxygen-free environment that maximizes sulfur incorporation.
mastering these variables allows you to dictate the preferred orientation and quality of the final WS2 film.
Summary Table:
| Physical Parameter | Required Condition | Functional Role in WS2 Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Up to 800 °C | Activates phase transformation from amorphous to hexagonal |
| Heating Rate | 10 °C/min | Prevents thermal shock and ensures uniform reaction |
| Pressure | 30 kPa (Positive) | Maintains high sulfur vapor concentration at the surface |
| Atmosphere | Argon (Inert) | Carrier gas that prevents oxidation and contamination |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your research with KINTEK’s advanced laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically designed to meet the rigorous demands of 2D material synthesis like Tungsten Disulfide (WS2).
Whether you require a standard configuration or a fully customizable high-temperature furnace tailored to your unique experimental needs, our equipment provides the thermal stability and atmospheric control necessary for breakthrough results.
Ready to optimize your thin-film growth? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- F. Sava, Alin Velea. Synthesis of WS2 Ultrathin Films by Magnetron Sputtering Followed by Sulfurization in a Confined Space. DOI: 10.3390/surfaces7010008
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the heat treatment process using a tube furnace essential in the preparation of Mn7Co3Ce1Ox catalysts?
- How does tube furnace cracking compare to fuel furnaces in terms of efficiency? Discover Higher Efficiency and Precision
- What are the industrial design advantages of using a tube furnace for ex-situ reduction of catalysts? Optimize Efficiency
- What is the function of Argon gas flow within a Tube Furnace during the heat treatment of Molybdenum Disulfide? Expert Guide
- What is a tubular furnace used for? A Guide to Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the purpose of maintaining a specific argon flow in a tube furnace? Optimize LFP/C Composite Synthesis
- What are the primary benefits of using a split tube furnace? Enhance Lab Efficiency with Unmatched Flexibility
- What are the key advantages of a horizontal electric furnace? Achieve Superior Process Control and Accessibility



















