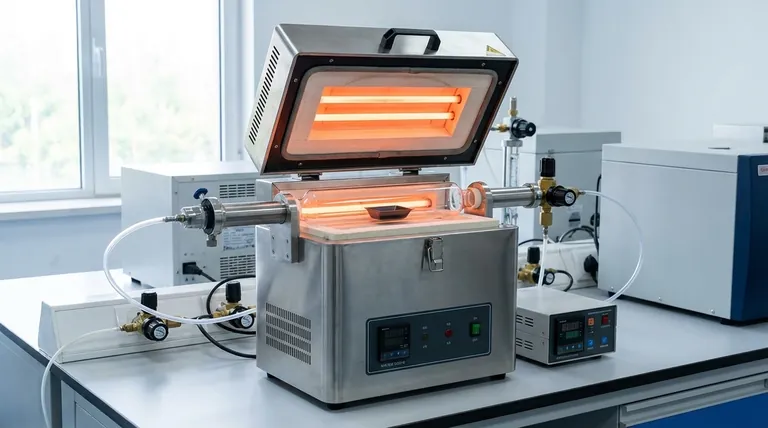
In short, a modern tube furnace is significantly more efficient for processes like cracking than a traditional fuel-fired furnace. This efficiency stems from its fundamental design, which converts electrical energy directly into usable heat with minimal waste. Unlike fuel furnaces that lose a substantial amount of energy through hot exhaust, electric tube furnaces contain and direct nearly all of their energy into the process chamber.
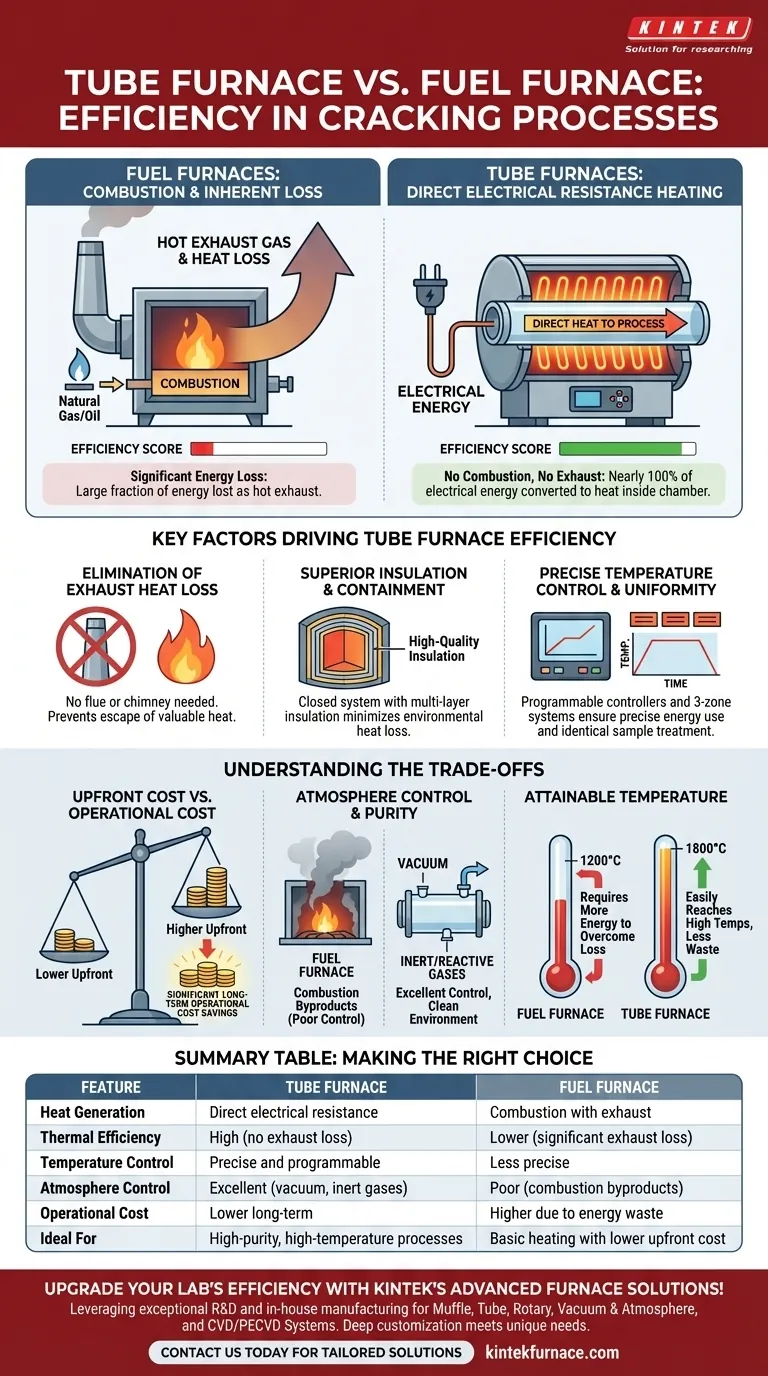
The core difference lies in how heat is generated and lost. Fuel furnaces lose a large fraction of their energy as hot exhaust gas. Electric tube furnaces have no combustion and therefore no exhaust, allowing them to achieve much higher thermal efficiency.

The Fundamental Difference in Heat Generation
To understand the efficiency gap, we must first look at how each furnace type creates heat. The method itself dictates the potential for energy loss.
Fuel Furnaces: Combustion and Inherent Loss
A fuel furnace works by burning a combustible material, such as natural gas or oil. This chemical reaction releases heat.
However, the combustion process also produces hot waste gases (flue gas or exhaust). These gases must be vented from the furnace, and they carry a significant percentage of the generated heat with them. This exhaust heat loss is the single largest source of inefficiency in a fuel furnace.
Tube Furnaces: Direct Electrical Resistance Heating
An electric tube furnace uses resistive heating elements. When electricity passes through these elements, they heat up due to resistance, directly converting electrical energy into thermal energy.
Crucially, there is no combustion. This means there are no exhaust gases to vent, and the primary source of energy loss found in fuel furnaces is completely eliminated. Nearly 100% of the electrical energy is converted into heat inside the furnace chamber.
Key Factors Driving Tube Furnace Efficiency
Beyond the absence of exhaust, several design features contribute to the superior efficiency of modern tube furnaces, making them ideal for high-temperature applications like thermal cracking.
Elimination of Exhaust Heat Loss
As established, this is the most critical advantage. By not burning fuel, a tube furnace doesn't need a chimney or flue, preventing the escape of valuable heat.
Superior Insulation and Containment
Tube furnaces are engineered as closed systems. They utilize high-quality, multi-layer insulation to minimize heat loss to the surrounding environment. The cylindrical, contained nature of the tube ensures that the heat is concentrated directly on the sample material.
Precise Temperature Control and Uniformity
Modern tube furnaces feature programmable digital controllers. These allow for precise management of heating cycles, ramps, and dwell times, ensuring that no more energy is used than is absolutely necessary.
Furthermore, advanced models with three heating zones provide exceptional temperature uniformity along the entire length of the tube. This process efficiency ensures the entire sample is treated identically, improving yield and preventing wasted energy from uneven heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While tube furnaces are more thermally efficient, a complete picture requires looking at other practical considerations.
Upfront Cost vs. Operational Cost
Fuel-fired furnaces may sometimes have a lower initial purchase price. However, the superior energy efficiency of a tube furnace translates directly into lower long-term operational costs, which can quickly offset a higher upfront investment. The final cost-benefit analysis will depend on local electricity and gas prices.
Atmosphere Control and Purity
Tube furnaces excel at creating a controlled process atmosphere. Because the chamber is sealed and free of combustion byproducts, it is easy to perform processes under a vacuum or in the presence of specific inert or reactive gases. This is extremely difficult and inefficient to achieve in a direct-fired fuel furnace.
Attainable Temperature
Tube furnaces are designed to easily and efficiently reach very high temperatures (1200°C to 1800°C). Reaching these temperatures in a fuel furnace requires significantly more energy input to overcome the constant heat loss through the exhaust stack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which furnace characteristic is most important.
- If your primary focus is process precision and purity: The superior temperature uniformity and atmosphere control of a tube furnace make it the only logical choice for sensitive applications.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: The fundamental energy efficiency of a tube furnace will result in significant cost savings over the life of the equipment.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: A tube furnace can achieve and maintain high temperatures more easily and with far less wasted energy than a comparable fuel furnace.
For demanding thermal processes like cracking, the combination of energy efficiency, precision control, and atmospheric purity makes the tube furnace the superior technical solution.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Fuel Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Direct electrical resistance | Combustion with exhaust |
| Thermal Efficiency | High (no exhaust loss) | Lower (significant exhaust loss) |
| Temperature Control | Precise and programmable | Less precise |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent (vacuum, inert gases) | Poor (combustion byproducts) |
| Operational Cost | Lower long-term | Higher due to energy waste |
| Ideal For | High-purity, high-temperature processes | Basic heating with lower upfront cost |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for cracking and other processes. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your precision and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















